Linear Polarization 5.2.4 Polarization and Materials
... of the two, of course): 1. The index of refraction depends on the crystal direction. The optical effects resulting from this are called "birefringence" or double refraction (Latin: bi = two, twice, refringere = to break up, to refract). 2. The absorption depends on the polarization (and the crystal ...
... of the two, of course): 1. The index of refraction depends on the crystal direction. The optical effects resulting from this are called "birefringence" or double refraction (Latin: bi = two, twice, refringere = to break up, to refract). 2. The absorption depends on the polarization (and the crystal ...
micro-bending, macro-bending and less bend sensitive optical
... Macro-bends can be most easily classified as being optical fibres, or cables containing optical fibres, that are subjected to bend radii below the manufacturers recommended values to such an extent that the light cannot be guided along the core of optical fibre – thereby resulting in attenuation i.e ...
... Macro-bends can be most easily classified as being optical fibres, or cables containing optical fibres, that are subjected to bend radii below the manufacturers recommended values to such an extent that the light cannot be guided along the core of optical fibre – thereby resulting in attenuation i.e ...
7.1 textbook answers - aiss-science-9
... 10 Sunsets and sunrises are caused by scattering in which molecules of gas and dust particles in the atmosphere alter the direction of light rays. The dust and gas is better at scattering blue light than red light, which is why the sky usually appears blue. The red light escapes into space. At sunri ...
... 10 Sunsets and sunrises are caused by scattering in which molecules of gas and dust particles in the atmosphere alter the direction of light rays. The dust and gas is better at scattering blue light than red light, which is why the sky usually appears blue. The red light escapes into space. At sunri ...
OOSpecActivities
... Introduction: Computer monitors are capable of producing millions of colors. However, close examination with a magnifying lens and the OO spec yields what may be some surprises. Only red, green, and blue pixels can be seen on a monitor. The computer adjusts the relative brightness of each color to p ...
... Introduction: Computer monitors are capable of producing millions of colors. However, close examination with a magnifying lens and the OO spec yields what may be some surprises. Only red, green, and blue pixels can be seen on a monitor. The computer adjusts the relative brightness of each color to p ...
Exp7. Birefringence in Calcite Crystals
... 8. Discuss whether the Snells’ law applies for normal and extraordinary light passage. ...
... 8. Discuss whether the Snells’ law applies for normal and extraordinary light passage. ...
The page, which you have just visited, was created for students of
... There is still much about the molecular physics and thermodynamics of glass, that is not well understood, but it could give a general account of what is thought to be the case. Many solids have a crystalline structure on microscopic scales. The molecules are arranged in a regular lattice. Usually wh ...
... There is still much about the molecular physics and thermodynamics of glass, that is not well understood, but it could give a general account of what is thought to be the case. Many solids have a crystalline structure on microscopic scales. The molecules are arranged in a regular lattice. Usually wh ...
Meteorology Frameworks Kindergarten Students know
... place by checking on today’s weather somewhere else. And if they see low-pressure closures (discussed above), they can predict stormy or fair weather from high-pressure closures. Very small changes in temperature and pressure, however, may significantly ...
... place by checking on today’s weather somewhere else. And if they see low-pressure closures (discussed above), they can predict stormy or fair weather from high-pressure closures. Very small changes in temperature and pressure, however, may significantly ...
Lecture 26 - Auger at LAL
... Mie theory is used when size parameter x is about 1 (particle about the same size as the wavelength). If x << 1 (particles small compared with the wavelength) we use Rayleigh regime, in which scattering and extinction coefficient are given by approximate expressions. Rayleigh regime: Qsc ~ -4 and Q ...
... Mie theory is used when size parameter x is about 1 (particle about the same size as the wavelength). If x << 1 (particles small compared with the wavelength) we use Rayleigh regime, in which scattering and extinction coefficient are given by approximate expressions. Rayleigh regime: Qsc ~ -4 and Q ...
Name:__________________ Date: Pre
... Base your answer to question 15-17 on the experiment description and diagram below. A student was interested in how the angle of insolation affects absorption of radiation. The student took three black metal plates, each containing a built-in thermometer, and placed them at the same distance from t ...
... Base your answer to question 15-17 on the experiment description and diagram below. A student was interested in how the angle of insolation affects absorption of radiation. The student took three black metal plates, each containing a built-in thermometer, and placed them at the same distance from t ...
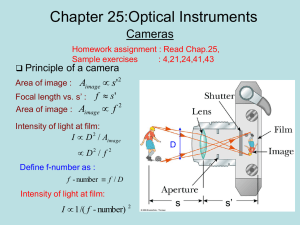
Chapter 25
... nature of light If two sources of light are close together, they can be treated as noncoherent sources Because of diffraction, the images consist of bright central regions flanked by weaker bright and dark rings ...
... nature of light If two sources of light are close together, they can be treated as noncoherent sources Because of diffraction, the images consist of bright central regions flanked by weaker bright and dark rings ...
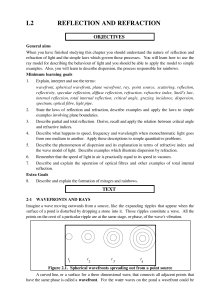
L2 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
... We see objects when light from them enters our eyes. Apart from self-luminous objects, such as the sun, lamps, flames and television screens, all other objects are seen only because they reflect light. Hence the apparent shape, texture and colour of objects depend upon the light which falls on them, ...
... We see objects when light from them enters our eyes. Apart from self-luminous objects, such as the sun, lamps, flames and television screens, all other objects are seen only because they reflect light. Hence the apparent shape, texture and colour of objects depend upon the light which falls on them, ...
What is remote sensing?
... along successive lines over finite time called scanning systems. The size of scene which is determined by the aperture and optics called field of view (FOV). ...
... along successive lines over finite time called scanning systems. The size of scene which is determined by the aperture and optics called field of view (FOV). ...
Electro-optical photonic circuits for classical and
... environment is ultimately dictated by diffraction and scattering, the latter being especially important in biological settings. At present, standard imaging methods in the visible can only penetrate a few hundreds of micrometers inside a biological tissue [3]. To overcome this, several modern techni ...
... environment is ultimately dictated by diffraction and scattering, the latter being especially important in biological settings. At present, standard imaging methods in the visible can only penetrate a few hundreds of micrometers inside a biological tissue [3]. To overcome this, several modern techni ...
absorbance, a - srmbiotech25
... • Beer’s law is successful in describing the absorption behavior of dilute solutions only ; in this sense it is a limiting law. At high concentrations ( > 0.01M ),the average distance between the species responsible for absorption is diminished to the point where each affects the charge distribution ...
... • Beer’s law is successful in describing the absorption behavior of dilute solutions only ; in this sense it is a limiting law. At high concentrations ( > 0.01M ),the average distance between the species responsible for absorption is diminished to the point where each affects the charge distribution ...
Review ! a
... ! Note that this result applies only to the case where of a material with index of refraction n and air on both sides, like a soap bubble ...
... ! Note that this result applies only to the case where of a material with index of refraction n and air on both sides, like a soap bubble ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.