CHAPTER 9 : CHEMICAL BONDING I
... 9.74 The formulas for the fluorides of the third-period elements are NaF, MgF2, AlF3, SiF4, PF5, SF6, and CLF3. Classify these compounds as covalent or ionic. 9.76 Describe some characteristics of an ionic compound such as KF that would distinguish it from a covalent compound such as benzene (C6H6). ...
... 9.74 The formulas for the fluorides of the third-period elements are NaF, MgF2, AlF3, SiF4, PF5, SF6, and CLF3. Classify these compounds as covalent or ionic. 9.76 Describe some characteristics of an ionic compound such as KF that would distinguish it from a covalent compound such as benzene (C6H6). ...
Alkenes: Overview
... •Combustion gave C6H6 - Benzene. •Put yourself in Faraday’s place. •C6H6 suggests unsaturation. (Alkanes are normally CnH2n+2) •Logically the unknown compound should decolourise Br2. ...
... •Combustion gave C6H6 - Benzene. •Put yourself in Faraday’s place. •C6H6 suggests unsaturation. (Alkanes are normally CnH2n+2) •Logically the unknown compound should decolourise Br2. ...
Name: Date: AP Chemistry/Chemistry 145 Summer Assignment
... purified iron. The other product of the reaction is carbon dioxide gas. 2.10 g of iron is recovered from one such trial. ...
... purified iron. The other product of the reaction is carbon dioxide gas. 2.10 g of iron is recovered from one such trial. ...
2011 Spring 1 key
... 2. Electronegativity is a measure of the electron-attracting ability of an atom in a chemical bond. 3. A(n) oxyanion is a polyatomic ions with the general formula HaXbOcd-. (The a can be 0.) 4. Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different molecular structures. 5. Molar ma ...
... 2. Electronegativity is a measure of the electron-attracting ability of an atom in a chemical bond. 3. A(n) oxyanion is a polyatomic ions with the general formula HaXbOcd-. (The a can be 0.) 4. Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different molecular structures. 5. Molar ma ...
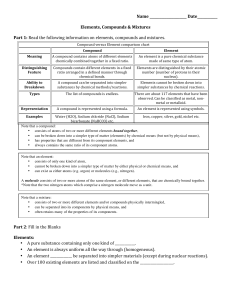
Compound vs Element chart
... • consists of atoms of two or more different elements bound together, • can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (elements) by chemical means (but not by physical means), • has properties that are different from its component elements, and • always contains the same ratio of its component at ...
... • consists of atoms of two or more different elements bound together, • can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (elements) by chemical means (but not by physical means), • has properties that are different from its component elements, and • always contains the same ratio of its component at ...
Chapter 11
... •Inorganic compounds: cpds which are NOT hydrocarbons (~1.5 million) •Organic compounds: cpds which contain hydrogen & carbon (thus, hydrocarbons & derivatives) (~ 7 million) •“Organic Chemistry” started, as a branch of chemistry, when F. Wohler disproved the idea of “vital force.” - previously, it ...
... •Inorganic compounds: cpds which are NOT hydrocarbons (~1.5 million) •Organic compounds: cpds which contain hydrogen & carbon (thus, hydrocarbons & derivatives) (~ 7 million) •“Organic Chemistry” started, as a branch of chemistry, when F. Wohler disproved the idea of “vital force.” - previously, it ...
AP Chemistry Placement Test To be successful in AP Chemistry
... 15) A metal having a mass of 44 grams is dropped in 118.2 mL of water and sinks to the bottom. The volume of the water and the metal is 124.3 mL. What is the density of the metal? A. 0.37 g/mL B. 7.2 g/mL C. 0.35 g/mL D. 2.7 g/mL ...
... 15) A metal having a mass of 44 grams is dropped in 118.2 mL of water and sinks to the bottom. The volume of the water and the metal is 124.3 mL. What is the density of the metal? A. 0.37 g/mL B. 7.2 g/mL C. 0.35 g/mL D. 2.7 g/mL ...
O - Clark College
... 1. Complete the following Lewis structures by filling in missing electrons (as lone pairs and bonds), computing formal charges, and indicating equivalent resonance structures, where they exist. The number of resonance structures that can be drawn is indicated next to the structure. For each set of s ...
... 1. Complete the following Lewis structures by filling in missing electrons (as lone pairs and bonds), computing formal charges, and indicating equivalent resonance structures, where they exist. The number of resonance structures that can be drawn is indicated next to the structure. For each set of s ...
twelve important naval substances – bonding
... (contains only carbon and hydrogen) in which there are only single bonds. These are called alkanes. (You are supposed to know the names of straight chain alkanes containing from 1 to 10 carbon atoms.) C-C single bonds have very limited reactivity. The primary commercial uses of alkanes are as fuels ...
... (contains only carbon and hydrogen) in which there are only single bonds. These are called alkanes. (You are supposed to know the names of straight chain alkanes containing from 1 to 10 carbon atoms.) C-C single bonds have very limited reactivity. The primary commercial uses of alkanes are as fuels ...
Notes, Part II
... One or more of the hydrogens in a hydrocarbon has been replaced by a hydroxyl group (-OH) Note: the –OH group here does not dissociate in water; so is chemically different than the hydroxide ion (OH-) The –OH group in alcohols makes them reasonable polar in small molecules (up to 4 carbons), a ...
... One or more of the hydrogens in a hydrocarbon has been replaced by a hydroxyl group (-OH) Note: the –OH group here does not dissociate in water; so is chemically different than the hydroxide ion (OH-) The –OH group in alcohols makes them reasonable polar in small molecules (up to 4 carbons), a ...
Chapter 8 - TeacherWeb
... A single covalent bond occurs when two atoms share one pair of valence electrons A double covalent bond occurs when two atoms share two pairs of valence electrons A triple covalent bond occurs when two atoms share three pairs of covalent bonds ...
... A single covalent bond occurs when two atoms share one pair of valence electrons A double covalent bond occurs when two atoms share two pairs of valence electrons A triple covalent bond occurs when two atoms share three pairs of covalent bonds ...
131 Learning Objectives
... Name organic compounds with carbon-heteroatom single bonds (oxygen, halogens, sulfur) Identify 1°, 2°, 3° alcohols and alkyl halides Predict the products or reactants for following reactions: Alcohol dehydration Alcohol oxidation Sulfur oxidation Sulfur reduction Chapter 15: The 3-D Shape of M ...
... Name organic compounds with carbon-heteroatom single bonds (oxygen, halogens, sulfur) Identify 1°, 2°, 3° alcohols and alkyl halides Predict the products or reactants for following reactions: Alcohol dehydration Alcohol oxidation Sulfur oxidation Sulfur reduction Chapter 15: The 3-D Shape of M ...
AP Chemistry
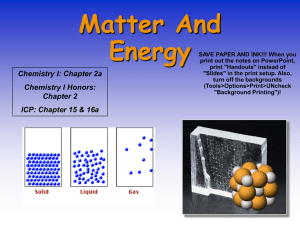
... Composed of molecules, all of which are alike Small! One billionth of a drop of water has 1 trillion molecules!!! ...
... Composed of molecules, all of which are alike Small! One billionth of a drop of water has 1 trillion molecules!!! ...
File
... Amides and carboxylic acids both contain carbonyl groups. Amides have the carbonyl carbon bonded to a nitrogen atom, but carboxylic acids have the carbonyl carbon bonded to a hydroxyl group. 19. What happens to the double bond of a monomer participating in the formation of an addition polymer? One o ...
... Amides and carboxylic acids both contain carbonyl groups. Amides have the carbonyl carbon bonded to a nitrogen atom, but carboxylic acids have the carbonyl carbon bonded to a hydroxyl group. 19. What happens to the double bond of a monomer participating in the formation of an addition polymer? One o ...
Worksheet Key - UCSB C.L.A.S.
... monochlorination CH3CH2Cl dichlorination ClCH2CH2Cl or CH3CHCl2 trichlorination Cl2CHCH2Cl or CH3CCl3 tetrachlorination Cl2CHCHCl2 or ClCH2CCl3 pentachlorination Cl2CHCCl3 ...
... monochlorination CH3CH2Cl dichlorination ClCH2CH2Cl or CH3CHCl2 trichlorination Cl2CHCH2Cl or CH3CCl3 tetrachlorination Cl2CHCHCl2 or ClCH2CCl3 pentachlorination Cl2CHCCl3 ...
Mass Spectrometry and Infrared Spectroscopy
... Plot mass of ions (m/z) (x-axis) versus the intensity of the signal (roughly corresponding to the number of ions) (yaxis) Tallest peak is base peak (100%) Other peaks listed as the % of that peak Peak that corresponds to the unfragmented radical cation is parent peak or molecular ion (M+) ...
... Plot mass of ions (m/z) (x-axis) versus the intensity of the signal (roughly corresponding to the number of ions) (yaxis) Tallest peak is base peak (100%) Other peaks listed as the % of that peak Peak that corresponds to the unfragmented radical cation is parent peak or molecular ion (M+) ...
Assignment Sheet
... Explain how structure and bonding of carbon lead to the diversity and number of organic compounds. Compare structural and geometric isomers of organic compounds. Distinguish among the structures of alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic hydrocarbons. Write structural formulas and names for alkanes, ...
... Explain how structure and bonding of carbon lead to the diversity and number of organic compounds. Compare structural and geometric isomers of organic compounds. Distinguish among the structures of alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic hydrocarbons. Write structural formulas and names for alkanes, ...
Use the following to answer questions 1-14:
... electrons in the valence shell. ____ 2. Metallic elements form cations. ____ 3. Cations are negatively charged ions. ____ 4. Valence electrons are located in the outermost electron shell of the atom. ____ 5. Noble gases are very stable; other elements give up, gain, or share electrons to acquire a v ...
... electrons in the valence shell. ____ 2. Metallic elements form cations. ____ 3. Cations are negatively charged ions. ____ 4. Valence electrons are located in the outermost electron shell of the atom. ____ 5. Noble gases are very stable; other elements give up, gain, or share electrons to acquire a v ...
Summary – Consumer Products
... Alcohol can be quickly absorbed into the bloodstream where it can interfere with some of the chemical reactions in the body. Alcohol slows reaction time down. In small quantities it can relax a person, but in larger quantities it can slow reactions so much that a person can have trouble speaking, m ...
... Alcohol can be quickly absorbed into the bloodstream where it can interfere with some of the chemical reactions in the body. Alcohol slows reaction time down. In small quantities it can relax a person, but in larger quantities it can slow reactions so much that a person can have trouble speaking, m ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.