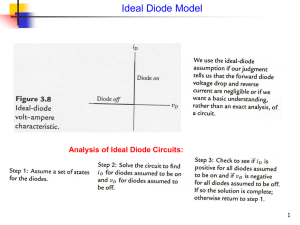
Exercise 3.4.1
... area of the pn-junction of a solar cell might have weak points (locally, e.g. at the edge) which short-circuit the junction somewhat. These defects are summarily described by a shunt resistor. The constant current source mimics the current generated in the junction by light. it simply defines a curr ...
... area of the pn-junction of a solar cell might have weak points (locally, e.g. at the edge) which short-circuit the junction somewhat. These defects are summarily described by a shunt resistor. The constant current source mimics the current generated in the junction by light. it simply defines a curr ...
Calculating electric power
... An historical note: it was James Prescott Joule, not Georg Simon Ohm, who first discovered the mathematical relationship between power dissipation and current through a resistance. This discovery, published in 1841, followed the form of the last equation (P = I2R), and is properly known as Joule's L ...
... An historical note: it was James Prescott Joule, not Georg Simon Ohm, who first discovered the mathematical relationship between power dissipation and current through a resistance. This discovery, published in 1841, followed the form of the last equation (P = I2R), and is properly known as Joule's L ...
LM317T 12V Lead-acid charger
... The charge indicator monitors the charge current and when this charge current decreases to the set level the LED is turned on. The colored wires are as follows: Red connected to point A, Yellow connected to point B, and Black connected to point C. All connections are to the charger schematic IC1 is ...
... The charge indicator monitors the charge current and when this charge current decreases to the set level the LED is turned on. The colored wires are as follows: Red connected to point A, Yellow connected to point B, and Black connected to point C. All connections are to the charger schematic IC1 is ...
Ohms - HCC Learning Web
... 1) Convert the unit of OHM into its combination of the fundamental SI units. ...
... 1) Convert the unit of OHM into its combination of the fundamental SI units. ...
LTC Design Note: High-voltage CMOS amplifier enables high
... Introduction Accurately measuring voltages requires minimizing the impact of the instrument connection to the tested circuit. Typical digital voltmeters (DVMs) use 10MΩ resistor networks to keep loading effects to an inconspicuous level, but even this can introduce significant error, particularly in ...
... Introduction Accurately measuring voltages requires minimizing the impact of the instrument connection to the tested circuit. Typical digital voltmeters (DVMs) use 10MΩ resistor networks to keep loading effects to an inconspicuous level, but even this can introduce significant error, particularly in ...
Sheet (3)
... 1) The input voltage to the cycloconverter is 120V (rms). 60Hz. The load resistance is 5Ω and the load inductance is L=40mH . The frequency of the output voltage is 20Hz. If the converters are operated as semiconverters such that 0≤α≤π and the delay angle is αp = 2π/3 , Determine : a) The rms value ...
... 1) The input voltage to the cycloconverter is 120V (rms). 60Hz. The load resistance is 5Ω and the load inductance is L=40mH . The frequency of the output voltage is 20Hz. If the converters are operated as semiconverters such that 0≤α≤π and the delay angle is αp = 2π/3 , Determine : a) The rms value ...
ET 9
... 1. Explain the terms "electric field strength", permittivity" and "relative permittivity". A P.D. of 10 kV is applied to the terminals of a condenser consisting of two circular plates each having an area of 100 sq. cm separated by a dielectric 1 mm. thick. If the capacitance is 3 10 micro-farad, c ...
... 1. Explain the terms "electric field strength", permittivity" and "relative permittivity". A P.D. of 10 kV is applied to the terminals of a condenser consisting of two circular plates each having an area of 100 sq. cm separated by a dielectric 1 mm. thick. If the capacitance is 3 10 micro-farad, c ...
Ohm`s Law
... 5. A certain electric stove has a 16 Ω heating element (the resistance is 16 Ω) The current going through the element is 15 A. Calculate the voltage across the element. ...
... 5. A certain electric stove has a 16 Ω heating element (the resistance is 16 Ω) The current going through the element is 15 A. Calculate the voltage across the element. ...
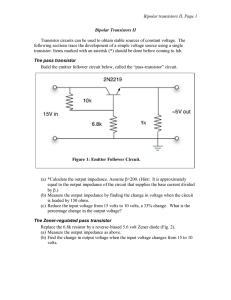
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... Figure 4: Feedback Voltage Regulator. load conditions are variable. These can give output impedances less than an ohm and high stability against temperature variation. Figure 4 is a common example of a negative-feedback circuit. Transistor Q1 is normally conducting because of the bias current throug ...
... Figure 4: Feedback Voltage Regulator. load conditions are variable. These can give output impedances less than an ohm and high stability against temperature variation. Figure 4 is a common example of a negative-feedback circuit. Transistor Q1 is normally conducting because of the bias current throug ...
Reverse polarity and overvoltage protection
... You can use a diode in series and zener diode (or better – a transient voltage suppressor) in parallel in combination with a fuse. But you can do it better. First, the diode in series can be replaced by Pchannel MOSFET (Q1). Drain connected to input and source to output. Gate is connected to ground. ...
... You can use a diode in series and zener diode (or better – a transient voltage suppressor) in parallel in combination with a fuse. But you can do it better. First, the diode in series can be replaced by Pchannel MOSFET (Q1). Drain connected to input and source to output. Gate is connected to ground. ...
Transistor Switch and Emitter Follower Phys 3610/6610 Lab 18 Student: TA:
... 1.) Apply the input and examine the output waveform using a scope. Document the phase shift. What is the output impedance when Vout = 5 V? 2.) Let us load this transistor switch with a 10 kΩ resistor to simulate the more realistic situation where your circuit drives some other input. How does the lo ...
... 1.) Apply the input and examine the output waveform using a scope. Document the phase shift. What is the output impedance when Vout = 5 V? 2.) Let us load this transistor switch with a 10 kΩ resistor to simulate the more realistic situation where your circuit drives some other input. How does the lo ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.