TDB-5: Standards and conventions for TDB publications
... in square brackets [71JEN, Rule 7.21]. However, in cases where the absence of brackets may cause ambiguities or make presentations unclear, exceptions may be made. ii. The prefixes “oxy-” and “hydroxy-” are retained if used in a general way, e.g., “gaseous uranium oxyfluorides”. For specific formula ...
... in square brackets [71JEN, Rule 7.21]. However, in cases where the absence of brackets may cause ambiguities or make presentations unclear, exceptions may be made. ii. The prefixes “oxy-” and “hydroxy-” are retained if used in a general way, e.g., “gaseous uranium oxyfluorides”. For specific formula ...
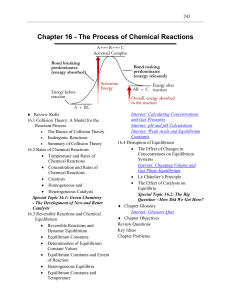
Study Guide Chapter 16: The Process of Chemical Reactions
... temperature and pressure. The gas is composed of O2 molecules that are moving constantly in the container. For a typical gas, the average distance between particles is about ten times the diameter of each particle. This leads to the gas particles themselves taking up only about 0.1% of the total vol ...
... temperature and pressure. The gas is composed of O2 molecules that are moving constantly in the container. For a typical gas, the average distance between particles is about ten times the diameter of each particle. This leads to the gas particles themselves taking up only about 0.1% of the total vol ...
Unit 02 - Delivery Guide
... Displacement is a vector quantity that refers to an object's overall change in position. Drift current is the electric current, or movement of charge carriers, which is due to an applied electric field. I = nAve, where n is the number of conduction electrons per unit volume, A the cross sectional ar ...
... Displacement is a vector quantity that refers to an object's overall change in position. Drift current is the electric current, or movement of charge carriers, which is due to an applied electric field. I = nAve, where n is the number of conduction electrons per unit volume, A the cross sectional ar ...
1. True
... 1. The total amount of energy and matter in the Universe is constant. 2. Breaking chemical bonds is an endothermic process. 3. It is more efficient to use a primary energy source than a secondary energy source. 4. Entropy must be conserved in all chemical reactions. The Second Law of Thermodynamics ...
... 1. The total amount of energy and matter in the Universe is constant. 2. Breaking chemical bonds is an endothermic process. 3. It is more efficient to use a primary energy source than a secondary energy source. 4. Entropy must be conserved in all chemical reactions. The Second Law of Thermodynamics ...
thermodynamics
... used to do mechanical work when a fuel burns in an engine or to provide electrical energy through a galvanic cell like dry cell. Thus, various forms of energy are interrelated and under certain conditions, these may be transformed from one form into another. The study of these energy transformations ...
... used to do mechanical work when a fuel burns in an engine or to provide electrical energy through a galvanic cell like dry cell. Thus, various forms of energy are interrelated and under certain conditions, these may be transformed from one form into another. The study of these energy transformations ...
AP® Chemistry
... of arrangements of atoms. These atoms retain their identity in chemical reactions. 2) Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules and the forces between them. 3) Changes in matter involve the rearrangement and/or reorga ...
... of arrangements of atoms. These atoms retain their identity in chemical reactions. 2) Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules and the forces between them. 3) Changes in matter involve the rearrangement and/or reorga ...
Description: This is an advanced placement course designed to
... For homework and quizzes, you have as many days to turn the assignment as you were absent. For tests and labs, you may choose to have an extension until the following day provided that you use WHAT/ after school to make up the work. If you do not use WHAT/after school to make up the test or lab, you ...
... For homework and quizzes, you have as many days to turn the assignment as you were absent. For tests and labs, you may choose to have an extension until the following day provided that you use WHAT/ after school to make up the work. If you do not use WHAT/after school to make up the test or lab, you ...
Thermal Flux through a Surface of n-Octane. A Non
... 1. The position of a molecule in the cell was given by its center of mass. A molecule belonged to a layer if its position was located in that layer. The 10 layers at the ends of the cell were defined as hot zones, and the 20 central layers as a cold zone, see Figure 1. The temperatures in these laye ...
... 1. The position of a molecule in the cell was given by its center of mass. A molecule belonged to a layer if its position was located in that layer. The 10 layers at the ends of the cell were defined as hot zones, and the 20 central layers as a cold zone, see Figure 1. The temperatures in these laye ...
4.6 M - Thierry Karsenti
... Equilibrium. A condition in which an infinitesimal change in a variable in the opposite direction results in opposite change in the state. In chemical reactions, it represents the situation in which the reactants and products are producing each other at the same rate. Exothermic process. A process t ...
... Equilibrium. A condition in which an infinitesimal change in a variable in the opposite direction results in opposite change in the state. In chemical reactions, it represents the situation in which the reactants and products are producing each other at the same rate. Exothermic process. A process t ...
Energy Flow and Chemical Change
... Indeed, energy is often converted from one form to another during transfers. For example, when gasoline burns in a car engine, the reaction releases energy that is transferred as heat and work. The heat warms the car parts, passenger compartment, and surrounding air. The work is done when mechanical ...
... Indeed, energy is often converted from one form to another during transfers. For example, when gasoline burns in a car engine, the reaction releases energy that is transferred as heat and work. The heat warms the car parts, passenger compartment, and surrounding air. The work is done when mechanical ...
Chemistry 12 is an intensive course, covering a great deal of
... 2. describe the dynamic nature of chemical equilibrium 3. relate the changes in rates of the forward and reverse reactions to the changing concentrations of the reactants and products as equilibrium is established 4. describe chemical equilibrium as a closed system at constant temperature: ...
... 2. describe the dynamic nature of chemical equilibrium 3. relate the changes in rates of the forward and reverse reactions to the changing concentrations of the reactants and products as equilibrium is established 4. describe chemical equilibrium as a closed system at constant temperature: ...
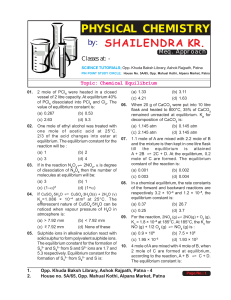
Chemical Equilibrium - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... concentration of C at equilibrium is increased by a factor 2, it will cause the equilibrium concentration of B to change to: (a) two times of its original value (b) one half of its original value (c) 2√2 times of its original value (d) 1/2√2 times of its original value ...
... concentration of C at equilibrium is increased by a factor 2, it will cause the equilibrium concentration of B to change to: (a) two times of its original value (b) one half of its original value (c) 2√2 times of its original value (d) 1/2√2 times of its original value ...
The Fluctuation-imposed Limit for Temperature Measurement
... link to a thermal reservoir (Fig 2). The beryllium copper (BeCu) holder for the two pills must also be treated as a parallel thermal link to the reservoir. The temperature changes of each pill were measured independently using separate SQUID magnetometers. This design allowed us to monitor the flow ...
... link to a thermal reservoir (Fig 2). The beryllium copper (BeCu) holder for the two pills must also be treated as a parallel thermal link to the reservoir. The temperature changes of each pill were measured independently using separate SQUID magnetometers. This design allowed us to monitor the flow ...
PHY115 Concepts of Physics
... 1) Discuss what is meant by the term ‘thermal energy’. 2) Write 2 definitions for the concept of ‘temperature’. b) temperature scales and c) absolute temperature scales 1) List the four most commonly used temperature scales along with the proper abbreviation for each of the ‘units of temperature’ on ...
... 1) Discuss what is meant by the term ‘thermal energy’. 2) Write 2 definitions for the concept of ‘temperature’. b) temperature scales and c) absolute temperature scales 1) List the four most commonly used temperature scales along with the proper abbreviation for each of the ‘units of temperature’ on ...
chemistry 1 notes ~ thermochemistry
... A. HEAT (q)—energy flowing from warmer to cooler objects or areas B. THERMOCHEMISTRY 1) the study of heat changes in chemical reactions and physical changes 2) the study of heat flow between a system and its surroundings a. SYSTEM—specific part being analyzed b. SURROUNDINGS—everything outside the s ...
... A. HEAT (q)—energy flowing from warmer to cooler objects or areas B. THERMOCHEMISTRY 1) the study of heat changes in chemical reactions and physical changes 2) the study of heat flow between a system and its surroundings a. SYSTEM—specific part being analyzed b. SURROUNDINGS—everything outside the s ...