RC (Resistor-Capacitor) Circuits
... Initially, the capacitor is UNCHARGED (q = 0) and the current through the resistor is zero. A switch (in red) then closes the circuit by moving upwards. The question is: What happens to the current and voltage across the resistor and capacitor as the capacitor begins to charge as a function of time? ...
... Initially, the capacitor is UNCHARGED (q = 0) and the current through the resistor is zero. A switch (in red) then closes the circuit by moving upwards. The question is: What happens to the current and voltage across the resistor and capacitor as the capacitor begins to charge as a function of time? ...
current electricity
... the source of electromotive force (emf). Electromotive force is not a force, but energy. It is the amount of energy needed to push a unit charge through a source. Charge flows externally from the positive pole of a cell to the negative cell. This indeed, is due to electrons going from the negative t ...
... the source of electromotive force (emf). Electromotive force is not a force, but energy. It is the amount of energy needed to push a unit charge through a source. Charge flows externally from the positive pole of a cell to the negative cell. This indeed, is due to electrons going from the negative t ...
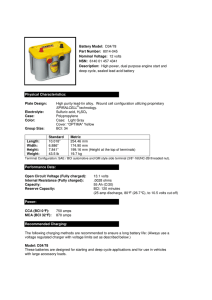
Battery Model: D34/78 Part Number: 8014
... Approximate time to 90% charge 100 amps 35 minutes 50 amps 75 minutes 25 amps 140 minutes Recharge time will vary according to temperature and charger characteristics. When using Constant Voltage chargers, amperage will taper down as the battery becomes recharged. When amperage drops below 1 amp, th ...
... Approximate time to 90% charge 100 amps 35 minutes 50 amps 75 minutes 25 amps 140 minutes Recharge time will vary according to temperature and charger characteristics. When using Constant Voltage chargers, amperage will taper down as the battery becomes recharged. When amperage drops below 1 amp, th ...
DC Fundamentals, 9-2 - Lab-Volt
... Exercise 2: Voltage in a Series/Parallel Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Ohm’s law. You will verify your results with a multimeter. DISCUSSION In a series/parallel circuit, voltage across each circuit branch is distributed in proportion to the resistive value of each branch. In this circuit, the applied ...
... Exercise 2: Voltage in a Series/Parallel Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Ohm’s law. You will verify your results with a multimeter. DISCUSSION In a series/parallel circuit, voltage across each circuit branch is distributed in proportion to the resistive value of each branch. In this circuit, the applied ...
Chapter 19 Notes 19C
... the respiratory system may occur. • If 70mA or more passes through the torso or heart region for more than a second, ventricular fibrulation may occur and cause death. • Dry skin has a resistance of 104 to 106W ... Wet skin has 103 W . I=V/R means 120 V could be lethal. • See p 574 ...
... the respiratory system may occur. • If 70mA or more passes through the torso or heart region for more than a second, ventricular fibrulation may occur and cause death. • Dry skin has a resistance of 104 to 106W ... Wet skin has 103 W . I=V/R means 120 V could be lethal. • See p 574 ...
PowerPoint-Electromagnetism
... conducting solution. Most car batteries have a series of six cells, each containing lead and lead oxide in a sulfuric acid solution. ...
... conducting solution. Most car batteries have a series of six cells, each containing lead and lead oxide in a sulfuric acid solution. ...
TDE3247
... specifically to drive lamps, relays and stepping motors. The Device is essentialy blow-out proof. Current limiting is available to limit the peak output current to a safe value, the adjustment only required an external resistor. In addition, thermal shut-down is provided to keep the IC from overheat ...
... specifically to drive lamps, relays and stepping motors. The Device is essentialy blow-out proof. Current limiting is available to limit the peak output current to a safe value, the adjustment only required an external resistor. In addition, thermal shut-down is provided to keep the IC from overheat ...
Sample Problem
... voltage across its terminals drops below its rated EMF. • The chemical reactions in the battery cannot supply charge fast enough to maintain the full EMF. • Thus the battery is said to have an internal resistance, designated r. • Ex: Starting a car with the headlights on, the lights dim. The starter ...
... voltage across its terminals drops below its rated EMF. • The chemical reactions in the battery cannot supply charge fast enough to maintain the full EMF. • Thus the battery is said to have an internal resistance, designated r. • Ex: Starting a car with the headlights on, the lights dim. The starter ...
Power Electronics
... – AC-DC-AC frequency converter (for AC motor drive) – AC-DC-AC constant-voltage constant-frequency converter (for uninterruptable power supplies) – AC-DC-AC Converters for induction heating – AC-DC-AC-DC switching power supplies ...
... – AC-DC-AC frequency converter (for AC motor drive) – AC-DC-AC constant-voltage constant-frequency converter (for uninterruptable power supplies) – AC-DC-AC Converters for induction heating – AC-DC-AC-DC switching power supplies ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... To gain an understanding of the circuit quantities, voltage, current and resistance, and the application of ohm’s law using series and parallel circuits via a computer simulation. TIME ALLOWANCE: This activity should take no more than 60 minutes. ASSESSMENT: Individual completion of this worksheet f ...
... To gain an understanding of the circuit quantities, voltage, current and resistance, and the application of ohm’s law using series and parallel circuits via a computer simulation. TIME ALLOWANCE: This activity should take no more than 60 minutes. ASSESSMENT: Individual completion of this worksheet f ...
Chapter 10
... electric current. It produces a voltage drop that is proportional to the electric current. •A resister has two terminals, which are usually not necessary to be distinguished. • Resistors are specified by their resistance, measured by ohms (W). There are many values of resistance available (e.g., 0.1 ...
... electric current. It produces a voltage drop that is proportional to the electric current. •A resister has two terminals, which are usually not necessary to be distinguished. • Resistors are specified by their resistance, measured by ohms (W). There are many values of resistance available (e.g., 0.1 ...
Transformer Basics
... • Measured currents greater than those shown on the CT curves would indicate trouble within the CT. ...
... • Measured currents greater than those shown on the CT curves would indicate trouble within the CT. ...
4 Current Electricity
... Resistance can be increased by using a long, thin wire made of a metal with high resistivity eg tungsten. Copper has a low resistivity Potential difference (or voltage, V), current (I) and resistance (R) are related by Ohm’s Law where V = IR in a simple electrical circuit. ...
... Resistance can be increased by using a long, thin wire made of a metal with high resistivity eg tungsten. Copper has a low resistivity Potential difference (or voltage, V), current (I) and resistance (R) are related by Ohm’s Law where V = IR in a simple electrical circuit. ...
Charging_Capacitors
... Charging Capacitors Apparatus range of large capacitors and resistors connected in series to a low voltage power supply, oscilloscope to view charging/discharging curves Note – depending on the students experience in connecting circuits, the circuits can be set up in advance or left for the students ...
... Charging Capacitors Apparatus range of large capacitors and resistors connected in series to a low voltage power supply, oscilloscope to view charging/discharging curves Note – depending on the students experience in connecting circuits, the circuits can be set up in advance or left for the students ...
Battery Model: D34 Part Number: 8012-021
... Approximate time to 90% charge 100 amps 35 minutes 50 amps 75 minutes 25 amps 140 minutes Recharge time will vary according to temperature and charger characteristics. When using Constant Voltage chargers, amperage will taper down as the battery becomes recharged. When amperage drops below 1 amp, th ...
... Approximate time to 90% charge 100 amps 35 minutes 50 amps 75 minutes 25 amps 140 minutes Recharge time will vary according to temperature and charger characteristics. When using Constant Voltage chargers, amperage will taper down as the battery becomes recharged. When amperage drops below 1 amp, th ...
PN Junction Diodes and Applications
... A PN Junction diode is a 2-terminal semiconductor electronic On/Off switch that allows current flow in only one direction. The circuit symbol is shown below. The terminals are called the Anode (A) and the Cathode (K). The state of the diode switch (open or closed) is determined by the polarity of th ...
... A PN Junction diode is a 2-terminal semiconductor electronic On/Off switch that allows current flow in only one direction. The circuit symbol is shown below. The terminals are called the Anode (A) and the Cathode (K). The state of the diode switch (open or closed) is determined by the polarity of th ...
BJT in Saturation Mode
... VBC <400 mV because the current in the B-C junction is negligible, provided that various tolerances in the component values do not drive the device into deep saturation. • For a device in soft saturation or active region, we approximate IC as Isexp(VBE/VT) • In the deep saturation region, the collec ...
... VBC <400 mV because the current in the B-C junction is negligible, provided that various tolerances in the component values do not drive the device into deep saturation. • For a device in soft saturation or active region, we approximate IC as Isexp(VBE/VT) • In the deep saturation region, the collec ...
The Superposition Theorem - madalina
... For the following circuit determine the current through R resistor and the voltage across it, using: Kirchhoff’s theorem Thevenin and/or Norton equivalence (use the superposition theorem) R3 ...
... For the following circuit determine the current through R resistor and the voltage across it, using: Kirchhoff’s theorem Thevenin and/or Norton equivalence (use the superposition theorem) R3 ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.