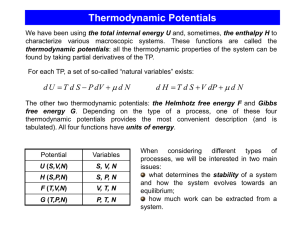
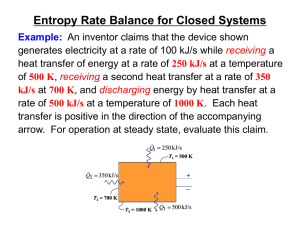
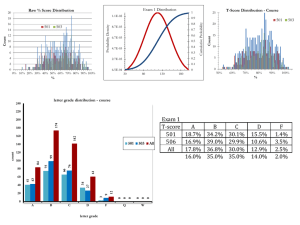
Screen Version
... Thermodynamics is concerned with the maximum fraction of a quantity of heat that can be converted into work. A discussion of the Carnot cycle can be found in Wallace & Hobbs. It is also described in most standard texts on thermodynamics. We will provide only an outline here. ...
... Thermodynamics is concerned with the maximum fraction of a quantity of heat that can be converted into work. A discussion of the Carnot cycle can be found in Wallace & Hobbs. It is also described in most standard texts on thermodynamics. We will provide only an outline here. ...
EGR 107 FALL 2001
... methods this can be solved for an ideal gas (tables or constant specific heats). Discuss two methods this can be solved for liquids (tables or constant specific heats). b. For a constant pressure process in a closed system q h ; list any assumptions required. Discuss two methods this can be solve ...
... methods this can be solved for an ideal gas (tables or constant specific heats). Discuss two methods this can be solved for liquids (tables or constant specific heats). b. For a constant pressure process in a closed system q h ; list any assumptions required. Discuss two methods this can be solve ...
Full-Text PDF
... compared with that of entropy. Under the environmental conditions of T0 and p0, the available energy transfer accompanying heat transfer is the maximal possible useful work produced from heat, while the available energy of a system is the maximum useful work obtainable during a process that brings t ...
... compared with that of entropy. Under the environmental conditions of T0 and p0, the available energy transfer accompanying heat transfer is the maximal possible useful work produced from heat, while the available energy of a system is the maximum useful work obtainable during a process that brings t ...
The Energy-Entropy Principle
... proposed, with simultaneous corroboration. The use of a well known book with physical interpretations, like Fermi's, permits to achieve this goal. In fact, Fermi sacriÍices the logic consistency of the phenomenological view to the obvious interpretation emerging from the kinetic view. In point I it ...
... proposed, with simultaneous corroboration. The use of a well known book with physical interpretations, like Fermi's, permits to achieve this goal. In fact, Fermi sacriÍices the logic consistency of the phenomenological view to the obvious interpretation emerging from the kinetic view. In point I it ...
thermodynamics
... converted into heat and vice versa. In winter, when we rub our palms together, we feel warmer; here work done in rubbing produces the ‘heat’. Conversely, in a steam engine, the ‘heat’ of the steam is used to do useful work in moving the pistons, which in turn rotate the wheels of the train. In physi ...
... converted into heat and vice versa. In winter, when we rub our palms together, we feel warmer; here work done in rubbing produces the ‘heat’. Conversely, in a steam engine, the ‘heat’ of the steam is used to do useful work in moving the pistons, which in turn rotate the wheels of the train. In physi ...
Engines and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
... 20-2 Heat Engines We will discuss only engines that run in a repeating cycle; the change in internal energy over a cycle is zero, as the system returns to its initial state. The high-temperature reservoir transfers an amount of heat QH to the engine, where part of it is transformed into work W and ...
... 20-2 Heat Engines We will discuss only engines that run in a repeating cycle; the change in internal energy over a cycle is zero, as the system returns to its initial state. The high-temperature reservoir transfers an amount of heat QH to the engine, where part of it is transformed into work W and ...
ch06C-2013
... component such as the throttling valve considered here often does not have much significance by itself. The significance of the entropy production of any component is normally determined through comparison with the entropy production values of other components combined with that component to form an ...
... component such as the throttling valve considered here often does not have much significance by itself. The significance of the entropy production of any component is normally determined through comparison with the entropy production values of other components combined with that component to form an ...
File
... = 1.5) is taken through an adiabatic process in which the volume is compressed from 1600cc to 400cc. If the initial pressure is 150kpa, what is the final pressure and how much work is done on the gas in the process? ...
... = 1.5) is taken through an adiabatic process in which the volume is compressed from 1600cc to 400cc. If the initial pressure is 150kpa, what is the final pressure and how much work is done on the gas in the process? ...
Thermodynamics - WordPress.com
... The concepts of temperature and heat were often confused before Joseph Black (1728–1799) carefully distinguished between the two in the late eighteenth century. While both are uniquely thermodynamic concepts, each plays its own role within the subject. Temperature, for instance, is an intensive stat ...
... The concepts of temperature and heat were often confused before Joseph Black (1728–1799) carefully distinguished between the two in the late eighteenth century. While both are uniquely thermodynamic concepts, each plays its own role within the subject. Temperature, for instance, is an intensive stat ...
Contents - MyCourses
... of energy and matter between the two goes as follows: Open system: both energy and matter may be exchanged. Closed system: particle number(s) fixed, energy may be exchanged. Isolated system: no exchange of matter or energy. Thermodynamic equilibrium. State of matter without any macroscopic changes o ...
... of energy and matter between the two goes as follows: Open system: both energy and matter may be exchanged. Closed system: particle number(s) fixed, energy may be exchanged. Isolated system: no exchange of matter or energy. Thermodynamic equilibrium. State of matter without any macroscopic changes o ...
1 CHAPTER 17 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS 17.1 Equilibrium
... now going to discuss systems consisting of more than one phase and more than one component. The Gibbs Phase Law provides a relation between the number of phases, the number of components and the number of degrees of freedom. But Whoa, there! We have been using several technical terms here: Phase, Co ...
... now going to discuss systems consisting of more than one phase and more than one component. The Gibbs Phase Law provides a relation between the number of phases, the number of components and the number of degrees of freedom. But Whoa, there! We have been using several technical terms here: Phase, Co ...
Second Law of Thermodynamics
... The second law of thermodynamics explains the direction in which the thermodynamic processes tend to go. That is, it limits the types of final states of the system that naturally evolve from a given initial state. The second law has many practical applications. For example it explains the limits of ...
... The second law of thermodynamics explains the direction in which the thermodynamic processes tend to go. That is, it limits the types of final states of the system that naturally evolve from a given initial state. The second law has many practical applications. For example it explains the limits of ...
Document
... • When a system process is exothermic, it adds heat to the surroundings, increasing the entropy of the surroundings • When a system process is endothermic, it takes heat from the surroundings, decreasing the entropy of the surroundings. • The amount the entropy of the surroundings changes depends on ...
... • When a system process is exothermic, it adds heat to the surroundings, increasing the entropy of the surroundings • When a system process is endothermic, it takes heat from the surroundings, decreasing the entropy of the surroundings. • The amount the entropy of the surroundings changes depends on ...
The Ensembles
... The canonical ensemble is generally the most useful in practice since we most often deal with systems in thermal equilibrium (constant T ) with their surroundings. The energy states fluctuate and the probability of observing the system in a given energy state at constant T is given by eq. (6.5). We ...
... The canonical ensemble is generally the most useful in practice since we most often deal with systems in thermal equilibrium (constant T ) with their surroundings. The energy states fluctuate and the probability of observing the system in a given energy state at constant T is given by eq. (6.5). We ...
Meandering Road from Dynamics to Thermodynamics and Vice Versa
... the description of more complete modern knowledge. Some definitions and conventions in dynamics and thermodynamics are given differently and can be confusing to unsuspecting undergraduate students who are taking them in their curricula. To a certain extent, this is the case with the terms heat, work ...
... the description of more complete modern knowledge. Some definitions and conventions in dynamics and thermodynamics are given differently and can be confusing to unsuspecting undergraduate students who are taking them in their curricula. To a certain extent, this is the case with the terms heat, work ...
Meandering Road From Dynamics To Thermodynamics And Vice
... that has the ability to cause changes. Energy is a property possessed by a system, but heat is not a property possessed by any system. In daily life, “heat” and “thermal energy” are often synonymously used. In thermodynamics, “heat transfer” and “energy transfer by heat” are interchangeably used. To ...
... that has the ability to cause changes. Energy is a property possessed by a system, but heat is not a property possessed by any system. In daily life, “heat” and “thermal energy” are often synonymously used. In thermodynamics, “heat transfer” and “energy transfer by heat” are interchangeably used. To ...
The Local-Nonequilibrium Temperature Field
... go beyond the local-equilibrium assumption, have received little attention in the literature. The most active branch in phenomenological nonequilibrium thermodynamics, which does not adopt the local-equilibrium assumption, is t h e so-called extended irreversible thermodynamics (EIT) [ 14]. EIT intr ...
... go beyond the local-equilibrium assumption, have received little attention in the literature. The most active branch in phenomenological nonequilibrium thermodynamics, which does not adopt the local-equilibrium assumption, is t h e so-called extended irreversible thermodynamics (EIT) [ 14]. EIT intr ...
The First and Second Laws of Thermodynamics
... degradation of energy during a process. As discussed later in this chapter, more of high-temperature energy can be converted to work, and thus it has a higher quality than the same amount of energy at a lower temperature. The second law of thermodynamics is also used in determining the theoretical l ...
... degradation of energy during a process. As discussed later in this chapter, more of high-temperature energy can be converted to work, and thus it has a higher quality than the same amount of energy at a lower temperature. The second law of thermodynamics is also used in determining the theoretical l ...
Thermodynamics and Kinetics
... Enthalpy changes are not the only factors that determine whether a process is spontaneous. Most spontaneous reactions are exothermic, but there are many that are not exothermic, however, reactions can be both spontaneous and highly endothermic. ...
... Enthalpy changes are not the only factors that determine whether a process is spontaneous. Most spontaneous reactions are exothermic, but there are many that are not exothermic, however, reactions can be both spontaneous and highly endothermic. ...