Dr Davids Essential Chemistry Definitions Bk1
... Catalyst: A positive catalyst speeds up a chemical reaction by providing an alternative reaction path with a lower acti vation energy. Negative catalysts do the opposite. Concentration: The amount of substance in solution expressed as moles per dm3. ...
... Catalyst: A positive catalyst speeds up a chemical reaction by providing an alternative reaction path with a lower acti vation energy. Negative catalysts do the opposite. Concentration: The amount of substance in solution expressed as moles per dm3. ...
Stoich Powerpoint Review
... • Sometimes they will give you molar mass of a compound and its empirical formula. • You must find the “empirical formula mass” and divide the molar mass by the efm. ...
... • Sometimes they will give you molar mass of a compound and its empirical formula. • You must find the “empirical formula mass” and divide the molar mass by the efm. ...
Document
... The internal energy (E) of a system is the sum of KE and PE of all particles in the system. The internal energy of a system can be changed by a flow of work, heat, or both. i.e. ΔE = q + w ΔE: change of E, q: heat, w: work Thermodynamic quantities always consist of two parts: a number, giving the ma ...
... The internal energy (E) of a system is the sum of KE and PE of all particles in the system. The internal energy of a system can be changed by a flow of work, heat, or both. i.e. ΔE = q + w ΔE: change of E, q: heat, w: work Thermodynamic quantities always consist of two parts: a number, giving the ma ...
Chapters 6 and 17: Chemical Thermodynamics
... Determine the change in standard enthalpy of a reaction (delta H) Determine the change in standard entropy of a reaction (delta S) Determine the change in standard Gibbs Free Energy of a reaction (delta G) Determine the heat of combustion for a reaction Determine if the reaction is exother ...
... Determine the change in standard enthalpy of a reaction (delta H) Determine the change in standard entropy of a reaction (delta S) Determine the change in standard Gibbs Free Energy of a reaction (delta G) Determine the heat of combustion for a reaction Determine if the reaction is exother ...
2nd nine weeks benchmark review homework
... to the number of ___ in the nucleus. a- atomic number, neutrons b- atomic number, protons c- atomic mass, neutrons d- atomic mass, protons When the physical composition of a substance changes, the chemical composition- ...
... to the number of ___ in the nucleus. a- atomic number, neutrons b- atomic number, protons c- atomic mass, neutrons d- atomic mass, protons When the physical composition of a substance changes, the chemical composition- ...
Document
... thermodynamic (state) function will not depend on the path or intermediate steps. p p • Hess’s law: Standard enthalpy (entropy, Gibbs free energy etc.) of an overall reaction is the sum of the enthalpies (entropies, Gibbs free energies etc.) of the individual reaction it mayy be divided into. • Stan ...
... thermodynamic (state) function will not depend on the path or intermediate steps. p p • Hess’s law: Standard enthalpy (entropy, Gibbs free energy etc.) of an overall reaction is the sum of the enthalpies (entropies, Gibbs free energies etc.) of the individual reaction it mayy be divided into. • Stan ...
Thermodynamics states that `the change in internal energy (∆ ) of a
... more ordered, however the release of thermal energy will increase the disorder of the molecules in the surroundings by a greater amount. Generally speaking a liquid has greater entropy than a solid, and a gas has greater entropy than both. Gibbs free energy We have seen that exothermic and endotherm ...
... more ordered, however the release of thermal energy will increase the disorder of the molecules in the surroundings by a greater amount. Generally speaking a liquid has greater entropy than a solid, and a gas has greater entropy than both. Gibbs free energy We have seen that exothermic and endotherm ...
chemical reactions
... within the first few weeks of life they begin to show neurologic disturbances such as epilepsy. Signs also include skeletal changes such as a small head, short stature, and flat feet. PKU sufferers may also have a skin disorder called ...
... within the first few weeks of life they begin to show neurologic disturbances such as epilepsy. Signs also include skeletal changes such as a small head, short stature, and flat feet. PKU sufferers may also have a skin disorder called ...
Chemical Equations & Reactions
... Determine the heat of reaction, ΔH, (enthalpy change) for this reaction. Determine the activation energy, Ea for this reaction. How much energy is released or absorbed during the reaction? How much energy is required for this reaction to occur? ...
... Determine the heat of reaction, ΔH, (enthalpy change) for this reaction. Determine the activation energy, Ea for this reaction. How much energy is released or absorbed during the reaction? How much energy is required for this reaction to occur? ...
Writing and Classifying Balanced Equations
... 11. How many H atoms are on the products side of the equation? 12. Is the number of O atoms the same on both sides of the arrow? 13. Is the equation completely balanced as written? 14. If no, what would need to be done to make it balanced. Explain with a sentence and write the final balanced equatio ...
... 11. How many H atoms are on the products side of the equation? 12. Is the number of O atoms the same on both sides of the arrow? 13. Is the equation completely balanced as written? 14. If no, what would need to be done to make it balanced. Explain with a sentence and write the final balanced equatio ...
6. Thermodynamics - Sakshi Education
... equilibrium temperature (T) during the transformation. The units of ∆S are J mol–1 K–1. Entropy is a state function and is an extensive property. Ex: Ice ⇌ Water ⇌ Vapour .The order of entropy is S(g) > S(l) > S(s) Entropy increases in all spontaneous processes 6. State second law of Thermodynamics. ...
... equilibrium temperature (T) during the transformation. The units of ∆S are J mol–1 K–1. Entropy is a state function and is an extensive property. Ex: Ice ⇌ Water ⇌ Vapour .The order of entropy is S(g) > S(l) > S(s) Entropy increases in all spontaneous processes 6. State second law of Thermodynamics. ...
Thermochemistry and Measuring Energy Change Complete NOTES
... The experimental determination of Hfo values is often difficult or impossible. Combustion of organic compounds involves the reaction with molecular oxygen to form gaseous carbon dioxide and liquid water, as seen in this example with sucrose: ...
... The experimental determination of Hfo values is often difficult or impossible. Combustion of organic compounds involves the reaction with molecular oxygen to form gaseous carbon dioxide and liquid water, as seen in this example with sucrose: ...
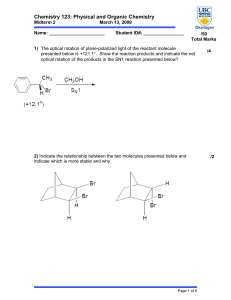
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry
... to -10°C. Describe each step of the process and calculate the amount of energy that would need to flow in or out of the system. At each step indicate if the entropy is increasing or decreasing and under what conditions the reaction would be spontaneous. ...
... to -10°C. Describe each step of the process and calculate the amount of energy that would need to flow in or out of the system. At each step indicate if the entropy is increasing or decreasing and under what conditions the reaction would be spontaneous. ...
Thermodynamics
... In gas, more ways to distribute energy than a solid. Energy in solid is due to vibrations between molecules. Energy in gas is due to translational, rotational, and ...
... In gas, more ways to distribute energy than a solid. Energy in solid is due to vibrations between molecules. Energy in gas is due to translational, rotational, and ...
Chemical Equations & Reactions
... Active metals displace less active metals or hydrogen from their compounds in aqueous solution. Refer to the Activity Series. a. Al + CuCl2 AlCl3 + Cu b. metal + H2O metal hydroxide + H2 Metals include the alkali metals and calcium. 2Na + 2H2O 2NaOH + H2 ...
... Active metals displace less active metals or hydrogen from their compounds in aqueous solution. Refer to the Activity Series. a. Al + CuCl2 AlCl3 + Cu b. metal + H2O metal hydroxide + H2 Metals include the alkali metals and calcium. 2Na + 2H2O 2NaOH + H2 ...
Lecture 10 Activity of chemical components
... where Z is the charge on the ion and I is called as net ionic strength, ci is the concentration of the i th ion. The factor –0.0509 depends on the solvent dielectric constant and temperature. Thus we can see that Debye model predicts a reduction in activity coefficients. (1) Higher the charge, lower ...
... where Z is the charge on the ion and I is called as net ionic strength, ci is the concentration of the i th ion. The factor –0.0509 depends on the solvent dielectric constant and temperature. Thus we can see that Debye model predicts a reduction in activity coefficients. (1) Higher the charge, lower ...
File
... Entropy- a measure of disorder of a system The more ordered a system is, the more entropy it has – for example a clean, organized room has less entropy than a messy room. ...
... Entropy- a measure of disorder of a system The more ordered a system is, the more entropy it has – for example a clean, organized room has less entropy than a messy room. ...
11 Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry
... The value of ∆G may be obtained by the formula below if ∆H, T, and ∆S is known: ∆G = ∆H - T∆S . When using this formula the temperature must be in Kelvin, and the units of energy for ∆H and ∆S must be the same. The relationship between ∆H, T, and ∆S as they relates to spontaneity is shown in ...
... The value of ∆G may be obtained by the formula below if ∆H, T, and ∆S is known: ∆G = ∆H - T∆S . When using this formula the temperature must be in Kelvin, and the units of energy for ∆H and ∆S must be the same. The relationship between ∆H, T, and ∆S as they relates to spontaneity is shown in ...
CHEM 1A General Chemistry I (1)
... This course introduces atomic structure, bonding, stoichiometry, thermochemistry, gases, matter and energy, oxidation-reduction, chemical equations, liquids and solids, solutions, chemical energetics and equilibrium. The first semester of a one-year course in chemistry intended for majors in the nat ...
... This course introduces atomic structure, bonding, stoichiometry, thermochemistry, gases, matter and energy, oxidation-reduction, chemical equations, liquids and solids, solutions, chemical energetics and equilibrium. The first semester of a one-year course in chemistry intended for majors in the nat ...
pretest - Allen County Schools
... 8. The temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid is its… a. boiling point c. sublimation point b. melting point d. evaporation point 9. The temperature at which a liquid changes into a liquid to a solid is its… a. boiling point c. sublimation point b. melting point d. freezin ...
... 8. The temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid is its… a. boiling point c. sublimation point b. melting point d. evaporation point 9. The temperature at which a liquid changes into a liquid to a solid is its… a. boiling point c. sublimation point b. melting point d. freezin ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.