Ch17 Lecture
... • Three common pain relievers that are also antiinflammatory agents contain a carboxyl group: ...
... • Three common pain relievers that are also antiinflammatory agents contain a carboxyl group: ...
Final Exam Review Packet
... Hydrate: A compound in which a specific number of water molecules are associated with each formula unit. Hydrated ion: An ion in which a specific number of water molecules is associated with each formula unit. Hydration: Solvation in water. Limiting reactant: The reactant that is consumed when a rea ...
... Hydrate: A compound in which a specific number of water molecules are associated with each formula unit. Hydrated ion: An ion in which a specific number of water molecules is associated with each formula unit. Hydration: Solvation in water. Limiting reactant: The reactant that is consumed when a rea ...
Chemistry 3202 Grading Standards June 2006
... enrich and enhance material in each unit of the course. It is essential that teachers complete all core labs and STSE units to ensure that students are prepared for the examination. On provincial examinations, Core Lab and STSE outcomes are often assessed at higher levels of learning. Teachers, ther ...
... enrich and enhance material in each unit of the course. It is essential that teachers complete all core labs and STSE units to ensure that students are prepared for the examination. On provincial examinations, Core Lab and STSE outcomes are often assessed at higher levels of learning. Teachers, ther ...
the beginnings of synthetic organic chemistry: zinc alkyls and the
... between organozinc reagents and a variety of compounds. The co-author on many of these early works was another of the brilliant organic chemists to come from the Kazan’ school: Egor Egorevich Vagner (18491903), who later became Professor of Chemistry at the University of Warsaw. Better known in the ...
... between organozinc reagents and a variety of compounds. The co-author on many of these early works was another of the brilliant organic chemists to come from the Kazan’ school: Egor Egorevich Vagner (18491903), who later became Professor of Chemistry at the University of Warsaw. Better known in the ...
Carbonyl Compounds
... of the difference in the electronegativity of carbon and oxygen. • The carbon atom carries a partial positive charge while oxygen atom carries a partial negative charge. • Aldehydes and ketones are susceptible to attack both by nucleophiles at the carbonyl carbon atom and by electrophiles at the oxy ...
... of the difference in the electronegativity of carbon and oxygen. • The carbon atom carries a partial positive charge while oxygen atom carries a partial negative charge. • Aldehydes and ketones are susceptible to attack both by nucleophiles at the carbonyl carbon atom and by electrophiles at the oxy ...
6. Low valent of Vanadium catalyst in organic synthesis
... *the coordination of the phosphorus raises the reduction capability and selectivity. *the bulky reductant is liable to approach the bromide from the ...
... *the coordination of the phosphorus raises the reduction capability and selectivity. *the bulky reductant is liable to approach the bromide from the ...
Aromatic compounds
... • Substituents already present on a ring determine the position taken by a new substituent • Some are ortho,para-directing • Amino, hydroxy, alkyl, halo ...
... • Substituents already present on a ring determine the position taken by a new substituent • Some are ortho,para-directing • Amino, hydroxy, alkyl, halo ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... Alcohols • Alcohols contain one or more hydroxyl groups, —OH. • They are named from the parent hydrocarbon; the suffix is changed to -ol and a number designates the carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... Alcohols • Alcohols contain one or more hydroxyl groups, —OH. • They are named from the parent hydrocarbon; the suffix is changed to -ol and a number designates the carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... Alcohols • Alcohols contain one or more hydroxyl groups, —OH. • They are named from the parent hydrocarbon; the suffix is changed to -ol and a number designates the carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... Alcohols • Alcohols contain one or more hydroxyl groups, —OH. • They are named from the parent hydrocarbon; the suffix is changed to -ol and a number designates the carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols
... ¾ Alkene double bonds will be reduced as well. ...
... ¾ Alkene double bonds will be reduced as well. ...
the carbon grazing story - Australian Rangeland Society
... Carbon takes many different forms after it moves from the atmosphere to the landscape via photosynthesis. These different carbon compounds add to the resilience of the landscape. The resilience of the landscape relies on the resilience of both plants and the soil. Allowing carbon to flow into plants ...
... Carbon takes many different forms after it moves from the atmosphere to the landscape via photosynthesis. These different carbon compounds add to the resilience of the landscape. The resilience of the landscape relies on the resilience of both plants and the soil. Allowing carbon to flow into plants ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... Alcohols • Alcohols contain one or more hydroxyl groups, —OH. • They are named from the parent hydrocarbon; the suffix is changed to -ol and a number designates the carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... Alcohols • Alcohols contain one or more hydroxyl groups, —OH. • They are named from the parent hydrocarbon; the suffix is changed to -ol and a number designates the carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... Alcohols • Alcohols contain one or more hydroxyl groups, —OH. • They are named from the parent hydrocarbon; the suffix is changed to -ol and a number designates the carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... Alcohols • Alcohols contain one or more hydroxyl groups, —OH. • They are named from the parent hydrocarbon; the suffix is changed to -ol and a number designates the carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... Alcohols • Alcohols contain one or more hydroxyl groups, —OH. • They are named from the parent hydrocarbon; the suffix is changed to -ol and a number designates the carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... Alcohols • Alcohols contain one or more hydroxyl groups, —OH. • They are named from the parent hydrocarbon; the suffix is changed to -ol and a number designates the carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... Alcohols • Alcohols contain one or more hydroxyl groups, —OH. • They are named from the parent hydrocarbon; the suffix is changed to -ol and a number designates the carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... Alcohols • Alcohols contain one or more hydroxyl groups, —OH. • They are named from the parent hydrocarbon; the suffix is changed to -ol and a number designates the carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Sheet #24 (archive) Medicinal Plants
... color such as the orange color of carrots ,or the red color of tomatoes) ,and therefore they are widely used in the pharmaceutical industry as coloring agents . The primary classes of tetratepines ,we have: carotene ,indicating already hydrocarbons Xanthophylls, composed of carbon, hydrogen & oxygen ...
... color such as the orange color of carrots ,or the red color of tomatoes) ,and therefore they are widely used in the pharmaceutical industry as coloring agents . The primary classes of tetratepines ,we have: carotene ,indicating already hydrocarbons Xanthophylls, composed of carbon, hydrogen & oxygen ...
Alcohols, phenols, thiols and ethers notes
... Classify each as an alcohol (1), phenol (2), or an ether (3): A. _____ CH3CH2-O-CH3 OH ...
... Classify each as an alcohol (1), phenol (2), or an ether (3): A. _____ CH3CH2-O-CH3 OH ...
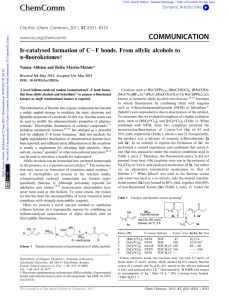
Ir-catalysed formation of C− F bonds. From allylic alcohols to α
... (IIb).15b,19 In step (iii), the C–F bond is formed upon reaction with the electrophilic SelectF. Step (iii) can occur directly from II, or via formation of the free enol.y In conclusion, we have shown that a-fluorinated ketones can be prepared as single constitutional isomers by combining a tandem ir ...
... (IIb).15b,19 In step (iii), the C–F bond is formed upon reaction with the electrophilic SelectF. Step (iii) can occur directly from II, or via formation of the free enol.y In conclusion, we have shown that a-fluorinated ketones can be prepared as single constitutional isomers by combining a tandem ir ...
Structure Determination for Organic Compounds - Rose
... The most useful band in the double-bond region is the carbonyl C=O stretch at ~1710 cm-1. Careful analysis of the exact position of the carbonyl stretch can yield information about the atoms that surround the carbonyl because different groups alter the strength of the C=O bond. Esters and 5-membered ...
... The most useful band in the double-bond region is the carbonyl C=O stretch at ~1710 cm-1. Careful analysis of the exact position of the carbonyl stretch can yield information about the atoms that surround the carbonyl because different groups alter the strength of the C=O bond. Esters and 5-membered ...
UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS
... Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons that have double or triple covalent bonds between adjacent carbon atoms. Those with at least one double bond are called alkenes and those with at least one triple bond are called alkynes. Alkenes with two double bonds are called dienes. ...
... Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons that have double or triple covalent bonds between adjacent carbon atoms. Those with at least one double bond are called alkenes and those with at least one triple bond are called alkynes. Alkenes with two double bonds are called dienes. ...
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry
... Number of individual molecules are difficult to deal with => definition of a “package” of molecules or particles ...
... Number of individual molecules are difficult to deal with => definition of a “package” of molecules or particles ...
AP Stoichiometry
... 3. Divide each by the smallest number of moles to obtain the simplest whole number ratio. 4. If whole numbers are not obtained* in step 3), multiply through by the smallest number that will give all whole numbers * Be ...
... 3. Divide each by the smallest number of moles to obtain the simplest whole number ratio. 4. If whole numbers are not obtained* in step 3), multiply through by the smallest number that will give all whole numbers * Be ...
Document
... volumes of gas, at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of particles. Moles are numbers of particles You can treat reactions as if they happen liters at a time, as long as you keep the temperature and pressure the same. 1 mole = 22.4 L @ STP ...
... volumes of gas, at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of particles. Moles are numbers of particles You can treat reactions as if they happen liters at a time, as long as you keep the temperature and pressure the same. 1 mole = 22.4 L @ STP ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.