Solutions - Seattle Central
... Indicators are chemical compounds used to detect the presence of other compounds. They change shape in the presence of certain compounds as a result of chemical reactions. ...
... Indicators are chemical compounds used to detect the presence of other compounds. They change shape in the presence of certain compounds as a result of chemical reactions. ...
Chapter 4: Life is based on molecules with carbon (organic
... A. organic compounds have at least one carbon atom covalently bound to another carbon atom or to hydrogen; the chemistry of organic molecules is organized around the carbon atom B. carbon atoms have six electrons - 2 in level 1, and 4 in their valence (outer) shell (level 2) ...
... A. organic compounds have at least one carbon atom covalently bound to another carbon atom or to hydrogen; the chemistry of organic molecules is organized around the carbon atom B. carbon atoms have six electrons - 2 in level 1, and 4 in their valence (outer) shell (level 2) ...
Organic Chemistry
... • A cis-isomer has the two substituted groups on the same side of the double bond. • A trans-isomer has the two • substituted groups on • opposite sides of the double ...
... • A cis-isomer has the two substituted groups on the same side of the double bond. • A trans-isomer has the two • substituted groups on • opposite sides of the double ...
Organic Notes for Chapter 4 and 5
... Highly polar; therefore water soluble Acts as a weak acid (releases H+) Found in amino acids and fatty acids ...
... Highly polar; therefore water soluble Acts as a weak acid (releases H+) Found in amino acids and fatty acids ...
(a) Structural isomers
... Concept 4.1: Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds • Organic chemistry is the study of compounds that contain carbon • Organic compounds range from simple molecules to colossal ones • Most organic compounds contain hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon atoms ...
... Concept 4.1: Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds • Organic chemistry is the study of compounds that contain carbon • Organic compounds range from simple molecules to colossal ones • Most organic compounds contain hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon atoms ...
Mandatory Class: 1 st Organic chemistry CH 122
... The mechanisms can be described in terms of electron shifts, Radical substitution vice versa of alkanes. The physical properties will be explained in terms of the intermolecular forces. NO ...
... The mechanisms can be described in terms of electron shifts, Radical substitution vice versa of alkanes. The physical properties will be explained in terms of the intermolecular forces. NO ...
Review Sheet for Chemistry* First Semester Final
... 8. How many liters are in 128 g of nitrogen gas, N2? ...
... 8. How many liters are in 128 g of nitrogen gas, N2? ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... alkene (11.1) a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon-carbon double bonds; an unsaturated hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n. alkyne (11.1) a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon-carbon triple bonds; an unsaturated hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n-2. aromatic compoun ...
... alkene (11.1) a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon-carbon double bonds; an unsaturated hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n. alkyne (11.1) a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon-carbon triple bonds; an unsaturated hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n-2. aromatic compoun ...
Organic chemistry is the study of carbon
... double bonds with two different oxygen atoms. The structural formula, O = C = O, shows that each atom has completed its valence shells. While CO2 can be classified as either organic or inorganic, its importance to the living world is clear. CO2 is the source for all organic molecules in organisms vi ...
... double bonds with two different oxygen atoms. The structural formula, O = C = O, shows that each atom has completed its valence shells. While CO2 can be classified as either organic or inorganic, its importance to the living world is clear. CO2 is the source for all organic molecules in organisms vi ...
Chapter 11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Part 2
... 5. The two isomers, configurations (a) and (b), are enantiomers because each molecule contains two stereogenic centers (asymmetric carbon atoms) and their mirror images are non-superimposable to each other. 6. A. ...
... 5. The two isomers, configurations (a) and (b), are enantiomers because each molecule contains two stereogenic centers (asymmetric carbon atoms) and their mirror images are non-superimposable to each other. 6. A. ...
Bell Work
... one of the fatty acids is a phosphorous containing group. This gives half of the molecule a polarity; while the other half is nonpolar. Great for membranes (cellular ...
... one of the fatty acids is a phosphorous containing group. This gives half of the molecule a polarity; while the other half is nonpolar. Great for membranes (cellular ...
6.5 Main Group
... Both materials are very hard, in fact diamond is the hardest material known – a direct consequence of the molecular structure. ...
... Both materials are very hard, in fact diamond is the hardest material known – a direct consequence of the molecular structure. ...
Name: ______ Aim 36: Elements, atoms, compounds and miztures
... All elements retain their original properties. New properties are formed. Only metals retain their original properties. New elements are formed. ...
... All elements retain their original properties. New properties are formed. Only metals retain their original properties. New elements are formed. ...
Organic Chemistry Unit
... Found in all living matter Found in body tissue Found in food Found in fuels (coal, wood, petroleum) Found in Nature ( ranked 17th in crust) ...
... Found in all living matter Found in body tissue Found in food Found in fuels (coal, wood, petroleum) Found in Nature ( ranked 17th in crust) ...
Organic/Biological Chemistry
... Therefore, alkynes have one and two bonds between two C atoms. Ethyne (acetylene) is a reactive alkyne: HCCH. When acetylene is burned in the presence of oxygen (oxyacetylene torch) the temperature is about 3200 K. Alkynes are named in the same way as alkenes with the suffix -yne replacing the ...
... Therefore, alkynes have one and two bonds between two C atoms. Ethyne (acetylene) is a reactive alkyne: HCCH. When acetylene is burned in the presence of oxygen (oxyacetylene torch) the temperature is about 3200 K. Alkynes are named in the same way as alkenes with the suffix -yne replacing the ...
04 Carbon
... – Carbon has little tendency to form ionic bonds by loosing or gaining 4 electrons. – Instead, carbon usually completes its valence shell by sharing electrons with other atoms in four covalent bonds. – This tetravalence by carbon makes large, complex molecules possible. ...
... – Carbon has little tendency to form ionic bonds by loosing or gaining 4 electrons. – Instead, carbon usually completes its valence shell by sharing electrons with other atoms in four covalent bonds. – This tetravalence by carbon makes large, complex molecules possible. ...
MSWord
... Wen-Xiong Zhang, Masayoshi Nishiura and Zhaomin Hou* Organometallic Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN, Hirosawa 2-1, Wako, Saitama 351-0198, Japan houz@riken.jp ...
... Wen-Xiong Zhang, Masayoshi Nishiura and Zhaomin Hou* Organometallic Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN, Hirosawa 2-1, Wako, Saitama 351-0198, Japan houz@riken.jp ...
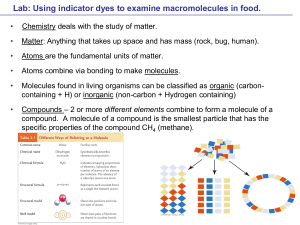
COMPOUNDS AND MOLECULES
... SiO2 (strong, rigid, high melting point) EXAMPLE: B. Network structure - IONS NaCl (strong, rigid, high melting point) EXAMPLE: C. Molecule groups C12H22O11 (weak bonds, low melting point) EXAMPLE: ...
... SiO2 (strong, rigid, high melting point) EXAMPLE: B. Network structure - IONS NaCl (strong, rigid, high melting point) EXAMPLE: C. Molecule groups C12H22O11 (weak bonds, low melting point) EXAMPLE: ...
Organic Chemistry Chapter 25 - Ms. Ose's Chemistry Website
... stronger than single bonds; this results from decreasing bond length Most reactions between oxygen and organic compounds are exothermic and stable at room temperature Special stability is associated with the presence of aromatic rings due to the overlap of the pi orbitals of the carbon atoms tha ...
... stronger than single bonds; this results from decreasing bond length Most reactions between oxygen and organic compounds are exothermic and stable at room temperature Special stability is associated with the presence of aromatic rings due to the overlap of the pi orbitals of the carbon atoms tha ...
Unit Two : Carbon Compounds
... make acid rain. Carbon dioxide is also acidic and slightly soluble in water. Nitrogen dioxide is formed by an electrical spark in a car engine or lightning storms in air. This also contributes to acid rain. Crude oil is a mixture of compounds, mainly hydrocarbons. A hydrocarbon is a compound which c ...
... make acid rain. Carbon dioxide is also acidic and slightly soluble in water. Nitrogen dioxide is formed by an electrical spark in a car engine or lightning storms in air. This also contributes to acid rain. Crude oil is a mixture of compounds, mainly hydrocarbons. A hydrocarbon is a compound which c ...
Review Questions
... 5. Find the percent composition of Oxygen in Na2S2O3 __________________________ ...
... 5. Find the percent composition of Oxygen in Na2S2O3 __________________________ ...
Alkanes and alkenes
... Alkanes and alkenes are obtained from natural gas and crude oil (petroleum) which are mixtures of hydrocarbons. Natural gas contains CH4, C2H6, C3H8 and C4H10 and petroleum contains liquid hydrocarbons with gaseous hydrocarbons dissolved in the liquid. Substitution occurs when atoms in the molecule ...
... Alkanes and alkenes are obtained from natural gas and crude oil (petroleum) which are mixtures of hydrocarbons. Natural gas contains CH4, C2H6, C3H8 and C4H10 and petroleum contains liquid hydrocarbons with gaseous hydrocarbons dissolved in the liquid. Substitution occurs when atoms in the molecule ...
Carbon Chemistry Atoms of all elements (except Noble Gases) form
... Atoms of all elements (except Noble Gases) form chemical bonds But few elements have the ability of carbon to bond with both itself and other elements in so many different ways. o H, O, N can only form one, two, or three bonds. o However, with 4 valence electrons, each carbon atom is able to form ...
... Atoms of all elements (except Noble Gases) form chemical bonds But few elements have the ability of carbon to bond with both itself and other elements in so many different ways. o H, O, N can only form one, two, or three bonds. o However, with 4 valence electrons, each carbon atom is able to form ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.