Earth`s Lithosphere System – Rock Cycle
... Colorless and transparent, white, variety of color possible; hardness 3; perfect rhombohedral cleavage; effervesces in dilute HCl Colorless, white, gray, greenish, yellow-brown; hardness 3.54; rhombohedral cleavage; powder effervesces in dilute HCl Colorless to white, gray, yellow-orange, or light b ...
... Colorless and transparent, white, variety of color possible; hardness 3; perfect rhombohedral cleavage; effervesces in dilute HCl Colorless, white, gray, greenish, yellow-brown; hardness 3.54; rhombohedral cleavage; powder effervesces in dilute HCl Colorless to white, gray, yellow-orange, or light b ...
What is a mineral?
... • To determine an unknown mineral’s hardness, you need to scratch it against a mineral of known hardness ...
... • To determine an unknown mineral’s hardness, you need to scratch it against a mineral of known hardness ...
Mineral - McEachern High School
... Mineral Identification • Hardness: most useful test; measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched. Measured using Mohs scale of hardness; determined by the arrangement of a mineral’s atoms. • Cleavage & Fracture: determined by atomic arrangement; cleavage: mineral that splits relatively easily ...
... Mineral Identification • Hardness: most useful test; measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched. Measured using Mohs scale of hardness; determined by the arrangement of a mineral’s atoms. • Cleavage & Fracture: determined by atomic arrangement; cleavage: mineral that splits relatively easily ...
Rocks and Minerals
... very hard reddish or purplish rock. Very hard and often has small column-like opaque crystals. Rubies and Sapphires. ...
... very hard reddish or purplish rock. Very hard and often has small column-like opaque crystals. Rubies and Sapphires. ...
Chapter 7
... • To find the density, find the mass on the scale. Then drop the mineral in a graduated cylinder. The amount of water that rises (displacement) is the volume. Then divide the mass by the volume. ...
... • To find the density, find the mass on the scale. Then drop the mineral in a graduated cylinder. The amount of water that rises (displacement) is the volume. Then divide the mass by the volume. ...
Minerals are NEAT!
... If we melted sulfur, would it be a mineral? If Calcite had a chemical composition of CaCO2, would it be a mineral? If we made a diamond with PERFECT cleavage, would it be a mineral? If a fossil had a hardness of 11, would it still be considered a mineral? ...
... If we melted sulfur, would it be a mineral? If Calcite had a chemical composition of CaCO2, would it be a mineral? If we made a diamond with PERFECT cleavage, would it be a mineral? If a fossil had a hardness of 11, would it still be considered a mineral? ...
There is a close connection between Geology and
... formation, stratigraphic age or localty or quarry name. For example, sandstone from County Tyrone was used as a popular dimension stone throughout Northern Ireland. Table 1 shows the three main types of rock groups and the stone types within those groups. ...
... formation, stratigraphic age or localty or quarry name. For example, sandstone from County Tyrone was used as a popular dimension stone throughout Northern Ireland. Table 1 shows the three main types of rock groups and the stone types within those groups. ...
Minerals
... Your fingernails (preferable still attached to your fingers!) A copper penny (or small –½ inch – piece of copper or short piece of heavy copper wire.) A small piece of fluorite (a broken cleavage piece is fine.) A pocket knife (NOT a Swiss Army knife – the steel in those is harder than in most cheap ...
... Your fingernails (preferable still attached to your fingers!) A copper penny (or small –½ inch – piece of copper or short piece of heavy copper wire.) A small piece of fluorite (a broken cleavage piece is fine.) A pocket knife (NOT a Swiss Army knife – the steel in those is harder than in most cheap ...
What is a Mineral?
... Are NOT alive and NEVER were alive Have a definite volume and shape Are elements or compounds with a unique chemical makeup Are made up of particles that are arranged in a pattern that is repeated over and over (called a CRYSTAL) ...
... Are NOT alive and NEVER were alive Have a definite volume and shape Are elements or compounds with a unique chemical makeup Are made up of particles that are arranged in a pattern that is repeated over and over (called a CRYSTAL) ...
Dynamic Earth Chapter 4-Highlights Rocks and Minerals Highlights
... Rarest—diamonds, rubies, sapphires, emeralds are precious stones All other gemstones are semiprecious—zircons, turquoises ...
... Rarest—diamonds, rubies, sapphires, emeralds are precious stones All other gemstones are semiprecious—zircons, turquoises ...
Minerals of the Earth`s Crust
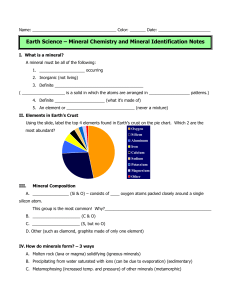
... A. Minerals have certain physical properties that can be used to identify them 1. Color- only good for a few minerals, because so many are different colors Ex. __________________ is always green, _______________ is always blue, Quartz comes in many colors, _______________ is always yellow -Not a rel ...
... A. Minerals have certain physical properties that can be used to identify them 1. Color- only good for a few minerals, because so many are different colors Ex. __________________ is always green, _______________ is always blue, Quartz comes in many colors, _______________ is always yellow -Not a rel ...
Diamonds in Ophiolites
... al. 2013). One very important aspect of this model is that podiform chromitites in ophiolites may not always originate at shallow depths in the uppermost mantle, as widely thought. The chromitite formation may initially begin within or near the mantle transition zone. The spherical shape of most car ...
... al. 2013). One very important aspect of this model is that podiform chromitites in ophiolites may not always originate at shallow depths in the uppermost mantle, as widely thought. The chromitite formation may initially begin within or near the mantle transition zone. The spherical shape of most car ...
Minerals - WordPress.com
... variety of colors because of different trace elements. For example purple amethyst contains ferric iron. • Color least reliable diagnostic test. The same mineral can have a variety of minerals, have impurities, or be affected by weathering. ...
... variety of colors because of different trace elements. For example purple amethyst contains ferric iron. • Color least reliable diagnostic test. The same mineral can have a variety of minerals, have impurities, or be affected by weathering. ...
L6 Mineral Profiles
... Moonstones are beautiful and rare gems made from white feldspar. It can also be pink, green, or red. Feldspar can be ground into clay to make potter and dishes. It is also a mineral found in Kaopectate which is a medicine. ...
... Moonstones are beautiful and rare gems made from white feldspar. It can also be pink, green, or red. Feldspar can be ground into clay to make potter and dishes. It is also a mineral found in Kaopectate which is a medicine. ...
Gems Rock! - North Carolina Museum of Natural Sciences
... (transparent), pass through in a distorted fashion (translucent) or not penetrate the surface of the mineral at all (opaque). ...
... (transparent), pass through in a distorted fashion (translucent) or not penetrate the surface of the mineral at all (opaque). ...
File
... carbon. It forms deep in the Earth at high pressures and it’s the hardest substance. It crystal structure is dense and compact. ...
... carbon. It forms deep in the Earth at high pressures and it’s the hardest substance. It crystal structure is dense and compact. ...
Physical Properties used in Mineral Identification
... TABLE 2-4. LUSTER: Non-metallic Section LIGHT STREAK Colorless or light colored PART 2. Hardness: 2 1 / 2 - 3 1 / 2 (cannot be scratched with thumbnail; will not scratch penny) Hardness ...
... TABLE 2-4. LUSTER: Non-metallic Section LIGHT STREAK Colorless or light colored PART 2. Hardness: 2 1 / 2 - 3 1 / 2 (cannot be scratched with thumbnail; will not scratch penny) Hardness ...
Minerals of Igneous Rocks
... content (and lower density), darker color more Fe (and higher density). Large crystals uncommon, almost always occurring as dominant or sole mineral in a rock, as small granular crystals. No cleavage – conchoidal fracture (like glass). ...
... content (and lower density), darker color more Fe (and higher density). Large crystals uncommon, almost always occurring as dominant or sole mineral in a rock, as small granular crystals. No cleavage – conchoidal fracture (like glass). ...
Name
... V. Mineral Crystal Size A. Small Crystals – indicates _______ cooling of molten rock B. Large Crystals – indicates ________ cooling of molten rock VI. Mineral Characteristics used for identification A. _______________ – the first property you notice – this is usually the 1st step in identification, ...
... V. Mineral Crystal Size A. Small Crystals – indicates _______ cooling of molten rock B. Large Crystals – indicates ________ cooling of molten rock VI. Mineral Characteristics used for identification A. _______________ – the first property you notice – this is usually the 1st step in identification, ...
I. Minerals
... you think about and work with the notes we just took. Work on both side, we will go over this afterwards. ...
... you think about and work with the notes we just took. Work on both side, we will go over this afterwards. ...
Minerals Notes
... The way a mineral breaks when it does not have cleavage. Kinds of fracture are; Conchoidal- bowl shaped structures like the inside of a clam shell; like obsidian Fibrous or splintery- fractured surface shows fibers or splinters; like asbestos Uneven- this surface is rough and irregular; like basalt ...
... The way a mineral breaks when it does not have cleavage. Kinds of fracture are; Conchoidal- bowl shaped structures like the inside of a clam shell; like obsidian Fibrous or splintery- fractured surface shows fibers or splinters; like asbestos Uneven- this surface is rough and irregular; like basalt ...
Gemstone

A gemstone or gem (also called a fine gem, jewel, or a precious or semi-precious stone) is a piece of mineral crystal, which, in cut and polished form, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. However, certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli) or organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber or jet), are also used for jewelry, and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well. Most gemstones are hard, but some soft minerals are used in jewelry because of their luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. Rarity is another characteristic that lends value to a gemstone. Apart from jewelry, from earliest antiquity engraved gems and hardstone carvings, such as cups, were major luxury art forms. A gem maker is called a lapidary or gemcutter; a diamond worker is a diamantaire.The carvings of Carl Fabergé are significant works in this tradition.