Slide ()
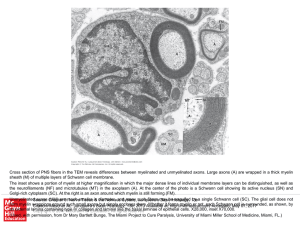
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
Study Guide Questions
... biochemical properties of the muscle, such as muscle glycogen, metabolite contractions, or enzyme activities. However, based on the known differences in metabolic capacities of muscle fibers between the different motor units, one would ...
... biochemical properties of the muscle, such as muscle glycogen, metabolite contractions, or enzyme activities. However, based on the known differences in metabolic capacities of muscle fibers between the different motor units, one would ...
Chapters 13b and 15: General and Special Senses I. General Terms
... a. felt over a large area than touch, deeper b. Pacinian corpuscle - lower layer of dermis 3. vibration - detect high and low frequency vibrations 4. thermosensation - respond to hot/cold; may be free nerve endings 5. pain (nociception) a. acute pain - very quick, not felt in deep areas b. chronic p ...
... a. felt over a large area than touch, deeper b. Pacinian corpuscle - lower layer of dermis 3. vibration - detect high and low frequency vibrations 4. thermosensation - respond to hot/cold; may be free nerve endings 5. pain (nociception) a. acute pain - very quick, not felt in deep areas b. chronic p ...
Specialized Tissue in Animals
... • Muscle tissue – the tissue that composes muscles and contracts to create movement • Muscles that are not connected to bones move substances through body • Skeletal muscles – a voluntary muscle connected to bone which allows skeletal movement • Contracts when stimulated by motor neurons • Movement ...
... • Muscle tissue – the tissue that composes muscles and contracts to create movement • Muscles that are not connected to bones move substances through body • Skeletal muscles – a voluntary muscle connected to bone which allows skeletal movement • Contracts when stimulated by motor neurons • Movement ...
Cell Structure - Action Duchenne
... A sarcomere is the basic unit of striated muscle tissue. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (myocytes called muscle fibers) which are formed in a process known as myogenesis. Muscle fibers are composed of tubular myofibrils. ...
... A sarcomere is the basic unit of striated muscle tissue. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (myocytes called muscle fibers) which are formed in a process known as myogenesis. Muscle fibers are composed of tubular myofibrils. ...
NOZ IV TACTICS: Switch on Muscle Energetics and Drive Up
... The primary objectives for effective training are to: 1) perform enough work to “temporarily“ damage target muscle cells, signaling the brain to launch the growth-and-repair cycle; 2) deliver nutrients to working muscles to invite an abundance of pressure (or a “pump”) inside the cell. Most athletes ...
... The primary objectives for effective training are to: 1) perform enough work to “temporarily“ damage target muscle cells, signaling the brain to launch the growth-and-repair cycle; 2) deliver nutrients to working muscles to invite an abundance of pressure (or a “pump”) inside the cell. Most athletes ...
PPT
... Structure of muscle •Muscle consists of thick fibers called myosin and thin fibers called actin. These are found in all types of muscles. •The actin fibers are attached to vertical structures called Z-lines. The actin and myosin fibers overlap and are in close proximity to each other. This is called ...
... Structure of muscle •Muscle consists of thick fibers called myosin and thin fibers called actin. These are found in all types of muscles. •The actin fibers are attached to vertical structures called Z-lines. The actin and myosin fibers overlap and are in close proximity to each other. This is called ...
Meiosisorder
... Spindle fibers pull homologous pairs to center of cell. Homologous pairs line up opposite each ...
... Spindle fibers pull homologous pairs to center of cell. Homologous pairs line up opposite each ...
Molecular Motors
... reticulum • Each sarcomere is capped by a transverse tubule (t-tubule), an extension of sarcolemmal membrane ...
... reticulum • Each sarcomere is capped by a transverse tubule (t-tubule), an extension of sarcolemmal membrane ...
CHRISTIAN_PECULIAR_1
... myosin filament is thicker, lending a darker appearance to the alternating A bands as observed with electron microscopy. However, in contrast to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle cells are typically branch-like instead of linear. Another histological difference between cardiac muscle and skeletal musc ...
... myosin filament is thicker, lending a darker appearance to the alternating A bands as observed with electron microscopy. However, in contrast to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle cells are typically branch-like instead of linear. Another histological difference between cardiac muscle and skeletal musc ...
Inside the Eukaryotic Cell
... Protein fibers found in eukaryotic cells Supports the cell like the bones support a body The cytoskeleton helps the cell move, keep its ...
... Protein fibers found in eukaryotic cells Supports the cell like the bones support a body The cytoskeleton helps the cell move, keep its ...
REVIEW QUESTIONS REVIEW ANSWERS
... 5. A very active cell, such as a skeletal muscle cell, has one type of organelle in much greater quantity than a cell that is less active. What organelle would this be? ...
... 5. A very active cell, such as a skeletal muscle cell, has one type of organelle in much greater quantity than a cell that is less active. What organelle would this be? ...
Sliding Filament Theory - Skeletal Muscle The sliding filament theory
... Sliding Filament Theory - Skeletal Muscle The sliding filament theory is the method by which muscles are thought to contract. It is recommended that you read the muscle structure page before continuing with the sliding filament theory. The diagram below is a common one used to explain sliding filame ...
... Sliding Filament Theory - Skeletal Muscle The sliding filament theory is the method by which muscles are thought to contract. It is recommended that you read the muscle structure page before continuing with the sliding filament theory. The diagram below is a common one used to explain sliding filame ...
Chapter 10 Notes - Las Positas College
... myofibrils and sarcomeres; these striated cells are controlled voluntarily. F. The mechanism of contraction is explained by the sliding filament theory. G. Muscle tissue can be stretched by the contraction of an opposing muscle. This is called muscle extension and should not be confused with muscle ...
... myofibrils and sarcomeres; these striated cells are controlled voluntarily. F. The mechanism of contraction is explained by the sliding filament theory. G. Muscle tissue can be stretched by the contraction of an opposing muscle. This is called muscle extension and should not be confused with muscle ...
Assignment 2 The Muscular System
... • P4 - Describe the function of the muscular system and the different fibre types Basic muscle rules How do muscles generate movement Characteristics of muscles Types of muscles ...
... • P4 - Describe the function of the muscular system and the different fibre types Basic muscle rules How do muscles generate movement Characteristics of muscles Types of muscles ...
Document
... • Endurance training: Exercise that increases a muscle’s ability to sustain moderate exercise over long periods Sometimes called aerobic training Allows more efficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients to a muscle via increased blood flow Increases the number of blood vessels in a muscle Does ...
... • Endurance training: Exercise that increases a muscle’s ability to sustain moderate exercise over long periods Sometimes called aerobic training Allows more efficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients to a muscle via increased blood flow Increases the number of blood vessels in a muscle Does ...
Vacuolar Myopathies: Ultrastructural Studies Benefit Diagnosis
... in these autophagosomes which may rupture and form large vacuoles that disrupt cell function. Ultrastructurally, vacuoles with aggregates of autophagosomal material and glycogen are seen within cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. Peculiar, membrane-bound vacuoles that are lined by a basal lamina can ...
... in these autophagosomes which may rupture and form large vacuoles that disrupt cell function. Ultrastructurally, vacuoles with aggregates of autophagosomal material and glycogen are seen within cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. Peculiar, membrane-bound vacuoles that are lined by a basal lamina can ...
Alpha Diagnostic Intl Inc., 6203 Woodlake Center Dr, San Antonio
... muscles (skeletal, cardiac and smooth): Skeletal muscle or "voluntary muscle" is anchored by tendons to bone. Smooth muscle or "involuntary muscle" is found within the walls of organs and structures such as the esophagus, stomach, intestines, bronchi, uterus, urethra, bladder, and blood vessels, and ...
... muscles (skeletal, cardiac and smooth): Skeletal muscle or "voluntary muscle" is anchored by tendons to bone. Smooth muscle or "involuntary muscle" is found within the walls of organs and structures such as the esophagus, stomach, intestines, bronchi, uterus, urethra, bladder, and blood vessels, and ...
Anatomy and Physiology of the Neuromuscular Junction
... Communication occurs between a neuron and a muscle fiber through neurotransmitters. Neural excitation causes the release of neurotransmitters from the synaptic terminal into the synaptic cleft, where they can then bind to the appropriate receptors on the motor endplate. The motor end-plate has folds ...
... Communication occurs between a neuron and a muscle fiber through neurotransmitters. Neural excitation causes the release of neurotransmitters from the synaptic terminal into the synaptic cleft, where they can then bind to the appropriate receptors on the motor endplate. The motor end-plate has folds ...
The Role of MMP9 in Satellite Cell Activation After
... exercise. Though little is known about the molecular mechanisms that regulate this plasticity, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is believed to play a large role. The basal lamina is a specialized layer of ECM that lies in direct contact with the cell membrane of muscle fibers and facilitates environme ...
... exercise. Though little is known about the molecular mechanisms that regulate this plasticity, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is believed to play a large role. The basal lamina is a specialized layer of ECM that lies in direct contact with the cell membrane of muscle fibers and facilitates environme ...
PDF
... satellite cells in muscle regeneration in yet another mouse model. They show that satellite cell ablation results in complete loss of regenerated muscle, misregulation of fibroblasts and a large increase in connective tissue after injury. In addition, they report that ablation of muscle connective t ...
... satellite cells in muscle regeneration in yet another mouse model. They show that satellite cell ablation results in complete loss of regenerated muscle, misregulation of fibroblasts and a large increase in connective tissue after injury. In addition, they report that ablation of muscle connective t ...
m5zn_cca357279231d9d
... e) Glucose. 3. All the following statements are true about sodium-potassium pump EXCEPT a) It is an active method of transport across cell membrane. b) It is responsible for maintaining the sodium and potassium concentration difference across the cell membrane. c) It is responsible for establishing ...
... e) Glucose. 3. All the following statements are true about sodium-potassium pump EXCEPT a) It is an active method of transport across cell membrane. b) It is responsible for maintaining the sodium and potassium concentration difference across the cell membrane. c) It is responsible for establishing ...
Myocyte

A myocyte (also known as a muscle cell) is the type of cell found in muscle tissue. Myocytes are long, tubular cells that develop from myoblasts to form muscles in a process known as myogenesis. There are various specialized forms of myocytes: cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells, with various properties. The striated cells of cardiac and skeletal muscles are referred to as muscle fibers. Cardiomyocytes are the muscle fibres that form the chambers of the heart, and have a single central nucleus. Skeletal muscle fibers help support and move the body and tend to have peripheral nuclei. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the stomach.























