Charge, Current, Voltage, & Resistors
... • "path independent“ • Voltage is measured in Joules/Coulomb or Volts (V) • A Joule to the unit of energy • Positive voltage is defined such that negatively charged particles are pulled towards higher voltages • Potential energy can be converted into other forms of energy ...
... • "path independent“ • Voltage is measured in Joules/Coulomb or Volts (V) • A Joule to the unit of energy • Positive voltage is defined such that negatively charged particles are pulled towards higher voltages • Potential energy can be converted into other forms of energy ...
Science 9 Unit 4: Electricity Name - Science 9 Portfolio
... ground to prevent buildup of electricity ...
... ground to prevent buildup of electricity ...
Slide 1
... 1. What is the current through a light if a charge of 2.50 C passes through it in 2.00 s? 2. How many electrons passed through? ...
... 1. What is the current through a light if a charge of 2.50 C passes through it in 2.00 s? 2. How many electrons passed through? ...
Test Procedure for the NCV8871SEPGEVB Evaluation Board
... 1. Connect a DC input voltage, within the 6 V to 40 V range, between VIN and GND. 2. Connect a DC enable voltage, within the 2.0 V to 5.0 V range, between EN/SYNC and GND. 3. The demo board feedback components were selected for continuous operation at rated 12 V/2 A output power at a minimum input v ...
... 1. Connect a DC input voltage, within the 6 V to 40 V range, between VIN and GND. 2. Connect a DC enable voltage, within the 2.0 V to 5.0 V range, between EN/SYNC and GND. 3. The demo board feedback components were selected for continuous operation at rated 12 V/2 A output power at a minimum input v ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint - INFN-LNF
... The diode (1/2) “In electronics, a diode is a two-terminal electronic component with an asymmetric transfer characteristic, with low resistance to current flow in one direction, and high resistance in the other.” (Wikipedia) ...
... The diode (1/2) “In electronics, a diode is a two-terminal electronic component with an asymmetric transfer characteristic, with low resistance to current flow in one direction, and high resistance in the other.” (Wikipedia) ...
Electricity and circuits
... Circuits are not only made up of power sources and loads. What are some other circuit elements? ...
... Circuits are not only made up of power sources and loads. What are some other circuit elements? ...
AC CIRCUITS : RC CIRCUIT 1. Aim 1. To study current voltage
... The RC circuit consists of a Capacitor and a Resistor connected in series supplied by a AC power supply in form of a Function Generator. As the applies signal is sinusoidal the current in each element is also sinusoidal, but are not in phase.A series combination of a resistor R and capacitor C if co ...
... The RC circuit consists of a Capacitor and a Resistor connected in series supplied by a AC power supply in form of a Function Generator. As the applies signal is sinusoidal the current in each element is also sinusoidal, but are not in phase.A series combination of a resistor R and capacitor C if co ...
Ohm`s Law & Electrical Power
... But once the path is closed the electrons are repelled by the negative pole of the voltage source and attracted to the positive pole of the voltage source. ...
... But once the path is closed the electrons are repelled by the negative pole of the voltage source and attracted to the positive pole of the voltage source. ...
Multi-functional Packaged Antennas for Next
... Thus the fixed bias circuit has the limitation that changes in does not change the base current. Thus the transistor can switch from active region operation to saturation or cut-off very easily. ...
... Thus the fixed bias circuit has the limitation that changes in does not change the base current. Thus the transistor can switch from active region operation to saturation or cut-off very easily. ...
Oct - Directorate General of Shipping
... 6. The terminal voltage of a three-phase alternator is set at 440V, by adjusting the field excitation when the speed is correct and when the full-load current is supplied at a power factor of 0.8 (lagging). When the machine circuit breaker is opened and the load thrown-off, the terminal voltage is s ...
... 6. The terminal voltage of a three-phase alternator is set at 440V, by adjusting the field excitation when the speed is correct and when the full-load current is supplied at a power factor of 0.8 (lagging). When the machine circuit breaker is opened and the load thrown-off, the terminal voltage is s ...
For the three-phase circuit given in this problem, firstly we... balanced or unbalanced system.
... For the three-phase circuit given in this problem, firstly we want to determine if it is a balanced or unbalanced system. We then want to find the current in phasor domain. The circuit can be divided into three portions: the source, the transmission line, and the load. Let’s take a look at the volta ...
... For the three-phase circuit given in this problem, firstly we want to determine if it is a balanced or unbalanced system. We then want to find the current in phasor domain. The circuit can be divided into three portions: the source, the transmission line, and the load. Let’s take a look at the volta ...
Unit 10 (Electricity) - Ms. Voit`s Physics Wiki
... Find the equivalent resistance of the circuit. Redraw the circuit with its equivalent resistance. Find the current through the battery. Using ohm’s law, find the current through and voltage drop across each resistor. (6A, 4A & 8V, 1.33A & 8V, 6.67A & 8V) V = 8 volts s ...
... Find the equivalent resistance of the circuit. Redraw the circuit with its equivalent resistance. Find the current through the battery. Using ohm’s law, find the current through and voltage drop across each resistor. (6A, 4A & 8V, 1.33A & 8V, 6.67A & 8V) V = 8 volts s ...
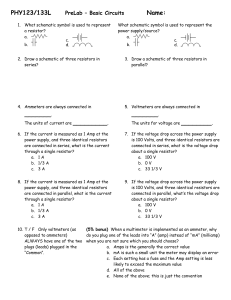
Basic Ciruits
... 9. If the voltage drop across the power supply is 100 Volts, and three identical resistors are connected in parallel, what’s the voltage drop about a single resistor? a. 100 V b. 0 V c. 33 1/3 V ...
... 9. If the voltage drop across the power supply is 100 Volts, and three identical resistors are connected in parallel, what’s the voltage drop about a single resistor? a. 100 V b. 0 V c. 33 1/3 V ...
Document
... If the distance d between the plates is much smaller than both the width and the length of the plates, the capacitance is approximately ...
... If the distance d between the plates is much smaller than both the width and the length of the plates, the capacitance is approximately ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.