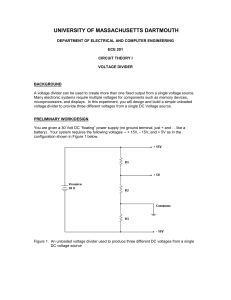
Skill Sheet 20.2 Network Circuits
... First notice that resistors R5 and R6 are in parallel and that they combine to give a resulting resistance of 1.5 ohms. Next, notice that resistors R3 and R4 are in series resulting in a resistance of 2 ohms. The resulting 2 ohms resistance is connected in parallel with another 2-ohm resistor. Thus ...
... First notice that resistors R5 and R6 are in parallel and that they combine to give a resulting resistance of 1.5 ohms. Next, notice that resistors R3 and R4 are in series resulting in a resistance of 2 ohms. The resulting 2 ohms resistance is connected in parallel with another 2-ohm resistor. Thus ...
ENGR 101 The Resistor Color Code Measuring Resistance
... Don't try to measure the resistance of a resistor while it is connected in a dead circuit. (You can possibly get an incorrect reading.) Disconnect at least one side of the resistor. ...
... Don't try to measure the resistance of a resistor while it is connected in a dead circuit. (You can possibly get an incorrect reading.) Disconnect at least one side of the resistor. ...
Capacitor Self
... monitor the voltage across the 10 ohm resistor. This is important because it has the same phase as the current. Use a frequency generator output of 1 kHz (i.e. a period of 1 ms on the oscilloscope graticule.) 2. Connect the Ch 1 input of the oscilloscope to point b to measure the amplitude of the vo ...
... monitor the voltage across the 10 ohm resistor. This is important because it has the same phase as the current. Use a frequency generator output of 1 kHz (i.e. a period of 1 ms on the oscilloscope graticule.) 2. Connect the Ch 1 input of the oscilloscope to point b to measure the amplitude of the vo ...
Slide 1
... Photo #1 - Power Connections on the Proto-Board Make sure there is visible wire at the terminals, so that the terminals are not clamping down on the wire insulation ...
... Photo #1 - Power Connections on the Proto-Board Make sure there is visible wire at the terminals, so that the terminals are not clamping down on the wire insulation ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... Answer all questions. All questions carry equal marks. ...
... Answer all questions. All questions carry equal marks. ...
AP Quiz #24 Circuits
... 3. A battery with an emf of 24 volts and an internal resistance of 1 ohm is connected to an external circuit as shown above. Determine each of the following (a) the equivalent resistance of the combination of the 4-ohm, 8-ohm, and 12-ohm resistors ...
... 3. A battery with an emf of 24 volts and an internal resistance of 1 ohm is connected to an external circuit as shown above. Determine each of the following (a) the equivalent resistance of the combination of the 4-ohm, 8-ohm, and 12-ohm resistors ...
Systems Repair Worksheet
... 18. In AC circuits, the actual resistance of a load is called its _______________. 19. _________ law is the name given to the formula that calculates electrical power used by a load. 20. Circuits must have consumers or _________, power ____________, & ____________ providing paths along with control ...
... 18. In AC circuits, the actual resistance of a load is called its _______________. 19. _________ law is the name given to the formula that calculates electrical power used by a load. 20. Circuits must have consumers or _________, power ____________, & ____________ providing paths along with control ...
Lecture 36
... generation of electron-hole pairs, so a large energy gap Eg means a small I0. Reverse breakdown At a certain reverse bias, usually around V = -0.2 volts, the current increases very dramatically. [[DIAGRAM]] There are two possible mechanisms for this so-called reverse breakdown. Zener tunneling When ...
... generation of electron-hole pairs, so a large energy gap Eg means a small I0. Reverse breakdown At a certain reverse bias, usually around V = -0.2 volts, the current increases very dramatically. [[DIAGRAM]] There are two possible mechanisms for this so-called reverse breakdown. Zener tunneling When ...
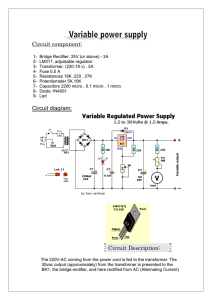
Circuit component
... current from R2, its voltage increases. This increases the output voltage. D1 is a general-purpose 1N4001 diode, used as a feedback blocker. It steers any current that might be coming from the device under power around the regulator to prevent the regulator from being damaged. Such reverse currents ...
... current from R2, its voltage increases. This increases the output voltage. D1 is a general-purpose 1N4001 diode, used as a feedback blocker. It steers any current that might be coming from the device under power around the regulator to prevent the regulator from being damaged. Such reverse currents ...
overloads - Controlled Power Company
... sources such as transformers are designed to perform optimally at or near full load. Small changes in current draw from this point do not effect the transformer. But when excessively large current draws occur the output voltage from the transformer decreases rapidly. ...
... sources such as transformers are designed to perform optimally at or near full load. Small changes in current draw from this point do not effect the transformer. But when excessively large current draws occur the output voltage from the transformer decreases rapidly. ...
multiple choice II
... Two lightbulbs A and B are connected in series to a constant voltage source. When a wire is connected across B, bulb A will: ...
... Two lightbulbs A and B are connected in series to a constant voltage source. When a wire is connected across B, bulb A will: ...
Victron BatteryProtect BP-40i The Victron Energy BatteryProtect
... Victron BatteryProtect BP-40i The Victron Energy BatteryProtect disconnects the battery from non essential loads before it is completely discharged (which would damage the battery) or before it has insufficient power left to crank the engine. 12/24V Auto Ranging The BatteryProtect automatically dete ...
... Victron BatteryProtect BP-40i The Victron Energy BatteryProtect disconnects the battery from non essential loads before it is completely discharged (which would damage the battery) or before it has insufficient power left to crank the engine. 12/24V Auto Ranging The BatteryProtect automatically dete ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.