Focal Point
... you can see four parallel rays of light on your construction paper. Move the flashlight closer and farther from the index card and adjust the angle of the slope so that the four slits are parallel to one another, just as they are on the index card. You should see four bright light rays on the black ...
... you can see four parallel rays of light on your construction paper. Move the flashlight closer and farther from the index card and adjust the angle of the slope so that the four slits are parallel to one another, just as they are on the index card. You should see four bright light rays on the black ...
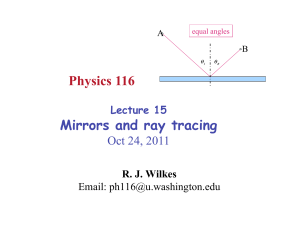
Physics 116 Mirrors and ray tracing
... If the surface is not smooth – light rays arriving at nearby points get reflected at very different angles – reflection will be diffuse ...
... If the surface is not smooth – light rays arriving at nearby points get reflected at very different angles – reflection will be diffuse ...
Questacon Wonderworks Teacher Notes
... Fundamental Exhibit Themes, Descriptions and Curriculum Links Questacon’s Fundamental exhibition in Gallery 2 (based in Canberra), contains hands-on exhibits suitable for visitors aged 7 years through to adults. This document lists Fundamental exhibit names, descriptions, key themes and subject area ...
... Fundamental Exhibit Themes, Descriptions and Curriculum Links Questacon’s Fundamental exhibition in Gallery 2 (based in Canberra), contains hands-on exhibits suitable for visitors aged 7 years through to adults. This document lists Fundamental exhibit names, descriptions, key themes and subject area ...
Chapter 8: Major Elements
... All intermediate values are called e’ (a variable value between e and w) ...
... All intermediate values are called e’ (a variable value between e and w) ...
The long march of slow photonics
... light has already been described by many researchers as a key to advances in optical signal processing, but in this new area many puzzles still have to be solved. A first enigma concerns the most promising approach for generating slow light. In the arena of photonic devices, ring resonators (RRs) an ...
... light has already been described by many researchers as a key to advances in optical signal processing, but in this new area many puzzles still have to be solved. A first enigma concerns the most promising approach for generating slow light. In the arena of photonic devices, ring resonators (RRs) an ...
Document
... that will allow multiple users to work and interact. Perceptive Pixel’s technology is currently being utilized, in the form of the Multi-Touch Collaboration Wall. ...
... that will allow multiple users to work and interact. Perceptive Pixel’s technology is currently being utilized, in the form of the Multi-Touch Collaboration Wall. ...
25-4 Diffraction: Double Slits and Circular Openings
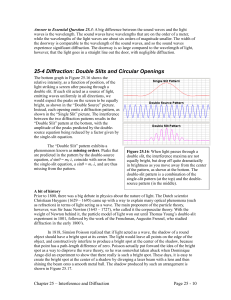
... the narrower the width of the central peak in the diffraction pattern. This dependence on the diameter of the opening has implications for how close two objects can be before you cannot resolve them. For instance, when you look up at the sky at night, two stars that are very close together may appea ...
... the narrower the width of the central peak in the diffraction pattern. This dependence on the diameter of the opening has implications for how close two objects can be before you cannot resolve them. For instance, when you look up at the sky at night, two stars that are very close together may appea ...
HW2_ASTR 289_2016_v2
... Problem 6) The Keck Telescopes: The two Keck Telescopes are each hexagonal, 10 meters in diameter, and have 17.5 meter focal length. Because they have hexagonal primary mirrors, we need to be careful how we define the mirror "diameter". So let's simplify by approximating the hexagons by circular mir ...
... Problem 6) The Keck Telescopes: The two Keck Telescopes are each hexagonal, 10 meters in diameter, and have 17.5 meter focal length. Because they have hexagonal primary mirrors, we need to be careful how we define the mirror "diameter". So let's simplify by approximating the hexagons by circular mir ...
How to turn your microscope into a phase contrast microscope
... Now let us use the language of wave mechanics to describe what happens. First, take the case that there is no object at all. If there is no disk, we will see an even distribution of light in the image. When putting the disk back, the image becomes dark. In terms of wave mechanics, we now argue that ...
... Now let us use the language of wave mechanics to describe what happens. First, take the case that there is no object at all. If there is no disk, we will see an even distribution of light in the image. When putting the disk back, the image becomes dark. In terms of wave mechanics, we now argue that ...
Magneto Optical Kerr Effect (MOKE)
... averaging techniques to investigate properties of large arrays of identical nanostructures, overcoming the problems associated to the study of a single nanoelement, like low signal or low size. ...
... averaging techniques to investigate properties of large arrays of identical nanostructures, overcoming the problems associated to the study of a single nanoelement, like low signal or low size. ...
Unit C POS Checklist
... predict the conditions required for diffraction to be observed. predict the conditions required for total internal reflection to occur. design an experiment to measure the speed of light. Performing and Recording Outcomes: I can: perform experiments to demonstrate refraction at plane and uni ...
... predict the conditions required for diffraction to be observed. predict the conditions required for total internal reflection to occur. design an experiment to measure the speed of light. Performing and Recording Outcomes: I can: perform experiments to demonstrate refraction at plane and uni ...
Snell`s Law - Initial Set Up
... When light travels from a less optically dense material to a more optically dense material, how does the light ray bend relative to the normal? When light travels from a more optically dense material to a less optically dense material, how does the light ray bend relative to the normal? ...
... When light travels from a less optically dense material to a more optically dense material, how does the light ray bend relative to the normal? When light travels from a more optically dense material to a less optically dense material, how does the light ray bend relative to the normal? ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.