Exercise 8.1-3 IV
... area of the pn-junction of a solar cell might have weak points (locally, e.g. at the edge) which short-circuits the junction somewhat. These defects are summarily described by a shunt resistor. The constant current source mimics the current generated in the junction by light. It simply defines a cur ...
... area of the pn-junction of a solar cell might have weak points (locally, e.g. at the edge) which short-circuits the junction somewhat. These defects are summarily described by a shunt resistor. The constant current source mimics the current generated in the junction by light. It simply defines a cur ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... To turn off the current source, we make the current equal to 0. We need to make it an open circuit here so the current is 0. To turn off the voltage source, we need to make it a short circuit. Look at the two 10 kΩ resistors. They are in parallel because they share the same pair of nodes. The two 10 ...
... To turn off the current source, we make the current equal to 0. We need to make it an open circuit here so the current is 0. To turn off the voltage source, we need to make it a short circuit. Look at the two 10 kΩ resistors. They are in parallel because they share the same pair of nodes. The two 10 ...
CT33-
... Answer: zero!! It's a trick question! Transformers only work with AC voltages. The DC voltage V from the battery produces a DC current in the primary coil, but produces no voltage of any kind in the secondary coil. Transformers work because of Faraday's Law: the changing flux produced by the AC curr ...
... Answer: zero!! It's a trick question! Transformers only work with AC voltages. The DC voltage V from the battery produces a DC current in the primary coil, but produces no voltage of any kind in the secondary coil. Transformers work because of Faraday's Law: the changing flux produced by the AC curr ...
Ohm`s Law and Resistance Exploratory
... 2. Click on the “Play with sims...” button. 3. Click on the “Physics” link in the left frame of the page. 4. In the right frame, scroll down to find the “Ohm’s Law” application and select it. You may select the “Run Now!” option. 5. Set the “Resistance” to 500 Ω. Set the “Voltage” to 4.0 V. 6. Only ...
... 2. Click on the “Play with sims...” button. 3. Click on the “Physics” link in the left frame of the page. 4. In the right frame, scroll down to find the “Ohm’s Law” application and select it. You may select the “Run Now!” option. 5. Set the “Resistance” to 500 Ω. Set the “Voltage” to 4.0 V. 6. Only ...
Current- Voltage Characteristics
... Current- Voltage Characteristics Apparatus low voltage variable power supply, voltmeter, ammeter, resistor, low voltage globe Action The students measure current through and voltage across the resistor and then the globe for several voltages of the power supply. They should sketch the current as a f ...
... Current- Voltage Characteristics Apparatus low voltage variable power supply, voltmeter, ammeter, resistor, low voltage globe Action The students measure current through and voltage across the resistor and then the globe for several voltages of the power supply. They should sketch the current as a f ...
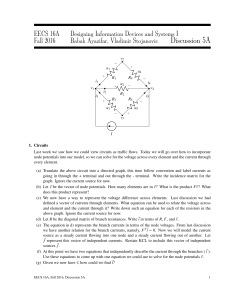
Circuit Analysis Handout
... Node– Any point you measure on a circuit. Every node has a voltage associated with it. Wires – Connecting nodes and elements, there is no voltage decrease across a wire o Elements/Nodes must be connected with wire for current to flow through them Current flows from high voltage to low voltage, the r ...
... Node– Any point you measure on a circuit. Every node has a voltage associated with it. Wires – Connecting nodes and elements, there is no voltage decrease across a wire o Elements/Nodes must be connected with wire for current to flow through them Current flows from high voltage to low voltage, the r ...
semi-conductors-16
... School: Max. Score: 35 Duration: 60 min Batch: 1. In a transistor, the doping level is slightly increased. How will affect the (a) collector current and (b) base current? (2) ...
... School: Max. Score: 35 Duration: 60 min Batch: 1. In a transistor, the doping level is slightly increased. How will affect the (a) collector current and (b) base current? (2) ...
CMGT 235 Quiz #8 Show all calculations! Name
... 7. What’s the power consumed in watts by a 12 AWG conductor that’s 200 feet long, and has a total resistance of 0.40 ohms, if the current (I) in the circuit conductors is 16A? (Round to nearest integer) ...
... 7. What’s the power consumed in watts by a 12 AWG conductor that’s 200 feet long, and has a total resistance of 0.40 ohms, if the current (I) in the circuit conductors is 16A? (Round to nearest integer) ...
Lecture #12 03/01/05
... •In an emf source, going – to + gives a positive V, + to - is a negative V •Solve all equations You might end up with many equations, but I trust that you can solve simultaneous equations. ...
... •In an emf source, going – to + gives a positive V, + to - is a negative V •Solve all equations You might end up with many equations, but I trust that you can solve simultaneous equations. ...
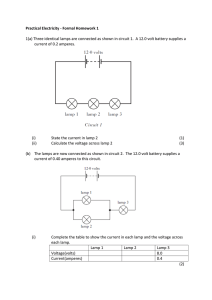
Practical Electricity 1
... Each resistor is placed in the circuit in turn and the following results are obtained. Resistor Voltage across resistor (v) Current (A) A ...
... Each resistor is placed in the circuit in turn and the following results are obtained. Resistor Voltage across resistor (v) Current (A) A ...
Measurement Lab
... R2 is in the opposite direction. For circuit two, we found that the current flows in a counterclockwise direction and not a clockwise direction, as we had assumed. We found out also that in a floating branch like in circuit two, the voltage and current running through is going to be zero. All in all ...
... R2 is in the opposite direction. For circuit two, we found that the current flows in a counterclockwise direction and not a clockwise direction, as we had assumed. We found out also that in a floating branch like in circuit two, the voltage and current running through is going to be zero. All in all ...
Current, Voltage and resistance
... Set up the circuits and record your answers on the sheet Voltage (P.D) is divided amongst the components in a series circuit Voltage (P.D) is the same across each branch in a parallel circuit ...
... Set up the circuits and record your answers on the sheet Voltage (P.D) is divided amongst the components in a series circuit Voltage (P.D) is the same across each branch in a parallel circuit ...
Ohm`s law. Linear Regression.
... When a conducting wire is subject to a voltage (U) at its terminals, it is run through by an electric current with a certain intensity (i). Ohm’s law states that at a constant temperature these two physical quantities are directly proportional. That is, for a 10% increase in voltage there is also a ...
... When a conducting wire is subject to a voltage (U) at its terminals, it is run through by an electric current with a certain intensity (i). Ohm’s law states that at a constant temperature these two physical quantities are directly proportional. That is, for a 10% increase in voltage there is also a ...
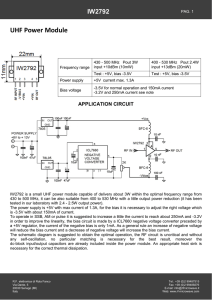
UHF Power Module IW2792
... IW2792 is a small UHF power module capable of delivery about 3W within the optimal frequency range from 430 to 500 MHz, it can be also suitable from 400 to 530 MHz with a little output power reduction (it has been tested in our laboratory with 2.4 - 2.5W output power). The power supply is +5V with m ...
... IW2792 is a small UHF power module capable of delivery about 3W within the optimal frequency range from 430 to 500 MHz, it can be also suitable from 400 to 530 MHz with a little output power reduction (it has been tested in our laboratory with 2.4 - 2.5W output power). The power supply is +5V with m ...
Series and Parallel Circuits 2 - Instructor Outline
... 3. The sum of the component’s voltages in a series circuit is equal to the voltage of the source (Kirchhoff’s Loop Rule). The Loop Rule results from the conservative nature of the electric force and is equivalent to the statement that the electric force does no net work over a closed loop path, exac ...
... 3. The sum of the component’s voltages in a series circuit is equal to the voltage of the source (Kirchhoff’s Loop Rule). The Loop Rule results from the conservative nature of the electric force and is equivalent to the statement that the electric force does no net work over a closed loop path, exac ...
SNC1P0 Ohm`s Law Practice
... the circuit diagram and calculate how many volts supply the CD player? 10. What current flows between a potential difference of 120 V through a resistance of 30 ohms? 11. A motor with an operating resistance of 30 ohms is connected to a voltage source. 4.0 A of current flow in the circuit. What is t ...
... the circuit diagram and calculate how many volts supply the CD player? 10. What current flows between a potential difference of 120 V through a resistance of 30 ohms? 11. A motor with an operating resistance of 30 ohms is connected to a voltage source. 4.0 A of current flow in the circuit. What is t ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.