HW14 - University of St. Thomas
... VIR01. The circuit at left consists of two 4.00 V batteries (the grey shaded areas) broken up into ideal EMF sources with internal c 9.00 Ω b 0.50 Ω resistances, along with two resistors. d a) What is the voltage difference 6.00 Ω between points a and d? 0.50 Ω a 8.00 Ω b) What is the terminal volta ...
... VIR01. The circuit at left consists of two 4.00 V batteries (the grey shaded areas) broken up into ideal EMF sources with internal c 9.00 Ω b 0.50 Ω resistances, along with two resistors. d a) What is the voltage difference 6.00 Ω between points a and d? 0.50 Ω a 8.00 Ω b) What is the terminal volta ...
Determine and plot as a function of time the current
... Answer: a) In case of a resistor the Ohm’s law as gives the current I = V/R For the first interval of time 0-5 ms the current is increasing with voltage from I = 0 at t = 0 to I = V/R = 15/7 = 2.143 A linearly and then remains constant with voltage for next 5 ms. After that as the voltage becomes ze ...
... Answer: a) In case of a resistor the Ohm’s law as gives the current I = V/R For the first interval of time 0-5 ms the current is increasing with voltage from I = 0 at t = 0 to I = V/R = 15/7 = 2.143 A linearly and then remains constant with voltage for next 5 ms. After that as the voltage becomes ze ...
AP_Physics_C_-_ohmslaw_Lab_II
... What is the resistance of a resistor with the color code of Red-Green –Brown? What is the resistance of a resistor with the color code of Orange-Red –Yellow Circuit Symbols Battery This symbol is actually for TWO batteries. The long line is positive and the short line is negative. To connect the two ...
... What is the resistance of a resistor with the color code of Red-Green –Brown? What is the resistance of a resistor with the color code of Orange-Red –Yellow Circuit Symbols Battery This symbol is actually for TWO batteries. The long line is positive and the short line is negative. To connect the two ...
Principles of Electronics
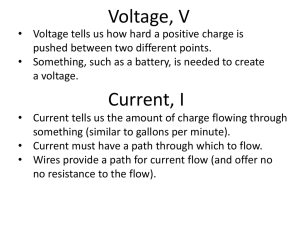
... Voltage: is the difference in charge between two points. Current: is the rate at which charge is flowing. Resistance: is a material’s tendency to resist the flow of charge (current). ...
... Voltage: is the difference in charge between two points. Current: is the rate at which charge is flowing. Resistance: is a material’s tendency to resist the flow of charge (current). ...
Ohm`s Law
... relationship between V and I for a particular circuit element is consistent with Ohm’s Law. Ohm’s Law states that the current I through a resistor is directly proportional to the voltage across the resistor V, and inversely proportional to the resistance, R, of the circuit. Mathematically this is wr ...
... relationship between V and I for a particular circuit element is consistent with Ohm’s Law. Ohm’s Law states that the current I through a resistor is directly proportional to the voltage across the resistor V, and inversely proportional to the resistance, R, of the circuit. Mathematically this is wr ...
Chapter 17: Introduction to Electricity
... (the opposition to the flow of electric charge), k) electric power (the rate at which electrical energy is converted into other forms of energy), ...
... (the opposition to the flow of electric charge), k) electric power (the rate at which electrical energy is converted into other forms of energy), ...
A circuit must contain a source of potential difference, and a path for
... to the potential difference between the terminals. As the charge moves through the external circuit it experiences a voltage drop equal in magnitude to the initial voltage rise. ...
... to the potential difference between the terminals. As the charge moves through the external circuit it experiences a voltage drop equal in magnitude to the initial voltage rise. ...
Electronics and Photonics Revision Sheet
... changing the value of R2 to 20k . What effect did this increased resistance have on the current through each resistor and the battery? ...
... changing the value of R2 to 20k . What effect did this increased resistance have on the current through each resistor and the battery? ...
... Electric Current Submitted by: I.D. 039622568 The problem: Given the values: ε1 = 1 V, ε2 = 0.5 V, ε3 = 0.6 V, R1 = R2 = 0.5 Ω, R3 = 1 Ω, R4 = 0.4 Ω, R5 = R6 = 0.6 Ω, R7 = 0.7 Ω 1. Calculate the current flowing through each resistor, and the potential difference between B and A when the switch is ...
Lecture-19 di / dt and dv / dt protection
... Converter grade and inverter grade thyristors Thyristor turn off and circuit turn off time Peak repetitive forward blocking voltage i2 t rating Explain the turn on and turn of dynamic characteristics of thyristor A string of series connected thyristors is to withstand a DC voltage of 12 KV. The maxi ...
... Converter grade and inverter grade thyristors Thyristor turn off and circuit turn off time Peak repetitive forward blocking voltage i2 t rating Explain the turn on and turn of dynamic characteristics of thyristor A string of series connected thyristors is to withstand a DC voltage of 12 KV. The maxi ...
ElectricCurrentMCquestions
... 4.The diagrams below show combinations X, Y and Z of three resistors, each resistor having the same resistance. ...
... 4.The diagrams below show combinations X, Y and Z of three resistors, each resistor having the same resistance. ...
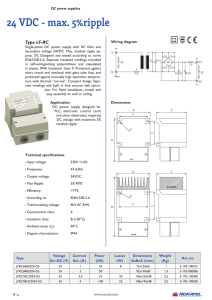
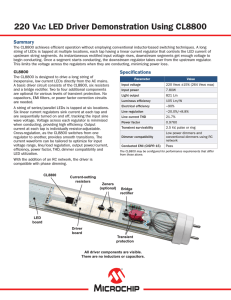
24 VDC - max. 5%ripple
... in plastic, IP44. Insulation class II. Protected against short circuit and overload with glass tube fuse, and protected against unusually high operation temperature with thermal ”cut-out”. Compact design. Separate windings and built in fuse ensures safe operation. For fixed installation, simple and ...
... in plastic, IP44. Insulation class II. Protected against short circuit and overload with glass tube fuse, and protected against unusually high operation temperature with thermal ”cut-out”. Compact design. Separate windings and built in fuse ensures safe operation. For fixed installation, simple and ...
Ohm`s Law Worksheet File
... circuit. This law states that the amount of ________________flowing in a circuit depends upon the amount of ______________ in the circuit and the amount of ______________ in the circuit. As the _______________ (v) increases, the current (I) _________________ Therefore, we can say that the current in ...
... circuit. This law states that the amount of ________________flowing in a circuit depends upon the amount of ______________ in the circuit and the amount of ______________ in the circuit. As the _______________ (v) increases, the current (I) _________________ Therefore, we can say that the current in ...
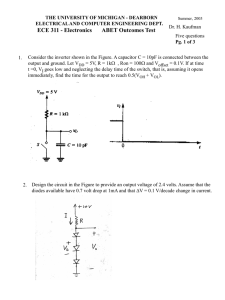
ECE 311 - Electronics ABET Outcomes Test
... 6. The circuit shown in the Figure is intended to supply current to floating loads (those for which both terminals are ungrounded) while making the greatest possible use of the available power supply. (a) Assuming ideal op amps, sketch the voltage waveforms at nodes B and C for a 1-V peak –to-peak s ...
... 6. The circuit shown in the Figure is intended to supply current to floating loads (those for which both terminals are ungrounded) while making the greatest possible use of the available power supply. (a) Assuming ideal op amps, sketch the voltage waveforms at nodes B and C for a 1-V peak –to-peak s ...
Resistors in Series and Parallel
... using a voltmeter and the current in a circuit using a ammeter. We need to connect these two devices in different ways. ...
... using a voltmeter and the current in a circuit using a ammeter. We need to connect these two devices in different ways. ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.