Unit 8 Vocabulary - Part 1 Atmosphere
... psychrometer: a hygrometer consisting of a wet-bulb and a dry-bulb thermometer, the difference in the two thermometer readings being used to determine atmospheric humidity ...
... psychrometer: a hygrometer consisting of a wet-bulb and a dry-bulb thermometer, the difference in the two thermometer readings being used to determine atmospheric humidity ...
Atmosphere and Weather Study Guide 2015 Name
... 12. Humidity is a measure of what ____________________ 13. As altitude in the troposphere increases, what happens to temperature? _________ 14. What storm has intense winds, a small “eye” , and forms often in the U.S. Midwest 15. What are the three main types of clouds? ___________ 16. What type of ...
... 12. Humidity is a measure of what ____________________ 13. As altitude in the troposphere increases, what happens to temperature? _________ 14. What storm has intense winds, a small “eye” , and forms often in the U.S. Midwest 15. What are the three main types of clouds? ___________ 16. What type of ...
Second Half of Chapter 5
... EL NIÑO Southern Oscillation event is a periodic warming of surface waters of the tropical East Pacific that alters both ocean & atmospheric circulation. ...
... EL NIÑO Southern Oscillation event is a periodic warming of surface waters of the tropical East Pacific that alters both ocean & atmospheric circulation. ...
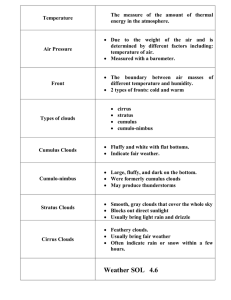
Chapter Notes
... temperature, the atmosphere is often divided into two layers based on composition. The homosphere consists of air that is uniform in terms of the proportions of its component gases. The heterosphere consists of gases arranged into four roughly spherical shells, each with a ...
... temperature, the atmosphere is often divided into two layers based on composition. The homosphere consists of air that is uniform in terms of the proportions of its component gases. The heterosphere consists of gases arranged into four roughly spherical shells, each with a ...
air temperature
... Due to the heat air absorbs from or gives off to the environment. SPECIFIC HEAT – amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a substance. Thermometer ...
... Due to the heat air absorbs from or gives off to the environment. SPECIFIC HEAT – amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a substance. Thermometer ...
Meteorology

Meteorology is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere. Studies in the field stretch back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not occur until the 18th century. The 19th century saw modest progress in the field after observing networks formed across several countries. It wasn't until after the development of the computer in the latter half of the 20th century that significant breakthroughs in weather forecasting were achieved.Meteorological phenomena are observable weather events that illuminate, and are explained by the science of meteorology. Those events are bound by the variables of Earth's atmosphere: temperature, air pressure, water vapor, and the gradients and interactions of each variable, and how they change over time. Different spatial scales are studied to determine how systems on local, regional, and global levels impact weather and climatology.Meteorology, climatology, atmospheric physics, and atmospheric chemistry are sub-disciplines of the atmospheric sciences. Meteorology and hydrology compose the interdisciplinary field of hydrometeorology. Interactions between Earth's atmosphere and the oceans are part of coupled ocean-atmosphere studies. Meteorology has application in many diverse fields such as the military, energy production, transport, agriculture and construction.The word ""meteorology"" is from Greek μετέωρος metéōros ""lofty; high (in the sky)"" (from μετα- meta- ""above"" and ἀείρω aeiro ""I lift up"") and -λογία -logia ""-(o)logy"", i.e. ""the study of things in the air"".