MOCT(Magneto Optic Current Transformer)
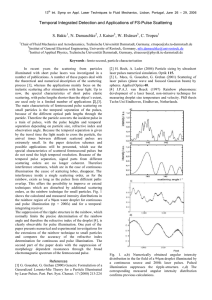
... A polarizer is used to convert the randomly polarized incident light into linearly polarized light. The orientation of the linearly polarized light rotates an angle after the light has passed through the magneto-optical material because of Faraday Effect. Then another polarization prism is used as ...
... A polarizer is used to convert the randomly polarized incident light into linearly polarized light. The orientation of the linearly polarized light rotates an angle after the light has passed through the magneto-optical material because of Faraday Effect. Then another polarization prism is used as ...
lecture 2
... With age, the lens becomes less flexible and accommodation becomes fixed at some distance. This fixing of the focal length of the lens is called PRESBYOPIA. The refracting power of the eye may not be the same in all dimensions. This is called ASTIGMATISM. ...
... With age, the lens becomes less flexible and accommodation becomes fixed at some distance. This fixing of the focal length of the lens is called PRESBYOPIA. The refracting power of the eye may not be the same in all dimensions. This is called ASTIGMATISM. ...
Spectral Brightness of Synchrotron Radiation
... Light takes time to travel from the particle to the observer By the time the observer sees the light, the particle is in a new position The position at which the particle is when it emits the light is known as the retarded position and the particle is at this point at the ...
... Light takes time to travel from the particle to the observer By the time the observer sees the light, the particle is in a new position The position at which the particle is when it emits the light is known as the retarded position and the particle is at this point at the ...
PHYSICS 504 OPTICS REVIEW: Important things to remember
... Ally and Conor perform an experiment in the lab. They place a light source at the bottom of a container filled with an unknown liquid. The light source in the unknown liquid gives off a ray that passes into air (as shown) and the results are recorded in the table below. Angle of Incidence ...
... Ally and Conor perform an experiment in the lab. They place a light source at the bottom of a container filled with an unknown liquid. The light source in the unknown liquid gives off a ray that passes into air (as shown) and the results are recorded in the table below. Angle of Incidence ...
optical quality standards
... OPTICAL QUALITY STANDARDS The U.S. Military defines Quality Level or Grade as different striae levels per Din 3140 and according to MIL-G-174-B. Striae is localized inhomogeneity within the optical material. Test is ...
... OPTICAL QUALITY STANDARDS The U.S. Military defines Quality Level or Grade as different striae levels per Din 3140 and according to MIL-G-174-B. Striae is localized inhomogeneity within the optical material. Test is ...
Temporal Integrated Detection and Applications of FS-Pulse Scattering S. Bakic
... small particles is the temporal separation of the pulses, because of the different optical path lengths through the particle. Therefore the particle converts the incident pulse in a train of pulses, with the pulse heights and temporal separation depending on particle size, refractive index and obser ...
... small particles is the temporal separation of the pulses, because of the different optical path lengths through the particle. Therefore the particle converts the incident pulse in a train of pulses, with the pulse heights and temporal separation depending on particle size, refractive index and obser ...
13 Int. Symp on Appl. Laser ...
... small particles is the temporal separation of the pulses, because of the different optical path lengths through the particle. Therefore the particle converts the incident pulse in a train of pulses, with the pulse heights and temporal separation depending on particle size, refractive index and obser ...
... small particles is the temporal separation of the pulses, because of the different optical path lengths through the particle. Therefore the particle converts the incident pulse in a train of pulses, with the pulse heights and temporal separation depending on particle size, refractive index and obser ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.