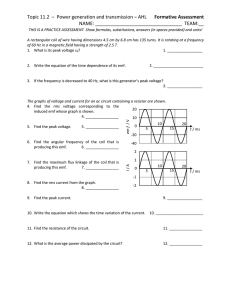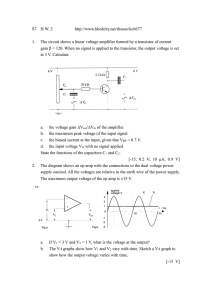
- EasyEDA
... In this test, the instantaneous, pulse-by-pulse output current sunk in the clamp is much higher than the measured (average) supply current. Therefore the output of SMPS goes into pulse-by-pulse current limiting which limits the average current drawn from the input supply. In the event of the series ...
... In this test, the instantaneous, pulse-by-pulse output current sunk in the clamp is much higher than the measured (average) supply current. Therefore the output of SMPS goes into pulse-by-pulse current limiting which limits the average current drawn from the input supply. In the event of the series ...
CENTRIPENTAL ACCELERATION AND FORCE PROBLEMS
... occurs in the current? 12. If the resistance of a circuit remains constant while the voltage across the circuit decreases to half its former value, what change occurs in the current? 13. Why is it that a bird can perch without harm on a high voltage wire? ...
... occurs in the current? 12. If the resistance of a circuit remains constant while the voltage across the circuit decreases to half its former value, what change occurs in the current? 13. Why is it that a bird can perch without harm on a high voltage wire? ...
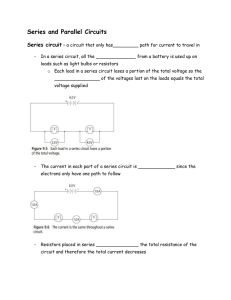
FN-Series and Parallel Circuits
... In a series circuit, all the ______________ from a battery is used up on loads such as light bulbs or resistors o Each load in a series circuit loses a portion of the total voltage so the ________________ of the voltages lost on the loads equals the total voltage supplied ...
... In a series circuit, all the ______________ from a battery is used up on loads such as light bulbs or resistors o Each load in a series circuit loses a portion of the total voltage so the ________________ of the voltages lost on the loads equals the total voltage supplied ...
Circuits and Circuit Diagrams
... Voltage drop across each device depends directly on its resistance (V = I x R) Total voltage divides among the individual electric devices in the circuit. ...
... Voltage drop across each device depends directly on its resistance (V = I x R) Total voltage divides among the individual electric devices in the circuit. ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... This gives i2 = 2 mA. We can solve for i1 using Equation (2). This gives i1 = 3 mA. We also know that i3 = ½ of i2 = 1 mA. Using Ohm’s law, solve for the resistance values. R1’s resistance is the voltage across it by the current through it. This gives R1 = 2 kΩ because V/mA = kΩ. R2’s value is 3 kΩ. ...
... This gives i2 = 2 mA. We can solve for i1 using Equation (2). This gives i1 = 3 mA. We also know that i3 = ½ of i2 = 1 mA. Using Ohm’s law, solve for the resistance values. R1’s resistance is the voltage across it by the current through it. This gives R1 = 2 kΩ because V/mA = kΩ. R2’s value is 3 kΩ. ...
Series Parallel Circuits 9.1 Key
... What happens to the total resistance of a series circuit wUen another resistor is added? ...
... What happens to the total resistance of a series circuit wUen another resistor is added? ...
Factsheet: Conductors, Connections and Polarity
... It takes a minimum of two wires to have an electrical circuit. Electric current involves the flow of electrons. Current is measured in amperes (amps for short). It travels from a source, through the device it operates, called the load, and then back to the source. In AC wiring, present in buildings, ...
... It takes a minimum of two wires to have an electrical circuit. Electric current involves the flow of electrons. Current is measured in amperes (amps for short). It travels from a source, through the device it operates, called the load, and then back to the source. In AC wiring, present in buildings, ...
Use the proportionality property of linear circuits to find the voltage Vx
... Find k by analysis of that circuit. We can then use k to find the output when given any input. So set Vx = 1 V and let the input be unknown. There is no current flowing through either the 22 Ω resistor or the 81 Ω resistor. This means that the voltage across each element is 0V. So we can replace the ...
... Find k by analysis of that circuit. We can then use k to find the output when given any input. So set Vx = 1 V and let the input be unknown. There is no current flowing through either the 22 Ω resistor or the 81 Ω resistor. This means that the voltage across each element is 0V. So we can replace the ...
HP ADS SIMULATION EXAMPLE – Basic Harmonic Balance
... response of a circuit, which contains nonlinear components. The basic HB analysis is usually applied to a single periodic source. The periodic source can be sinusoidal or non-sinusoidal. The HB method works by assuming the steady state response of a circuit being driven by a periodic source is als ...
... response of a circuit, which contains nonlinear components. The basic HB analysis is usually applied to a single periodic source. The periodic source can be sinusoidal or non-sinusoidal. The HB method works by assuming the steady state response of a circuit being driven by a periodic source is als ...
Electric Current - Wissahickon School District
... Voltage difference- push that causes charges to move- measured in volts (V) For charges to flow, the wire must always be connected in a closed path, or circuit http://www.school-for-champions.com/science/dc.htm ...
... Voltage difference- push that causes charges to move- measured in volts (V) For charges to flow, the wire must always be connected in a closed path, or circuit http://www.school-for-champions.com/science/dc.htm ...
OHMS LAW
... Ohm’s Law explains the relationship between voltage (V ), current (I) and resistance (R) Used by electricians, automotive technicians, stereo installers ...
... Ohm’s Law explains the relationship between voltage (V ), current (I) and resistance (R) Used by electricians, automotive technicians, stereo installers ...
Physics 536 - Assignment #6 - Due March 19
... which has IDSS ≈ 20 mA and VP = −4 V. The voltage source, Vin (t) has a peak-to-peak amplitude of 10 mV and a frequency of 10 kHz, modelled using VIN 5 0 DC 0 SIN(0 0.01V 10KHZ) and where R1 = 10 kΩ represents the large output impedance of a non-ideal voltage source, such as the element of a microph ...
... which has IDSS ≈ 20 mA and VP = −4 V. The voltage source, Vin (t) has a peak-to-peak amplitude of 10 mV and a frequency of 10 kHz, modelled using VIN 5 0 DC 0 SIN(0 0.01V 10KHZ) and where R1 = 10 kΩ represents the large output impedance of a non-ideal voltage source, such as the element of a microph ...
Hall Effect Devices as Current Sensors
... Monitoring current in a test fixture is typically accomplished by monitoring the voltage dropped across a resistor in series with the load. In Figure 1 we see a typical circuit. When the voltage across R5 reaches about 600 mV the transistor Q2 starts to conduct. As Q2 conducts the voltage across R7 ...
... Monitoring current in a test fixture is typically accomplished by monitoring the voltage dropped across a resistor in series with the load. In Figure 1 we see a typical circuit. When the voltage across R5 reaches about 600 mV the transistor Q2 starts to conduct. As Q2 conducts the voltage across R7 ...
Chapter 20 Test Review
... through the light bulb. The resistance of the light bulb is 2 ohms. What is the voltage of the ...
... through the light bulb. The resistance of the light bulb is 2 ohms. What is the voltage of the ...
Electronics Lab Intro (Lab#0) Introduction Procedure Part I. Ohm`s
... Electronics Lab Intro (Lab#0) Introduction The main purpose of this lab is to familiarize you with some of the equipment used for the electronics labs, while investigating Ohm’s Law and Resistive-Capacitive (RC) circuits. Recall that Ohm’s Law states that the electrical current through a circuit com ...
... Electronics Lab Intro (Lab#0) Introduction The main purpose of this lab is to familiarize you with some of the equipment used for the electronics labs, while investigating Ohm’s Law and Resistive-Capacitive (RC) circuits. Recall that Ohm’s Law states that the electrical current through a circuit com ...
university of california - Berkeley Robotics and Intelligent Machines
... e. What is the temperature coefficient of the bandgap voltage? Why? How would you fix it? 3. For the bandgap reference in Lab 4, if you were to cut the wires to the inputs of the op-amp, and apply a small positive disturbance in the differential voltage at the input of the op-amp, Vid. a. Estimate ...
... e. What is the temperature coefficient of the bandgap voltage? Why? How would you fix it? 3. For the bandgap reference in Lab 4, if you were to cut the wires to the inputs of the op-amp, and apply a small positive disturbance in the differential voltage at the input of the op-amp, Vid. a. Estimate ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.