Series and Parallel Circuits • Components in a circuit can be
... Advantages of parallel circuits ...
... Advantages of parallel circuits ...
Circuit electricity
... Because it is the electrons which move from atom to atom in reality negative charge flows from negative to positive. This has the same effect as positive charge moving from positive to negative Conventional current flows from positive to negative ...
... Because it is the electrons which move from atom to atom in reality negative charge flows from negative to positive. This has the same effect as positive charge moving from positive to negative Conventional current flows from positive to negative ...
ppt
... Active device (Voltage or Current Source): Current exits + side, Current enters – side + side is at a higher voltage than – side (if current direction is correct) ...
... Active device (Voltage or Current Source): Current exits + side, Current enters – side + side is at a higher voltage than – side (if current direction is correct) ...
Project Summary - Berkeley Cosmology Group
... broken down, by a process of ionization. As this occurs, the air conducts the electricity through, broken by the amount of current and power is running through it, and completes the circuit. As this occurs, we are able to see sparks, because of how the electricity has to jump from one rod to the oth ...
... broken down, by a process of ionization. As this occurs, the air conducts the electricity through, broken by the amount of current and power is running through it, and completes the circuit. As this occurs, we are able to see sparks, because of how the electricity has to jump from one rod to the oth ...
review for elec 105 midterm exam #1 (fall 2001)
... - all have the same current flowing through them, but different voltages across them - Req R1 R2 R N - if one resistor is orders of magnitude larger than the rest, then Req ≈ that value Parallel resistors - all have the same voltage across them, but different currents through them ...
... - all have the same current flowing through them, but different voltages across them - Req R1 R2 R N - if one resistor is orders of magnitude larger than the rest, then Req ≈ that value Parallel resistors - all have the same voltage across them, but different currents through them ...
95MET-4
... NB : (1)All Questions are Compulsory (2)All Questions carry equal marks (3)Neatness in handwriting and clarity in expression carries weightage 1. Describe an electric telegraph system and describe its operation. 2. (a) Draw a simple battery charging circuit showing a battery being charged from a sin ...
... NB : (1)All Questions are Compulsory (2)All Questions carry equal marks (3)Neatness in handwriting and clarity in expression carries weightage 1. Describe an electric telegraph system and describe its operation. 2. (a) Draw a simple battery charging circuit showing a battery being charged from a sin ...
Series Circuits File
... MA Curriculum Frameworks (2006): 5.3 Knowledge/Understanding Goals: the difference between series and parallel circuits ...
... MA Curriculum Frameworks (2006): 5.3 Knowledge/Understanding Goals: the difference between series and parallel circuits ...
Switching Regulators
... Although these regulators are easily set up and extremely useful, they suffer from several limitations. The most serious limitation has to do with the efficiency of the regulator. Since these series regulators all rely on the variable voltage dropped across the series resistor of the power transisto ...
... Although these regulators are easily set up and extremely useful, they suffer from several limitations. The most serious limitation has to do with the efficiency of the regulator. Since these series regulators all rely on the variable voltage dropped across the series resistor of the power transisto ...
9103 USB Picoammeter Datasheet
... If the current is in the range of measurement of the instrument, the voltage drop should be less than ± 26 μV + (3.2 * I), where I is the current flowing into the instrument, 3.2 is the resistance of the fuse, and ± 26 μV is the offset voltage spec. of the op-amp. The current measurement circuit use ...
... If the current is in the range of measurement of the instrument, the voltage drop should be less than ± 26 μV + (3.2 * I), where I is the current flowing into the instrument, 3.2 is the resistance of the fuse, and ± 26 μV is the offset voltage spec. of the op-amp. The current measurement circuit use ...
UNIT-1 Electric Circuit
... Any resistive circuit or network, no matter how complex, can be presented as a current source in parallel with a source resistance.Or According to this theorem any two terminal active network containing voltage sources and resistance when viewed from its output terminal is equivalent to a constant c ...
... Any resistive circuit or network, no matter how complex, can be presented as a current source in parallel with a source resistance.Or According to this theorem any two terminal active network containing voltage sources and resistance when viewed from its output terminal is equivalent to a constant c ...
Electricity: The flow of electrons through a conductor Electronics
... » Current want to flow to ground. » “True” Ground is literally, the ground. » Floating ground is relative to the circuit it’s a part of... » A reference point from which to measure Voltage » The earth is idealized as an infinite heat-sink for current. It can aborb an unlimited amount without changin ...
... » Current want to flow to ground. » “True” Ground is literally, the ground. » Floating ground is relative to the circuit it’s a part of... » A reference point from which to measure Voltage » The earth is idealized as an infinite heat-sink for current. It can aborb an unlimited amount without changin ...
R225-60-9
... circuit of the control, the control will respond to a raising circulating current to either raise or lower its tap position to limit the circulating current. This method has been described in greater detail in other papers in the industry for many years. The limitations to this method are that the l ...
... circuit of the control, the control will respond to a raising circulating current to either raise or lower its tap position to limit the circulating current. This method has been described in greater detail in other papers in the industry for many years. The limitations to this method are that the l ...
Ohm`s Law and Kirchhoff`s Rules
... The loop rule: The algebraic sum of the voltage differences around a circuit must equal zero. Another way to put this is: The sum of the voltage rises must equal the sum of the voltage drops. As current passes through a resistor it must do work to get through the resistor material. It loses energy w ...
... The loop rule: The algebraic sum of the voltage differences around a circuit must equal zero. Another way to put this is: The sum of the voltage rises must equal the sum of the voltage drops. As current passes through a resistor it must do work to get through the resistor material. It loses energy w ...
4.1 Ohm`s Law of Resistance to Current Electric current is the motion
... When current moves through a wire due to an electrical potential difference (a voltage), it is literally electric charges falling through the wire due to an electrical field. This is completely analogous to gravitational charges (masses) falling through the air due to a gravitational field. Differen ...
... When current moves through a wire due to an electrical potential difference (a voltage), it is literally electric charges falling through the wire due to an electrical field. This is completely analogous to gravitational charges (masses) falling through the air due to a gravitational field. Differen ...
Potential Dividers
... An LDR (light dependent resistor) has a resistance which decreases with increased illumination. Sketch a circuit to show how you could use a power supply, voltmeter, LDR and a fixed resistor to measure light intensities. What would be the point in replacing the fixed resistor with a variable resist ...
... An LDR (light dependent resistor) has a resistance which decreases with increased illumination. Sketch a circuit to show how you could use a power supply, voltmeter, LDR and a fixed resistor to measure light intensities. What would be the point in replacing the fixed resistor with a variable resist ...
Low Battery Indicator - Hobby Circuits and Projects
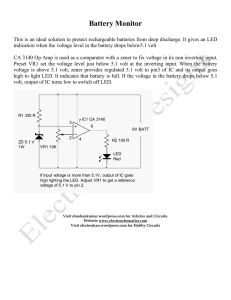
... Battery Monitor This is an ideal solution to protect rechargeable batteries from deep discharge. It gives an LED indication when the voltage level in the battery drops below5.1 volt CA 3140 Op Amp is used as a comparator with a zener to fix voltage in its non inverting input. Preset VR1 set the volt ...
... Battery Monitor This is an ideal solution to protect rechargeable batteries from deep discharge. It gives an LED indication when the voltage level in the battery drops below5.1 volt CA 3140 Op Amp is used as a comparator with a zener to fix voltage in its non inverting input. Preset VR1 set the volt ...
Electric Circuits
... Power Source-cells, photocell, thermocouple, generator Wire-Copper, aluminum Load-Energy consuming device;light bulb, motors, appliances ...
... Power Source-cells, photocell, thermocouple, generator Wire-Copper, aluminum Load-Energy consuming device;light bulb, motors, appliances ...
PHY2054_f11-09
... (a) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the 10 Ω and 5 Ω resistors. (b) Calculate the combined equivalent resistance of the 10 Ω, 5 Ω, and 4 Ω resistors. (c) Calculate the equivalent resistance found in part b and the parallel 3 Ω resistor. (d) Combine the equivalent resistance from part c and th ...
... (a) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the 10 Ω and 5 Ω resistors. (b) Calculate the combined equivalent resistance of the 10 Ω, 5 Ω, and 4 Ω resistors. (c) Calculate the equivalent resistance found in part b and the parallel 3 Ω resistor. (d) Combine the equivalent resistance from part c and th ...
Ohms Law - PHS Regents Physics
... it has all of the ______________________. through the wires and the R . 3. I = charge flowing _______________________________ The charge going __________ any circuit element must into equal leaving that element. Assume _________ the charge __________ + side of the source. ____ + charge flows out of ...
... it has all of the ______________________. through the wires and the R . 3. I = charge flowing _______________________________ The charge going __________ any circuit element must into equal leaving that element. Assume _________ the charge __________ + side of the source. ____ + charge flows out of ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.