Measurement considerations when specifying
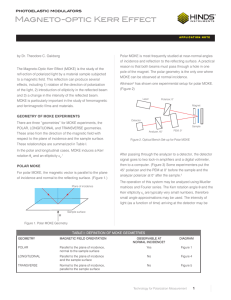
... FIGURE 2. Performance of a 1064 nm Brewster’s angle (56.6°) thin-film polarizer is shown as a function of incident angle. A 2–3° half-cone angle on the spectrophotometer test beam can have a significant effect on measured performance of the p-polarized (blue line) passband transmission. It is intere ...
... FIGURE 2. Performance of a 1064 nm Brewster’s angle (56.6°) thin-film polarizer is shown as a function of incident angle. A 2–3° half-cone angle on the spectrophotometer test beam can have a significant effect on measured performance of the p-polarized (blue line) passband transmission. It is intere ...
Wave Optics Theory and 3-D Deconvolution for the Light Field
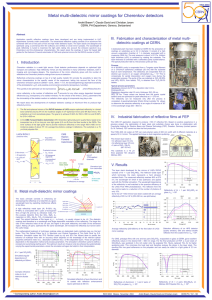
... A conventional microscope can be converted into a light field microscope by placing a microlens array at the native image plane as shown in Fig. 2(a). Light field imaging can be performed using any microscope objective so long as the f-number of the microlens array is matched to the numerical apertu ...
... A conventional microscope can be converted into a light field microscope by placing a microlens array at the native image plane as shown in Fig. 2(a). Light field imaging can be performed using any microscope objective so long as the f-number of the microlens array is matched to the numerical apertu ...
Lab 8: Polarization of Light
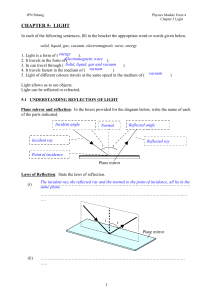
... the refractive indices (along the two different directhey don’t reduce the intensity of the incident light tions) and the thickness of the crystal. The phase difbeam. ference can be expressed as a path difference between the two components. To understand how retarders function, it is instructive to ...
... the refractive indices (along the two different directhey don’t reduce the intensity of the incident light tions) and the thickness of the crystal. The phase difbeam. ference can be expressed as a path difference between the two components. To understand how retarders function, it is instructive to ...
Mechanical mapping with chemical specificity by confocal Brillouin
... the microscopic analysis. The thickness of the air dried section was approximately 5 m. Brillouin spectra were collected with a microfocused setup26 using a tandem 3+3 Fabry-Perot interferometer.24 We used a single-mode Excelsior Diode-Pumped Solid-State (DPSS) laser with 532 nm wavelength and 5 mW ...
... the microscopic analysis. The thickness of the air dried section was approximately 5 m. Brillouin spectra were collected with a microfocused setup26 using a tandem 3+3 Fabry-Perot interferometer.24 We used a single-mode Excelsior Diode-Pumped Solid-State (DPSS) laser with 532 nm wavelength and 5 mW ...
LASER LIGHT SCATTERING FOR INVESTIGATION OF PARTICLE
... there by securing the best price possible. However, there is no universal grading system. Each producing country has their own national standard which fulfills the minimum export quality requirement suggested by the market[2,3,5]. Most probably the flavor and quality of coffee depends on the coffee ...
... there by securing the best price possible. However, there is no universal grading system. Each producing country has their own national standard which fulfills the minimum export quality requirement suggested by the market[2,3,5]. Most probably the flavor and quality of coffee depends on the coffee ...
optical properties of biaxial minerals
... one occupying opposing quadrants of the microscopic view. The 45° position, where hyperbolas occupy NE and SW quadrant is the most useful for determination of the optic sign. In this position Y optical direction or optic normal is aligned NW-SE. Optic axial plane is aligned NE-SW, where optic axial ...
... one occupying opposing quadrants of the microscopic view. The 45° position, where hyperbolas occupy NE and SW quadrant is the most useful for determination of the optic sign. In this position Y optical direction or optic normal is aligned NW-SE. Optic axial plane is aligned NE-SW, where optic axial ...
Superresolution size determination in fluorescence microscopy: A
... tion in the image data file. Distances between such objects down to about 15 nm have been measured with a precision 共95% confidence limit兲 as good as 10 nm using optically ‘‘conventional’’ fluorescence microscopes.19,24 In this article, results from a different far field light microscopical approach ...
... tion in the image data file. Distances between such objects down to about 15 nm have been measured with a precision 共95% confidence limit兲 as good as 10 nm using optically ‘‘conventional’’ fluorescence microscopes.19,24 In this article, results from a different far field light microscopical approach ...
S.72-227 Digital Communication Systems
... Traditionally two windows available: – 1.3 mm and 1.55 mm The lower window is used with Si and GaAlAs and the upper window with InGaAsP compounds Nowadays these attenuation windows no longer separate (water-spike attenuation region can be removed) There are single- and monomode fibers that may have ...
... Traditionally two windows available: – 1.3 mm and 1.55 mm The lower window is used with Si and GaAlAs and the upper window with InGaAsP compounds Nowadays these attenuation windows no longer separate (water-spike attenuation region can be removed) There are single- and monomode fibers that may have ...
Fine Structure Constant Defines Visual Transparency of Graphene
... velocity and k the wavevector), G was theoretically predicted (S6- S10) to exhibit a universal value G0 ≡e2/4=, if the photon energy E is much larger than both temperature and Fermi energy εF. Both conditions are stringently satisfied in our visible-optics experiments. The universal value of G also ...
... velocity and k the wavevector), G was theoretically predicted (S6- S10) to exhibit a universal value G0 ≡e2/4=, if the photon energy E is much larger than both temperature and Fermi energy εF. Both conditions are stringently satisfied in our visible-optics experiments. The universal value of G also ...
Chapter 4 - Refractometry - Index of Refraction
... If the fragments are isotropic (i.e. amorphous or isometric), they have only a single index of refraction to be measured, and orientation of the fragments is not important. If the fragments are anisotropic, however, each fragment passes two mutually perpendicular waves having different indices of re ...
... If the fragments are isotropic (i.e. amorphous or isometric), they have only a single index of refraction to be measured, and orientation of the fragments is not important. If the fragments are anisotropic, however, each fragment passes two mutually perpendicular waves having different indices of re ...
Optical Generation of the Visual Stimulus
... This can be accomplished by noting that, when the eye’s pupil is at the plane of the source image, slight movements of the head from side to side cause the target to dim uniformly. If the eye’s pupil is not at the proper distance from lens L1 then moving the head from side to side causes the target ...
... This can be accomplished by noting that, when the eye’s pupil is at the plane of the source image, slight movements of the head from side to side cause the target to dim uniformly. If the eye’s pupil is not at the proper distance from lens L1 then moving the head from side to side causes the target ...
CHAPTER 5: LIGHT
... ii) The object must be placed at a distance (more than f / same as f / less than f / between f and 2f / more than 2f) in order for the lens to act as a magnifying glass. iii) The characteristics of the image formed by a magnifying glass are yang (real / virtual) ; (inverted / upright) ; (magnified / ...
... ii) The object must be placed at a distance (more than f / same as f / less than f / between f and 2f / more than 2f) in order for the lens to act as a magnifying glass. iii) The characteristics of the image formed by a magnifying glass are yang (real / virtual) ; (inverted / upright) ; (magnified / ...
Optical, Confocal, and 4Pi Microscopy
... objective lens and holds the sample. In the center of the stage is a hole through which light passes and enters the sample. Lastly, the illumination source is below the stage and controllable through an optical device called a condenser. ...
... objective lens and holds the sample. In the center of the stage is a hole through which light passes and enters the sample. Lastly, the illumination source is below the stage and controllable through an optical device called a condenser. ...
PCT form - 1 - DESCRIPTION OPTICAL MEASURING DEVICE AND
... space-periodical concentration change by applying an electric field having a space period to a gel sample in which the particle group or particles are movably dispersed in a medium so as to form a pseudo diffraction grating; detecting diffracted light obtained by irradiating light ...
... space-periodical concentration change by applying an electric field having a space period to a gel sample in which the particle group or particles are movably dispersed in a medium so as to form a pseudo diffraction grating; detecting diffracted light obtained by irradiating light ...
Inexpensive optical tweezers for undergraduate laboratories
... In this section, detailed selection criteria for the components of the tweezers will be discussed. With other microscopes, lasers, or wavelengths, the selection criteria will remain the same, but the specific values for the required components may be different. A. Laser There are four important char ...
... In this section, detailed selection criteria for the components of the tweezers will be discussed. With other microscopes, lasers, or wavelengths, the selection criteria will remain the same, but the specific values for the required components may be different. A. Laser There are four important char ...
Advanced optics tutorials
... As a numerical example, let’s look at the case of the output from a Newport R-31005 HeNe laser focused to a spot using a Newport KPX043 plano-convex lens. This laser has a beam diameter of 0.63 mm and a divergence of 1.3 mrad. Note that these are beam diameter and full divergence, so in the notation ...
... As a numerical example, let’s look at the case of the output from a Newport R-31005 HeNe laser focused to a spot using a Newport KPX043 plano-convex lens. This laser has a beam diameter of 0.63 mm and a divergence of 1.3 mrad. Note that these are beam diameter and full divergence, so in the notation ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.