Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
... You have already studied most of the methods used in the synthesis of aldehydes and ketones in the previous lesson. Let us now refresh them. 1. Oxidation of Primary and Secondary Alcohols From the last lesson, you know that primary alcohols can be oxidised to aldehydes and secondary alcohols can be ...
... You have already studied most of the methods used in the synthesis of aldehydes and ketones in the previous lesson. Let us now refresh them. 1. Oxidation of Primary and Secondary Alcohols From the last lesson, you know that primary alcohols can be oxidised to aldehydes and secondary alcohols can be ...
Unit - 7.pmd
... covalency to four, nitrogen cannot form dπ –pπ bond as the heavier elements can e.g., R3P = O or R3P = CH2 (R = alkyl group). Phosphorus and arsenic can form dπ –dπ bond also with transition metals when their compounds like P(C2H5)3 and As(C6H5)3 act as ligands. (i) Reactivity towards hydrogen: All ...
... covalency to four, nitrogen cannot form dπ –pπ bond as the heavier elements can e.g., R3P = O or R3P = CH2 (R = alkyl group). Phosphorus and arsenic can form dπ –dπ bond also with transition metals when their compounds like P(C2H5)3 and As(C6H5)3 act as ligands. (i) Reactivity towards hydrogen: All ...
Chemistry (SPA)
... Differences between atoms give elements their different chemical properties. Atoms of one or more substances (reactants) undergo some ‘rearrangements’ during a chemical change (reaction). These rearrangements form new and different substances (products). After the chemical reaction, all the atoms of ...
... Differences between atoms give elements their different chemical properties. Atoms of one or more substances (reactants) undergo some ‘rearrangements’ during a chemical change (reaction). These rearrangements form new and different substances (products). After the chemical reaction, all the atoms of ...
CHEM 210 Nomenclature Lecture 1
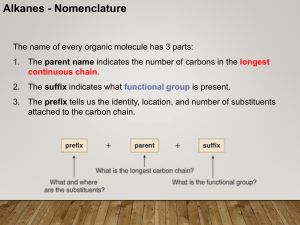
... 1. The parent name indicates the number of carbons in the longest continuous chain. 2. The suffix indicates what functional group is present. 3. The prefix tells us the identity, location, and number of substituents attached to the carbon chain. ...
... 1. The parent name indicates the number of carbons in the longest continuous chain. 2. The suffix indicates what functional group is present. 3. The prefix tells us the identity, location, and number of substituents attached to the carbon chain. ...
mass mass calc
... If 0.05 mol of AgNO3 is used, 0.025 mol of Ag2CrO4(s) is produced. If you are ratio impaired, try skipping right to this equation (it works every time): nunknown = n known x ratio from the balanced equation arranged so that the appropriate units will cancel… ...
... If 0.05 mol of AgNO3 is used, 0.025 mol of Ag2CrO4(s) is produced. If you are ratio impaired, try skipping right to this equation (it works every time): nunknown = n known x ratio from the balanced equation arranged so that the appropriate units will cancel… ...
Sign of enthalpy changes Exothermic vs endothermic Acid
... If n = 0.3 mol, Hm = H/n = –2.4 x 10–3 cal / (0.3 x 10–6 mol) = –8 kcal/mol If n = 0.2 mol, Hm = H/n = –2.4 x 10–3 cal / (0.2 x 10–6 mol) = –12 kcal/mol If n = 0.1 mol, Hm = H/n = –2.4 x 10–3 cal / (0.1 x 10–6 mol) = –24 kcal/mol ...
... If n = 0.3 mol, Hm = H/n = –2.4 x 10–3 cal / (0.3 x 10–6 mol) = –8 kcal/mol If n = 0.2 mol, Hm = H/n = –2.4 x 10–3 cal / (0.2 x 10–6 mol) = –12 kcal/mol If n = 0.1 mol, Hm = H/n = –2.4 x 10–3 cal / (0.1 x 10–6 mol) = –24 kcal/mol ...
HONORS CHEMISTRY
... 7. Acetylene gas, C2H2, burns in oxygen and forms carbon dioxide and water vapor. (a) How many liters of oxygen are needed to burn 15.0 L of acetylene? (b) How many liters of carbon dioxide are formed? c) How many moles of water are produced? 8. How many grams of sodium are needed to release 1.5 L o ...
... 7. Acetylene gas, C2H2, burns in oxygen and forms carbon dioxide and water vapor. (a) How many liters of oxygen are needed to burn 15.0 L of acetylene? (b) How many liters of carbon dioxide are formed? c) How many moles of water are produced? 8. How many grams of sodium are needed to release 1.5 L o ...
using hydrogen as a nucleophile in hydride reductions
... that taking place with carbonyl compounds, except that acid chlorides and esters have a leaving group (–Cl and –OR). So the reaction does not stop at formation of the alkoxide ion as a tetrahedral intermediate, but keeps going with an internal nucleophilic displacement of the leaving group. The dire ...
... that taking place with carbonyl compounds, except that acid chlorides and esters have a leaving group (–Cl and –OR). So the reaction does not stop at formation of the alkoxide ion as a tetrahedral intermediate, but keeps going with an internal nucleophilic displacement of the leaving group. The dire ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... • Five- and six-membered rings are most stable. Can take on conformation in which angles are very close to tetrahedral angle. Smaller rings are quite strained. ...
... • Five- and six-membered rings are most stable. Can take on conformation in which angles are very close to tetrahedral angle. Smaller rings are quite strained. ...
A Brief History of Organic Chemistry
... Hundreds of millions of years ago, the organisms that inhabited earth were quite different than those we find here today. Plants were fast growing and lacked the woody tissues associated with the trees that currently dominate the world's productive ecosystems. Giant plants with broccoli-like stems ...
... Hundreds of millions of years ago, the organisms that inhabited earth were quite different than those we find here today. Plants were fast growing and lacked the woody tissues associated with the trees that currently dominate the world's productive ecosystems. Giant plants with broccoli-like stems ...
File - cpprashanths Chemistry
... ANS :KCN is predominantly ionic and provides cyanide ions in solution. However both carbon and nitrogen atoms are in a position to donate electron pairs, the attack takes place mainly through carbon atom and not through nitrogen atom since C-C bond is more stable the C-N bond. However, AgCN is main ...
... ANS :KCN is predominantly ionic and provides cyanide ions in solution. However both carbon and nitrogen atoms are in a position to donate electron pairs, the attack takes place mainly through carbon atom and not through nitrogen atom since C-C bond is more stable the C-N bond. However, AgCN is main ...
Chapter 21 aldehydes and ketones
... • Since phosphorus is a second-row element, it can be surrounded by more than eight electrons. • Thus, a second resonance structure can be drawn that places a double bond between carbon and phosphorus. • Regardless of which resonance structure is drawn, a Wittig reagent has no net charge. • However, ...
... • Since phosphorus is a second-row element, it can be surrounded by more than eight electrons. • Thus, a second resonance structure can be drawn that places a double bond between carbon and phosphorus. • Regardless of which resonance structure is drawn, a Wittig reagent has no net charge. • However, ...
chm 205 - National Open University of Nigeria
... Tin shows polymorphism and exists in two crystalline forms: grey or αtin, which is a semimetallic form, stable below 286 K, and white or βtin, the stable metallic form, which is a good conductor of electricity. Grey tin has a diamond structure whereas the white tin has a tetragonal structure. Due to ...
... Tin shows polymorphism and exists in two crystalline forms: grey or αtin, which is a semimetallic form, stable below 286 K, and white or βtin, the stable metallic form, which is a good conductor of electricity. Grey tin has a diamond structure whereas the white tin has a tetragonal structure. Due to ...
Chemistry Revision Checklist F4 2017 (inc F3)
... Describe the concept of homologous series as a ‘family’ of similar compounds with similar chemical properties due to the presence of the same functional group Describe the general characteristics of an homologous series Recall that the compounds in a homologous series have the same general formula D ...
... Describe the concept of homologous series as a ‘family’ of similar compounds with similar chemical properties due to the presence of the same functional group Describe the general characteristics of an homologous series Recall that the compounds in a homologous series have the same general formula D ...
View
... known deficiencies of DFT in describing open-shell systems,[18] CASPT2 calculations (using appropriate basis sets) were also carried out on 5 and 6, the geometries of which were slightly modified to fulfill Ci and C2 symmetries, respectively. Consistent with the magnetic moments experimentally deter ...
... known deficiencies of DFT in describing open-shell systems,[18] CASPT2 calculations (using appropriate basis sets) were also carried out on 5 and 6, the geometries of which were slightly modified to fulfill Ci and C2 symmetries, respectively. Consistent with the magnetic moments experimentally deter ...
Organic - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... to give only the isomers from the more stable transition states derived from 4a in preference to those from 4b. We have also carried out the cyclization of the des-chloro analogue of 3, namely 1-((tert-butyldimethylsily1)oxy)2,6-dimethy1-5-hepten-2-01, under similar conditions (TBCD, CH2C.12,25 "C, ...
... to give only the isomers from the more stable transition states derived from 4a in preference to those from 4b. We have also carried out the cyclization of the des-chloro analogue of 3, namely 1-((tert-butyldimethylsily1)oxy)2,6-dimethy1-5-hepten-2-01, under similar conditions (TBCD, CH2C.12,25 "C, ...
Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols
... Thiols Thiols • are organic compounds that contain a –SH group. • are named in the IUPAC system by adding thiol to the alkane name of the longest carbon chain. ...
... Thiols Thiols • are organic compounds that contain a –SH group. • are named in the IUPAC system by adding thiol to the alkane name of the longest carbon chain. ...
Student Solutions Manual Errata
... occurs when two atoms are mutually attracted to a pair (or pairs) of electrons. Because the atoms share the electrons, we can think of the atoms (or the spheres in the diagram) as being joined together where the bond occurs. Ionic bonding is shown in A and D. In A, ionic bonding is indicated because ...
... occurs when two atoms are mutually attracted to a pair (or pairs) of electrons. Because the atoms share the electrons, we can think of the atoms (or the spheres in the diagram) as being joined together where the bond occurs. Ionic bonding is shown in A and D. In A, ionic bonding is indicated because ...
Synthetic Strategy – Lecture 2 (DC, 19.1.05)
... to think about the polarity of the simpler structures revealed by this disconnection. This is not usually the case; it is much more common for a disconnection to reveal two imaginary fragments, or synthons, which carry a positive or negative charge. Subsequently we need to identify the real (i.e. no ...
... to think about the polarity of the simpler structures revealed by this disconnection. This is not usually the case; it is much more common for a disconnection to reveal two imaginary fragments, or synthons, which carry a positive or negative charge. Subsequently we need to identify the real (i.e. no ...
Theoretical Competition - Austrian Chemistry Olympiad
... National Competition - Wieselburg Theoretical part – Tasks+Solutions June 15th, 2012 The kinetics of gas reactions are usually followed by measuring the total pressure of the gas mixture, which changes with time. In this case the partial pressure of oxygen derives in the following way from the total ...
... National Competition - Wieselburg Theoretical part – Tasks+Solutions June 15th, 2012 The kinetics of gas reactions are usually followed by measuring the total pressure of the gas mixture, which changes with time. In this case the partial pressure of oxygen derives in the following way from the total ...
Exames anteriores a 1994
... a) Show where the maxima lie by drawing the contour curves around the maxima, connecting points of equal electron densities. Label each maximum to show the identities of the atoms in E. b) When 450.0 mg of C was treated with an excess of mercury, 53.25 ml of A was liberated at a pressure of 101.0 kP ...
... a) Show where the maxima lie by drawing the contour curves around the maxima, connecting points of equal electron densities. Label each maximum to show the identities of the atoms in E. b) When 450.0 mg of C was treated with an excess of mercury, 53.25 ml of A was liberated at a pressure of 101.0 kP ...
Chapter 12: Alkanes
... There are over 18 million known, and many more unknown possible structures ranging from one C to over a million carbons, and containing other elements such as N, O, S. ...
... There are over 18 million known, and many more unknown possible structures ranging from one C to over a million carbons, and containing other elements such as N, O, S. ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.