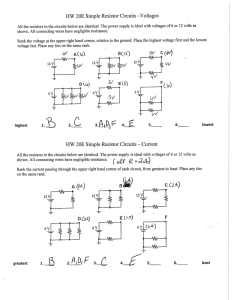
Current Intensity, Potential Difference and Ohm`s law
... How much electric energy did the heater use? A) 14 400 J B) 24 000 J C) 28 800 J D) 1 440 000 J 7. The following graph shows the variation of the voltage across the terminals of a ceramic element as a function of the intensity of the current passing through it. Voltage ...
... How much electric energy did the heater use? A) 14 400 J B) 24 000 J C) 28 800 J D) 1 440 000 J 7. The following graph shows the variation of the voltage across the terminals of a ceramic element as a function of the intensity of the current passing through it. Voltage ...
ANNOUNCEMENT
... The negative sign is because we have drawn the direction of the current such that positive current means charge is leaving the capacitor. ...
... The negative sign is because we have drawn the direction of the current such that positive current means charge is leaving the capacitor. ...
Name - mzaugg
... We have fuses or circuit breakers in our house to protect against too much current passing through the wires. Most circuits have a limit of 20 amperes of current. If this is exceeded, the circuit is broken. 4. Dizzy Dorey has all of the following appliances turned on in the same circuit. She has: ...
... We have fuses or circuit breakers in our house to protect against too much current passing through the wires. Most circuits have a limit of 20 amperes of current. If this is exceeded, the circuit is broken. 4. Dizzy Dorey has all of the following appliances turned on in the same circuit. She has: ...
2 Basic Components and Electric Circuits
... 2. charges occur in multiples of electron charge, i.e. multiples of 1.602 × 10−19 C. 3. law of conservation of charge: charge can neither be created nor be destroyed, only transferred. ⇒ algebraic sum of electric charges in a system does not change Universally accepted convention is that current is ...
... 2. charges occur in multiples of electron charge, i.e. multiples of 1.602 × 10−19 C. 3. law of conservation of charge: charge can neither be created nor be destroyed, only transferred. ⇒ algebraic sum of electric charges in a system does not change Universally accepted convention is that current is ...
Chapter 2
... 3. law of conservation of charge: charge can neither be created nor be destroyed, only transferred. ⇒ algebraic sum of electric charges in a system does not change Universally accepted convention is that current is the net flow of positive charges. Electric current is the time rate of change of char ...
... 3. law of conservation of charge: charge can neither be created nor be destroyed, only transferred. ⇒ algebraic sum of electric charges in a system does not change Universally accepted convention is that current is the net flow of positive charges. Electric current is the time rate of change of char ...
Electrical Circuits Revision - School
... What is the unit of current? The potential difference(pd) across a component is measured with a voltmeter. These are always placed in parallel with the component. What is the unit of potential ...
... What is the unit of current? The potential difference(pd) across a component is measured with a voltmeter. These are always placed in parallel with the component. What is the unit of potential ...
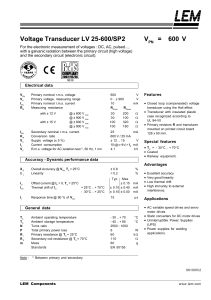
Voltage Transducer LV 25
... Primary voltage, measuring range Primary nominal r.m.s. current Measuring resistance with ± 12 V with ± 15 V ...
... Primary voltage, measuring range Primary nominal r.m.s. current Measuring resistance with ± 12 V with ± 15 V ...
Types of Circuits
... Wires and Voltage Since wires are conductors, they have no resistance, so they have no voltage difference. ...
... Wires and Voltage Since wires are conductors, they have no resistance, so they have no voltage difference. ...
Parallel and Series Circuit
... • As more bulbs are added, voltage remains the same • Current is split between pathways • If a bulb is removed, it will not affect the ...
... • As more bulbs are added, voltage remains the same • Current is split between pathways • If a bulb is removed, it will not affect the ...
Slide 1
... with a resistor R by a current source iS in parallel with a resistor R, or vice versa R ...
... with a resistor R by a current source iS in parallel with a resistor R, or vice versa R ...
Name Class Date Electric Current 1. Water doesn`t flow in the pipe
... CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS 152 Chapter 34 Electric Current ...
... CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS 152 Chapter 34 Electric Current ...
Ch 1 Electricity Slides 042909
... • Using Ohm's Law we can calculate the three electrical values in a circuit, i.e. Voltage, Amperage, and Resistance • The fourth electrical value is Power Power is measured in Watts Using the PIE equation we can calculate Power Using Ohm's Law and PIE equation if we know any two values we can ...
... • Using Ohm's Law we can calculate the three electrical values in a circuit, i.e. Voltage, Amperage, and Resistance • The fourth electrical value is Power Power is measured in Watts Using the PIE equation we can calculate Power Using Ohm's Law and PIE equation if we know any two values we can ...
4. Complex DC Circuits
... direction as we are looping produces a negative voltage. Current flowing opposite to our loop produces a positive voltage • I1 flows through R1 opposite to our loop, so I1R1 is positive. I2 flows through R2 in the same direction as our loop, so I2 R2 is negative ...
... direction as we are looping produces a negative voltage. Current flowing opposite to our loop produces a positive voltage • I1 flows through R1 opposite to our loop, so I1R1 is positive. I2 flows through R2 in the same direction as our loop, so I2 R2 is negative ...
MultiSIM – Lab #7 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The resistance of a Voltage Controlled Resistor (VCR) changes linearly as a function of the voltage. Its resistance is dependent on a pre-determined voltage. Dependent sources are used for circuit analysis but are not physical devices, thus are not available to be purchased in an electronics parts c ...
... The resistance of a Voltage Controlled Resistor (VCR) changes linearly as a function of the voltage. Its resistance is dependent on a pre-determined voltage. Dependent sources are used for circuit analysis but are not physical devices, thus are not available to be purchased in an electronics parts c ...
First occasion to measure
... QPS for IPQs, IPDs and Inner Triplets. Preparation, IST and Hardware Commissioning 2009 The DQGPUs (types B1, B2 and C) are presently being modified by QPS to separate the powering of the redundant Detector Boards between UPS1 (F3) and the new UPS2 (F4). Modifications are on the CRATE LEVEL, not o ...
... QPS for IPQs, IPDs and Inner Triplets. Preparation, IST and Hardware Commissioning 2009 The DQGPUs (types B1, B2 and C) are presently being modified by QPS to separate the powering of the redundant Detector Boards between UPS1 (F3) and the new UPS2 (F4). Modifications are on the CRATE LEVEL, not o ...
Specification Status: Released 2Pro Device Series
... processing, or specification of any product; and to discontinue or limit production or distribution of any product. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. Without expressed or written consent by an officer of TE, TE does not authorize the use of any of its prod ...
... processing, or specification of any product; and to discontinue or limit production or distribution of any product. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. Without expressed or written consent by an officer of TE, TE does not authorize the use of any of its prod ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.