White-light Fourier transformer with low chromatic aberration
... Throughout the study all distances are directed, with the sign convention that those in the same sense as the entering light are positive (in our case from left to right) and vice versa. In Fig. 1(a) 0 and O'(ur) are shown as real planes (d, and d1 ' are positive distances), but in general they can ...
... Throughout the study all distances are directed, with the sign convention that those in the same sense as the entering light are positive (in our case from left to right) and vice versa. In Fig. 1(a) 0 and O'(ur) are shown as real planes (d, and d1 ' are positive distances), but in general they can ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... the autocorrelation and minimize the cross-correlation function and then the receiver would be able to distinguish the correct address. In order to extract data with the desired optical pulse sequence, we therefore have to design sequences that satisfy some conditions: Each sequence can be disti ...
... the autocorrelation and minimize the cross-correlation function and then the receiver would be able to distinguish the correct address. In order to extract data with the desired optical pulse sequence, we therefore have to design sequences that satisfy some conditions: Each sequence can be disti ...
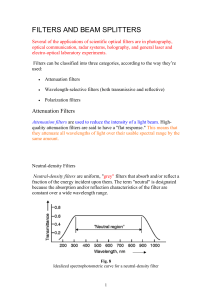
FILTERS AND BEAM SPLITTERS Several of the applications of
... The product t1t2 sometimes is called the "filter correction factor." For light incident normally on the filter surface, it’s given by, Equation 3 where: n = index of refraction of the filter glass (relative to air). The top curve in Figure 9 is for a filter two millimeters thick. The second curve is ...
... The product t1t2 sometimes is called the "filter correction factor." For light incident normally on the filter surface, it’s given by, Equation 3 where: n = index of refraction of the filter glass (relative to air). The top curve in Figure 9 is for a filter two millimeters thick. The second curve is ...
Optical Properties of Nanostructures
... Light Scattering is a physical process where light is forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by heterogeneity in the medium through which they pass. Everything except a vacuum is heterogeneous in some sense. Even in media that we usually consider to be homogeneous, it is possible to distinguis ...
... Light Scattering is a physical process where light is forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by heterogeneity in the medium through which they pass. Everything except a vacuum is heterogeneous in some sense. Even in media that we usually consider to be homogeneous, it is possible to distinguis ...
MICROSCOPY I: BRIGHT
... As light waves enter a medium from the air, they are slowed down, or retarded. On reemerging the light waves assume their original velocity. Since formed elements in living cells, such as chromosomes, generally have a higher refractive index than the surrounding cytoplasm, light passing through them ...
... As light waves enter a medium from the air, they are slowed down, or retarded. On reemerging the light waves assume their original velocity. Since formed elements in living cells, such as chromosomes, generally have a higher refractive index than the surrounding cytoplasm, light passing through them ...
S.72-227 Digital Communication Systems
... Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory Digital Hierarchy as applied in PSTN ...
... Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory Digital Hierarchy as applied in PSTN ...
Student Text, pp. 444-452
... If a wave encounters a straight barrier obliquely (i.e., at an angle other than 90°), the wave front is likewise reflected obliquely. The angle formed by the incident wave front and the normal is equal to the angle formed by the reflected wave front and the normal. These angles are called the angle ...
... If a wave encounters a straight barrier obliquely (i.e., at an angle other than 90°), the wave front is likewise reflected obliquely. The angle formed by the incident wave front and the normal is equal to the angle formed by the reflected wave front and the normal. These angles are called the angle ...
(NLPIP) - Full Spectrum Light Sources
... How valid are the claims regarding full-spectrum light sources? Full-spectrum light sources and color perception. Full-spectrum light sources will probably provide excellent color rendering. Color rendering index (CRI) values for full-spectrum lighting sources are typically greater than 90. Color is ...
... How valid are the claims regarding full-spectrum light sources? Full-spectrum light sources and color perception. Full-spectrum light sources will probably provide excellent color rendering. Color rendering index (CRI) values for full-spectrum lighting sources are typically greater than 90. Color is ...
Variability in ultraviolet total optical depth during the Southern
... one by the other introduces a bias. These di!erences have been discussed extensively in the literature (e.g., Thomason et al., 1983 or Tomasi et al., 1998). The elevation pro"le of ozone is one of the pro"les that di!ers most from the pro"le of the uniformly mixed atmospheric gases that is used for ...
... one by the other introduces a bias. These di!erences have been discussed extensively in the literature (e.g., Thomason et al., 1983 or Tomasi et al., 1998). The elevation pro"le of ozone is one of the pro"les that di!ers most from the pro"le of the uniformly mixed atmospheric gases that is used for ...
Polarization Beam Splitter Based on Self
... wave-vector. The group velocity is always perpendicular to the EFCs and it is aligned in the increasing (k) direction. Light propagates without diffraction in the flat (not curved) regions of the EFC. A mode can be identified by its unique combination (k, n), where n is called the band number in th ...
... wave-vector. The group velocity is always perpendicular to the EFCs and it is aligned in the increasing (k) direction. Light propagates without diffraction in the flat (not curved) regions of the EFC. A mode can be identified by its unique combination (k, n), where n is called the band number in th ...
HERCULES_Neutron_reflectivity
... Fig. 5 shows four scattering length density profiles which would give rise to the same reflectivity within the kinematic approximation of reflection[4]. In practise it is usually possible to distinguish between the a/b and c/d pairs from knowledge of the properties of the bulk media involved, but de ...
... Fig. 5 shows four scattering length density profiles which would give rise to the same reflectivity within the kinematic approximation of reflection[4]. In practise it is usually possible to distinguish between the a/b and c/d pairs from knowledge of the properties of the bulk media involved, but de ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.