Residential Wiring
... States for residential wiring. In PR we can use it for lamps wiring • 12: minimum approved width in Puerto Rico for residential wiring • 2: cable used from service panel to distribution panel, passes up to 100A of current ...
... States for residential wiring. In PR we can use it for lamps wiring • 12: minimum approved width in Puerto Rico for residential wiring • 2: cable used from service panel to distribution panel, passes up to 100A of current ...
Voltage Regulator
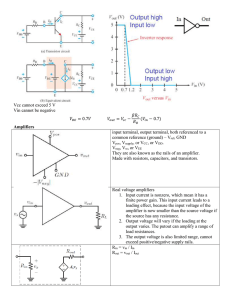
... zener diode. The error amplifier is a high gain differential amplifier with two inputs. The noninverting terminal is connected to the internally generated reference voltage. The inverting terminal is connected to full regulated output voltage. The series pass transistor is driven by the error amplif ...
... zener diode. The error amplifier is a high gain differential amplifier with two inputs. The noninverting terminal is connected to the internally generated reference voltage. The inverting terminal is connected to full regulated output voltage. The series pass transistor is driven by the error amplif ...
LT6108/LT6109 - Current Sense System
... Precise, Rugged and Fast Current Monitor and Control Linear Technology’s LT ®6108 and LT6109 are complete high side current sense devices that combine a high precision current sense amplifier with comparators and a precision voltage reference. When connected to a current shunt resistor, the high sid ...
... Precise, Rugged and Fast Current Monitor and Control Linear Technology’s LT ®6108 and LT6109 are complete high side current sense devices that combine a high precision current sense amplifier with comparators and a precision voltage reference. When connected to a current shunt resistor, the high sid ...
Electric Circuits
... • What is included in a circuit diagram? • How do series and parallel circuits differ? • How do you calculate electric power and electrical energy used? ...
... • What is included in a circuit diagram? • How do series and parallel circuits differ? • How do you calculate electric power and electrical energy used? ...
Alternating Current Applet Activity
... The root-mean-square (rms) value of an alternating current (or voltage) is that value of the direct current (or voltage) that dissipates power in a resistor at the same rate. In this activity you will determine the rms voltage of an ac resistor circuit and use it to show that its equivalent dc value ...
... The root-mean-square (rms) value of an alternating current (or voltage) is that value of the direct current (or voltage) that dissipates power in a resistor at the same rate. In this activity you will determine the rms voltage of an ac resistor circuit and use it to show that its equivalent dc value ...
Circuits
... Since there is only one path for the current with no junctions,we can say the current (I) remains constant throughout. IT = I1 = I2 …….. The equivalent resistance is the sum of all the resistances. Req = R1 + R2……… Since voltage drops occur across resistances, the sum of the drops equals the tot ...
... Since there is only one path for the current with no junctions,we can say the current (I) remains constant throughout. IT = I1 = I2 …….. The equivalent resistance is the sum of all the resistances. Req = R1 + R2……… Since voltage drops occur across resistances, the sum of the drops equals the tot ...
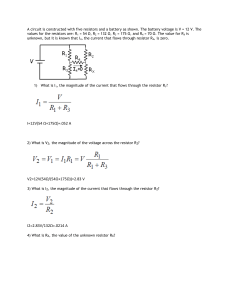
Activity 1.2.4 Circuit Calculation
... Activity 1.2.4 Circuit Calculations Introduction Regardless of circuit complexity, circuit designers as well as users need to be able to apply basic electrical theories to circuits in order to verify safe operation and troubleshoot unexpected circuit failure. In this activity you will gain experienc ...
... Activity 1.2.4 Circuit Calculations Introduction Regardless of circuit complexity, circuit designers as well as users need to be able to apply basic electrical theories to circuits in order to verify safe operation and troubleshoot unexpected circuit failure. In this activity you will gain experienc ...
Integral Resistor
... The integral resistor limits the supply current to approximately 12 mA -15 mA at the specified supply voltage as standard. Integral resistors for different supply voltages and currents are available, but may be limited by the space inside the indicator lamp body to dissipate the power generated. (Pl ...
... The integral resistor limits the supply current to approximately 12 mA -15 mA at the specified supply voltage as standard. Integral resistors for different supply voltages and currents are available, but may be limited by the space inside the indicator lamp body to dissipate the power generated. (Pl ...
Current - St John Brebeuf
... 7) Calculate the voltage supply needed to produce a current of 12A when used with a 48 ohm resistor ...
... 7) Calculate the voltage supply needed to produce a current of 12A when used with a 48 ohm resistor ...
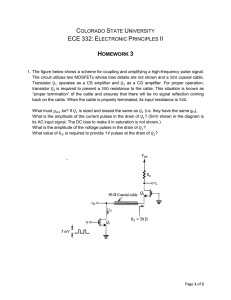
CIRCUIT IDEAS FOR DESIGNERS This current source can be built
... This current source can be built within a single IC package. The high input gate impedance of Q1 and Q2 eliminates any gate leakage current considerations in most cases, resulting in equal gate voltages of Q1 and Q2. Substantially all of the ISET current becomes the drain current of Q1. Drain curren ...
... This current source can be built within a single IC package. The high input gate impedance of Q1 and Q2 eliminates any gate leakage current considerations in most cases, resulting in equal gate voltages of Q1 and Q2. Substantially all of the ISET current becomes the drain current of Q1. Drain curren ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.