Muscle Fibres
... Myofibril is - the contractile unit of the muscle. These can be divided into units called Sarcomeres Each sarcomere contains 2 types of protein filaments - Actin & Myosin During contraction these slide across one another and connect or make cross bridges. This overlapping creates a striped ...
... Myofibril is - the contractile unit of the muscle. These can be divided into units called Sarcomeres Each sarcomere contains 2 types of protein filaments - Actin & Myosin During contraction these slide across one another and connect or make cross bridges. This overlapping creates a striped ...
Animal Tissues PowerPoint for Lab
... called a myelin sheath. This sheath is produced by Schwann cells, a type of supporting cell for the nervous system. The sheath not only protects the axon but also allows impulses to move more quickly along the axon. Axons arranged in ropelike bundles wrapped in connective tissue make up nerves. Nerv ...
... called a myelin sheath. This sheath is produced by Schwann cells, a type of supporting cell for the nervous system. The sheath not only protects the axon but also allows impulses to move more quickly along the axon. Axons arranged in ropelike bundles wrapped in connective tissue make up nerves. Nerv ...
Ch_49
... What do skeletons do? What are the 3 types of skeletons? What does a muscle cell look like? How do myosin & actin cause muscle contraction? Why is Ca+2 important for a muscle contraction? What is the signal that causes a muscle contraction? How are muscles contractions graded? - By varying the numbe ...
... What do skeletons do? What are the 3 types of skeletons? What does a muscle cell look like? How do myosin & actin cause muscle contraction? Why is Ca+2 important for a muscle contraction? What is the signal that causes a muscle contraction? How are muscles contractions graded? - By varying the numbe ...
of the smooth muscles
... It is characterized by the instability of its membrane potential and by the fact that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is no true "resting" value for the membrane potentia ...
... It is characterized by the instability of its membrane potential and by the fact that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is no true "resting" value for the membrane potentia ...
Document
... 1. Epitheliums: characteristics and general properties of the epithelial cell. Epithelial differentiation and structure-function relations. Epitheliums and their regional differentiation (tegument, respiratory tract, intestine). Glands and their secretion functions (exocrine glands: salivary glands, ...
... 1. Epitheliums: characteristics and general properties of the epithelial cell. Epithelial differentiation and structure-function relations. Epitheliums and their regional differentiation (tegument, respiratory tract, intestine). Glands and their secretion functions (exocrine glands: salivary glands, ...
Lecture 12 Electromyography
... 1.) Train of AP sweep into muscle membrane (sarcolemma) 2.) Travel INTO muscle cells through invaginations (T-tubules) 3.) AP trigger release of Ca2+ ions from sarcoplasmic reticulum into muscle cytoplasm 4.) Ca ions start the cascade of filament sliding *this is a EXTREMELY brief synopsis of the ex ...
... 1.) Train of AP sweep into muscle membrane (sarcolemma) 2.) Travel INTO muscle cells through invaginations (T-tubules) 3.) AP trigger release of Ca2+ ions from sarcoplasmic reticulum into muscle cytoplasm 4.) Ca ions start the cascade of filament sliding *this is a EXTREMELY brief synopsis of the ex ...
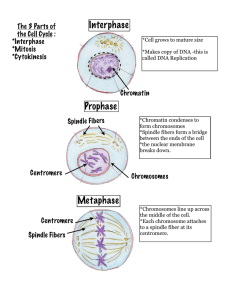
Interphase Prophase Metaphase
... form chromosomes *Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell *the nuclear membrane breaks down. ...
... form chromosomes *Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell *the nuclear membrane breaks down. ...
Chapter 9 A and B Questions
... What is oxygen debt and how is it repaid? How would one know it is being repaid? Is ATP depletion responsible for muscle fatigue? If not, what is? What determines whether a myofiber is fast-twitch or slow-twitch? Compare and contrast the three types of skeletal myofibers with respect to source of AT ...
... What is oxygen debt and how is it repaid? How would one know it is being repaid? Is ATP depletion responsible for muscle fatigue? If not, what is? What determines whether a myofiber is fast-twitch or slow-twitch? Compare and contrast the three types of skeletal myofibers with respect to source of AT ...
Muscle Tissue
... There are three basic types of cell in the muscle tissue. They are called Skeletal, Smooth and Cardiac cells. Skeletal Cells are what moves the bones in the body. They are voluntary striated muscle's and are striped. These muscles consist of 23% of a woman’s body weight and 40% of a man’s. Smooth mu ...
... There are three basic types of cell in the muscle tissue. They are called Skeletal, Smooth and Cardiac cells. Skeletal Cells are what moves the bones in the body. They are voluntary striated muscle's and are striped. These muscles consist of 23% of a woman’s body weight and 40% of a man’s. Smooth mu ...
Injuries to the Tissues
... Tissues • A collection of similar cells that work together to perform a particular function • Interstitial fluid – tissue fluid that occupies tiny spaces between cells • Dehydration = not enough tissue fluid • Edema (swelling) = too much tissue fluid ...
... Tissues • A collection of similar cells that work together to perform a particular function • Interstitial fluid – tissue fluid that occupies tiny spaces between cells • Dehydration = not enough tissue fluid • Edema (swelling) = too much tissue fluid ...
Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton
... • The number of muscle fibers does not change as the result of exercise – Muscle fibers can change size with training – The number of myofibrils increases, causing an increase in muscle fiber thickness – Increased muscle fiber thickness causes increased muscle strength ...
... • The number of muscle fibers does not change as the result of exercise – Muscle fibers can change size with training – The number of myofibrils increases, causing an increase in muscle fiber thickness – Increased muscle fiber thickness causes increased muscle strength ...
Physiology of GIT
... to the mouth & pharangeal regions , the cranial parasympathetic transmitted almost entirely in the vagus nerve, these fibers provide innervation to the esophagus ,stomach pancreas & somewhat less to the intestine down through the 1st half of large intestine ,the sacral parasympathetic originate in ...
... to the mouth & pharangeal regions , the cranial parasympathetic transmitted almost entirely in the vagus nerve, these fibers provide innervation to the esophagus ,stomach pancreas & somewhat less to the intestine down through the 1st half of large intestine ,the sacral parasympathetic originate in ...
What types of cells do not undergo mitosis?
... contain neurons that can still divide—namely, the subventricular region and the hippocampus. We're still not sure whether neuronal mitosis can help recovery after an incident such as a stroke. Cardiac muscle The story of cardiac muscle is remarkably similar to that of neurons. Traditionally, we have ...
... contain neurons that can still divide—namely, the subventricular region and the hippocampus. We're still not sure whether neuronal mitosis can help recovery after an incident such as a stroke. Cardiac muscle The story of cardiac muscle is remarkably similar to that of neurons. Traditionally, we have ...
document
... opening the gated ion channels so that Na+ can rush into the muscle cell Inside of muscle cell becomes more positive, triggering a muscle action potential that travels over the cell and down the T tubules The release of Ca+2 from the SR is triggered and the muscle cell will shorten & generate force ...
... opening the gated ion channels so that Na+ can rush into the muscle cell Inside of muscle cell becomes more positive, triggering a muscle action potential that travels over the cell and down the T tubules The release of Ca+2 from the SR is triggered and the muscle cell will shorten & generate force ...
Muscle Metabolism - Liberty Union High School District
... tissues in the body that are depleted first and need to be replaced • Phosphagen system: ATP must be made, then broken to give Pi back to creatine • Oxidizing lactic acid: most of lactic acid will be converted into glucose in the presence of oxygen • Metabolic rate: if body temp is high the metaboli ...
... tissues in the body that are depleted first and need to be replaced • Phosphagen system: ATP must be made, then broken to give Pi back to creatine • Oxidizing lactic acid: most of lactic acid will be converted into glucose in the presence of oxygen • Metabolic rate: if body temp is high the metaboli ...
Lectures 18-21 - Biology Courses Server
... f) sperm cell g) plant cell 3. Explain the mechanism of muscular contraction using actin, myosin, and ATPase. a. Would a muscle contract in the absence of calcium? Explain. 4. If both the thick and thin filaments of muscle are made up of subunits held together by weak non-covalent bonds, how is it p ...
... f) sperm cell g) plant cell 3. Explain the mechanism of muscular contraction using actin, myosin, and ATPase. a. Would a muscle contract in the absence of calcium? Explain. 4. If both the thick and thin filaments of muscle are made up of subunits held together by weak non-covalent bonds, how is it p ...
Muscle Contraction and Rigor Mortis KEY
... inside and outside of the cell. These ions then interact with actin and myosin filaments to cause muscle contraction. The muscles remain in the contracted state until adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binds to myosin, releasing the myosin and actin filaments from one another. Additionally, muscle cell me ...
... inside and outside of the cell. These ions then interact with actin and myosin filaments to cause muscle contraction. The muscles remain in the contracted state until adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binds to myosin, releasing the myosin and actin filaments from one another. Additionally, muscle cell me ...
Contraction - Anatomy Freaks
... • Increase in myofibrils • Increase in nuclei due to fusion of satellite cells • Increase in strength ...
... • Increase in myofibrils • Increase in nuclei due to fusion of satellite cells • Increase in strength ...
of the smooth muscles
... It is characterized by the instability of its membrane potential and by the fact that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is no true "resting" value for the membrane potentia ...
... It is characterized by the instability of its membrane potential and by the fact that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is no true "resting" value for the membrane potentia ...
NAME: IWORH CHINYERE MIRACLE MATRIC NO: 14/MHS02/031
... types of filaments: thick filaments, composed of myosin, and thin filaments, composed of actins. The individual filaments do not change in length during muscle contraction ; rather the thin filaments slide over the thick filaments to shorten the sarcomere. The nature of these filaments can be unders ...
... types of filaments: thick filaments, composed of myosin, and thin filaments, composed of actins. The individual filaments do not change in length during muscle contraction ; rather the thin filaments slide over the thick filaments to shorten the sarcomere. The nature of these filaments can be unders ...
Myocyte

A myocyte (also known as a muscle cell) is the type of cell found in muscle tissue. Myocytes are long, tubular cells that develop from myoblasts to form muscles in a process known as myogenesis. There are various specialized forms of myocytes: cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells, with various properties. The striated cells of cardiac and skeletal muscles are referred to as muscle fibers. Cardiomyocytes are the muscle fibres that form the chambers of the heart, and have a single central nucleus. Skeletal muscle fibers help support and move the body and tend to have peripheral nuclei. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the stomach.