Document
... for the formation of molecular clouds, the birth places of stars, which makes studying the distribution of HI and its evolution crucial for our understanding of various aspects of star formation. We know that shortly after the Big Bang, the initially hot plasma cools down as the Universe expands and ...
... for the formation of molecular clouds, the birth places of stars, which makes studying the distribution of HI and its evolution crucial for our understanding of various aspects of star formation. We know that shortly after the Big Bang, the initially hot plasma cools down as the Universe expands and ...
Search for Life in the Universe
... distance: 1.5 x 108 km (9.3 x 107 miles) • Equals 500 light seconds (8 min. 20 sec.) • Distance to nearest star, Cen: 4 light years • Distance to Galactic Center: 2.5 x 104 light years • Distance to the nearest big galaxy, Andromeda (M31): 2 x 106 light years ...
... distance: 1.5 x 108 km (9.3 x 107 miles) • Equals 500 light seconds (8 min. 20 sec.) • Distance to nearest star, Cen: 4 light years • Distance to Galactic Center: 2.5 x 104 light years • Distance to the nearest big galaxy, Andromeda (M31): 2 x 106 light years ...
The First Stars in the Universe - Scientific American
... after the big bang. The uniformity of this radiation indicates that matter was distributed very smoothly at that time. Because there were no large luminous objects to disturb the primordial soup, it must have remained smooth and featureless for millions of years afterward. As the cosmos expanded, th ...
... after the big bang. The uniformity of this radiation indicates that matter was distributed very smoothly at that time. Because there were no large luminous objects to disturb the primordial soup, it must have remained smooth and featureless for millions of years afterward. As the cosmos expanded, th ...
Chapter 1
... its cataclysmic origin, and its likely fate. The vision of the heavens imagined by some of the ancients, an infinite cosmos populated with a myriad of Sun-like stars, turns out to be closer to reality than the overly constrained view that pertained for almost two thousand years up to the past century ...
... its cataclysmic origin, and its likely fate. The vision of the heavens imagined by some of the ancients, an infinite cosmos populated with a myriad of Sun-like stars, turns out to be closer to reality than the overly constrained view that pertained for almost two thousand years up to the past century ...
Neutrino mass and neutrino dark matter Do non
... • But light neutrinos are free streaming until trapped by galaxy cluster ...
... • But light neutrinos are free streaming until trapped by galaxy cluster ...
Study Guide for Quiz #2
... Can you define these key words? Static Infinite Olber’s Paradox Spacetime Hot Big Bang Cosmic Microwave Background Dark Energy Open Closed Flat Heat Death Can you answer these key questions? How do we know if the universe is infinite? How do we know if the universe is static? How do the distance and ...
... Can you define these key words? Static Infinite Olber’s Paradox Spacetime Hot Big Bang Cosmic Microwave Background Dark Energy Open Closed Flat Heat Death Can you answer these key questions? How do we know if the universe is infinite? How do we know if the universe is static? How do the distance and ...
Hubble Redshift
... galaxies, he was able to determine the recessional velocity of the galaxies in his sample. When Hubble plotted these distances against the velocities for each galaxy, he noted that the further a galaxy was from the Milky Way, the faster it was moving away. Was there something special about our place ...
... galaxies, he was able to determine the recessional velocity of the galaxies in his sample. When Hubble plotted these distances against the velocities for each galaxy, he noted that the further a galaxy was from the Milky Way, the faster it was moving away. Was there something special about our place ...
Paper
... halo dark matter of galaxies consists of planetary mass objects that formed soon after the plasma to neutral gas transition 300,000 years after the Big Bang. These objects are termed primordial fog particles (PFPs) and provide an explanation for Schild's 1996 "rogue planets ... likely to be the miss ...
... halo dark matter of galaxies consists of planetary mass objects that formed soon after the plasma to neutral gas transition 300,000 years after the Big Bang. These objects are termed primordial fog particles (PFPs) and provide an explanation for Schild's 1996 "rogue planets ... likely to be the miss ...
Ch. 22
... • What do we mean when we ask whether dark matter is ordinary or extraordinary matter? • Ordinary matter is made from protons, neutrons, and electrons; we refer to it as baryonic matter because protons and neutrons are both classified as baryons. However, the baryonic matter we have found does not a ...
... • What do we mean when we ask whether dark matter is ordinary or extraordinary matter? • Ordinary matter is made from protons, neutrons, and electrons; we refer to it as baryonic matter because protons and neutrons are both classified as baryons. However, the baryonic matter we have found does not a ...
Think about the universe
... above right, is not a star. It is a quasar called PG 0052+251. It emits much more light than any star could. Quasars are found only at very large distances from the solar system. Observations of distant objects like quasars provide clues about how the universe began. THINK ...
... above right, is not a star. It is a quasar called PG 0052+251. It emits much more light than any star could. Quasars are found only at very large distances from the solar system. Observations of distant objects like quasars provide clues about how the universe began. THINK ...
22. Dark Matter and the Fate of the Universe
... • What do we mean when we ask whether dark matter is ordinary or extraordinary matter? • Ordinary matter is made from protons, neutrons, and electrons; we refer to it as baryonic matter because protons and neutrons are both classified as baryons. • However, the baryonic matter we have found does not ...
... • What do we mean when we ask whether dark matter is ordinary or extraordinary matter? • Ordinary matter is made from protons, neutrons, and electrons; we refer to it as baryonic matter because protons and neutrons are both classified as baryons. • However, the baryonic matter we have found does not ...
Einstein static universe in braneworld scenario
... (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/). Funded by SCOAP3 . ...
... (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/). Funded by SCOAP3 . ...
In fla tio n
... Vacuum, Λ, I What is vacuum? Not empty space but rather ground state of some physical theory ...
... Vacuum, Λ, I What is vacuum? Not empty space but rather ground state of some physical theory ...
Edgar Allan Poe: the first man to conceive a Newtonian evolving
... When he was composing Eureka, we used to walk up and down the garden, his arm around me, mine around him, until I was so tired I could not walk. He would stop every few minutes and explain his ideas to me, and ask if I understood him. 2The first lecture happened on the 2-3 February 1848. The Daily T ...
... When he was composing Eureka, we used to walk up and down the garden, his arm around me, mine around him, until I was so tired I could not walk. He would stop every few minutes and explain his ideas to me, and ask if I understood him. 2The first lecture happened on the 2-3 February 1848. The Daily T ...
chap8 (WP)
... 7. Three objects emerging fom an explosion have positions as a function of time [x(t),y(t)] given by (3t,0), (-6t,0) and (0,5t), where the positions are in meters and the time in seconds. Using the relative motion of all three objects, show that an observer moving with object #1 concludes that the s ...
... 7. Three objects emerging fom an explosion have positions as a function of time [x(t),y(t)] given by (3t,0), (-6t,0) and (0,5t), where the positions are in meters and the time in seconds. Using the relative motion of all three objects, show that an observer moving with object #1 concludes that the s ...
Document
... As the Universe expanded, it cooled down and around 1 s after the Big Bang the energy of neutrinos was so low that such processes could no longer occur and their number density was fixed to this day. This number is very similar to the one of the photons in the observed Cosmic Microwave Background Ra ...
... As the Universe expanded, it cooled down and around 1 s after the Big Bang the energy of neutrinos was so low that such processes could no longer occur and their number density was fixed to this day. This number is very similar to the one of the photons in the observed Cosmic Microwave Background Ra ...
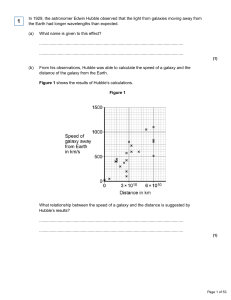
In 1929, the astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the light from
... The observations made by Hubble support the idea that the Universe is expanding. This means that galaxies are continually moving away from each other and from the Earth. Figure 2 shows a student using a balloon to model the idea of an expanding Universe. Some dots, which represent galaxies, were ma ...
... The observations made by Hubble support the idea that the Universe is expanding. This means that galaxies are continually moving away from each other and from the Earth. Figure 2 shows a student using a balloon to model the idea of an expanding Universe. Some dots, which represent galaxies, were ma ...
Critical Content/Concept Web
... 1. The Milky Way is our spiral galaxy 2. Where our solar system is located in the galaxy 3. How the Milky Way formed 4. The structure of the Milky Way 5. How stars and gas move in the galaxy 6. Where and how the Milky Way is forming additional stars 7. Galaxies are classified by shape 8. The Hubble ...
... 1. The Milky Way is our spiral galaxy 2. Where our solar system is located in the galaxy 3. How the Milky Way formed 4. The structure of the Milky Way 5. How stars and gas move in the galaxy 6. Where and how the Milky Way is forming additional stars 7. Galaxies are classified by shape 8. The Hubble ...
Dark Matter: What is it?
... They have no charge and have no mass And do not interact at all. The earth is just a silly ball To them, through which they simply pass, Like dustmaids down a drafty hall Or photons through a pane of glass. ...
... They have no charge and have no mass And do not interact at all. The earth is just a silly ball To them, through which they simply pass, Like dustmaids down a drafty hall Or photons through a pane of glass. ...
doc
... measuring the rotation curves of these galaxies. If the mass of the galaxy were centrally concentrated, the rotation speed should drop as the square of the distance from the nucleus. Instead it appears the rotation curves remain flat out to large distance (beyond the visible edge of the galaxy), ind ...
... measuring the rotation curves of these galaxies. If the mass of the galaxy were centrally concentrated, the rotation speed should drop as the square of the distance from the nucleus. Instead it appears the rotation curves remain flat out to large distance (beyond the visible edge of the galaxy), ind ...
GRADE 12A: Physics 7
... • The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy, and the Sun lies about two-thirds of the way out from the centre. • The nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way is the Andromeda galaxy (Andromeda nebula), which is also a spiral. • Even the nearest galaxy lies at a distance of a few million light-years. Light reach ...
... • The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy, and the Sun lies about two-thirds of the way out from the centre. • The nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way is the Andromeda galaxy (Andromeda nebula), which is also a spiral. • Even the nearest galaxy lies at a distance of a few million light-years. Light reach ...
6 The mysterious universe
... ever before. Observations using telescopes showed that many different types of objects in the sky could be identified. These included single or double stars, groups of stars called galaxies, clusters of galaxies, and clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. In 1718, English astronomer Edmond Halley, w ...
... ever before. Observations using telescopes showed that many different types of objects in the sky could be identified. These included single or double stars, groups of stars called galaxies, clusters of galaxies, and clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. In 1718, English astronomer Edmond Halley, w ...
www.astro.caltech.edu
... as HIRES). These observations have shown us that even relatively small galaxies in the universe can be fairly chemically enriched, providing evidence that (at least in some systems) star formation and the synthesis of heavy elements must have proceeded relatively rapidly after the Big Bang. ...
... as HIRES). These observations have shown us that even relatively small galaxies in the universe can be fairly chemically enriched, providing evidence that (at least in some systems) star formation and the synthesis of heavy elements must have proceeded relatively rapidly after the Big Bang. ...
AWG recommendation on Cosmic Vision
... achieved within the Cosmic Vision programme. To maintain Europe's leading role in widefield imaging, and correspondingly, in weak lensing research, the optical/near-IR WFI should be implemented as soon as technically feasible. Experience from Planck will greatly benefit Europe's development of a CMB ...
... achieved within the Cosmic Vision programme. To maintain Europe's leading role in widefield imaging, and correspondingly, in weak lensing research, the optical/near-IR WFI should be implemented as soon as technically feasible. Experience from Planck will greatly benefit Europe's development of a CMB ...
Chapter 31
... – Some galaxies do not have distinct shapes, and thus do not fit into either the spiral or elliptical classification. – They are called irregular galaxies and are denoted by Irr. ...
... – Some galaxies do not have distinct shapes, and thus do not fit into either the spiral or elliptical classification. – They are called irregular galaxies and are denoted by Irr. ...
Big Bang

The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model for the universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale evolution. The model accounts for the fact that the universe expanded from a very high density and high temperature state, and offers a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background, large scale structure, and Hubble's Law. If the known laws of physics are extrapolated beyond where they are valid, there is a singularity. Modern measurements place this moment at approximately 13.8 billion years ago, which is thus considered the age of the universe. After the initial expansion, the universe cooled sufficiently to allow the formation of subatomic particles, and later simple atoms. Giant clouds of these primordial elements later coalesced through gravity to form stars and galaxies.Since Georges Lemaître first noted, in 1927, that an expanding universe might be traced back in time to an originating single point, scientists have built on his idea of cosmic expansion. While the scientific community was once divided between supporters of two different expanding universe theories, the Big Bang and the Steady State theory, accumulated empirical evidence provides strong support for the former. In 1929, from analysis of galactic redshifts, Edwin Hubble concluded that galaxies are drifting apart, important observational evidence consistent with the hypothesis of an expanding universe. In 1965, the cosmic microwave background radiation was discovered, which was crucial evidence in favor of the Big Bang model, since that theory predicted the existence of background radiation throughout the universe before it was discovered. More recently, measurements of the redshifts of supernovae indicate that the expansion of the universe is accelerating, an observation attributed to dark energy's existence. The known physical laws of nature can be used to calculate the characteristics of the universe in detail back in time to an initial state of extreme density and temperature.