Document
... being reflected. These curved mirrors are silvered on the concave side and are known as concave mirrors. Other curved mirrors are silvered on the convex side. They are commonly used too give a wider field view. These mirrors cause the parallel rays incident on their surface to be reflected as throug ...
... being reflected. These curved mirrors are silvered on the concave side and are known as concave mirrors. Other curved mirrors are silvered on the convex side. They are commonly used too give a wider field view. These mirrors cause the parallel rays incident on their surface to be reflected as throug ...
Circuit Activity Sheets
... Additional activity (if time allows or for further study) (Note: Use clear LEDs.) An LED can also work in reverse. That is, it can be used as a light sensor. Measure the voltage across one of your LEDs. Bring a white light source near the LED and note the increase in voltage. This should work for al ...
... Additional activity (if time allows or for further study) (Note: Use clear LEDs.) An LED can also work in reverse. That is, it can be used as a light sensor. Measure the voltage across one of your LEDs. Bring a white light source near the LED and note the increase in voltage. This should work for al ...
COLOR VOCABULARY
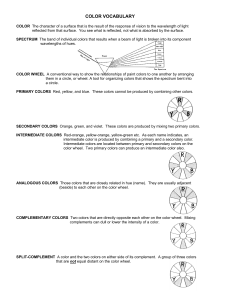
... INTENSITY The saturation or strength of a color determined by the quality of light reflected from it. The brightness or purity of a color. A pure color is in its brightest form and is most intense. The addition of any color lowers the intensity. ...
... INTENSITY The saturation or strength of a color determined by the quality of light reflected from it. The brightness or purity of a color. A pure color is in its brightest form and is most intense. The addition of any color lowers the intensity. ...
Past Questions On Stationary Waves and Refractive Index
... (c) A second prism, prism 2, made from transparent material of refractive index 1.37 is placed firmly against the original prism, prism 1, to form a cube as shown in Figure 2. ...
... (c) A second prism, prism 2, made from transparent material of refractive index 1.37 is placed firmly against the original prism, prism 1, to form a cube as shown in Figure 2. ...
Physics116_L22
... Covers material in Chs. 25 - 27 (not including material from ch. 28 yesterday) ...
... Covers material in Chs. 25 - 27 (not including material from ch. 28 yesterday) ...
Practical No 6
... 1. Turn the light source on using the button (2) and set it to the position when white light is emitted. 2. Turn the light meter on using the button (9). 3. Using the button (11) set the light meter at normal range (x1). 4. Set the diameter of the diaphragm to 6 mm and place the detector at the dist ...
... 1. Turn the light source on using the button (2) and set it to the position when white light is emitted. 2. Turn the light meter on using the button (9). 3. Using the button (11) set the light meter at normal range (x1). 4. Set the diameter of the diaphragm to 6 mm and place the detector at the dist ...
light and color - American Association of Physics Teachers
... One of the major goals of the Light and Color unit is to help the students develop a set of robust, meaningful, and valid ideas involving light and color phenomena. By the end of the unit, students who encounter a novel phenomenon should be able to account for it in terms of ideas that are closely a ...
... One of the major goals of the Light and Color unit is to help the students develop a set of robust, meaningful, and valid ideas involving light and color phenomena. By the end of the unit, students who encounter a novel phenomenon should be able to account for it in terms of ideas that are closely a ...
MSE 222 - UPenn School of Engineering and Applied Science
... 10 Interaction of light with metals/conductors. Concept of plasma frequency, skin depth, cyclotron resonance. Wave-particle duality, photoelectric effect. CCD camera. Relationship between conductivity and optical properties. Transparent electrodes and applications. Optical properties of metals/condu ...
... 10 Interaction of light with metals/conductors. Concept of plasma frequency, skin depth, cyclotron resonance. Wave-particle duality, photoelectric effect. CCD camera. Relationship between conductivity and optical properties. Transparent electrodes and applications. Optical properties of metals/condu ...
Coherent Light Transport in a Cold Strontium Cloud
... We also checked that the finite transverse size of the laser beam has no significant influence on the signal. Taking into account the systematic errors, we find that the CBS enhancement factor should rather be a 苷 1.91, consistent with the measured value. A remaining (but yet uncontrolled) source of ...
... We also checked that the finite transverse size of the laser beam has no significant influence on the signal. Taking into account the systematic errors, we find that the CBS enhancement factor should rather be a 苷 1.91, consistent with the measured value. A remaining (but yet uncontrolled) source of ...
Laser-scattering
... Let’s start with the conventional design: Here a sufficiently broad, parallel laser beam is generated, in which then the measuring cell with the scattering particles is inserted. Between the measurement cell and the detector the Fourier lens is positioned. With this alignment the focal distance of t ...
... Let’s start with the conventional design: Here a sufficiently broad, parallel laser beam is generated, in which then the measuring cell with the scattering particles is inserted. Between the measurement cell and the detector the Fourier lens is positioned. With this alignment the focal distance of t ...
Planet Notes 2 - 1 Notes 2: Physics of the solar system 2.1 Basics of
... So far we’ve just looked at how two objects move, usually one object going about the Sun. Since there are quite a large number of objects in the solar system, that is a rather simplistic way of looking at how things are set up. However, once you get beyond predicting the motion of 2 objects the math ...
... So far we’ve just looked at how two objects move, usually one object going about the Sun. Since there are quite a large number of objects in the solar system, that is a rather simplistic way of looking at how things are set up. However, once you get beyond predicting the motion of 2 objects the math ...
f - Uplift Education
... hot enough to emit visible light. Lamp A is cooler, and the radiation it emits is too low in frequency to be visible—it emits infrared waves, which aren’t seen with the eye. You emit waves as well. Even in a completely dark room your waves are there. Your friends may not be able to see you, but a ra ...
... hot enough to emit visible light. Lamp A is cooler, and the radiation it emits is too low in frequency to be visible—it emits infrared waves, which aren’t seen with the eye. You emit waves as well. Even in a completely dark room your waves are there. Your friends may not be able to see you, but a ra ...
Geometrical Optics: Curved Mirrors Worksheet Part I:
... animation, when the image is on the left of the mirror it is a real image, but when it is on the right it is a virtual image. Place the object so that the image is to the right of the mirror (a virtual image). Now, let’s identify where your eye/brain thinks the light is coming from. First, note that ...
... animation, when the image is on the left of the mirror it is a real image, but when it is on the right it is a virtual image. Place the object so that the image is to the right of the mirror (a virtual image). Now, let’s identify where your eye/brain thinks the light is coming from. First, note that ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.