Optical bistability in a Vertical-Cavity Semiconductor Optical Amplifier
... Fig. 2 shows the nonlinear response of the VCSOA with CW input [9]. Two curves in Fig. 2 have the same initial detuning but different bias currents: one is biased at 95% of its lasing threshold and the other at 98%. Experimentally, the input power in order to achieve optical switching is reduced fro ...
... Fig. 2 shows the nonlinear response of the VCSOA with CW input [9]. Two curves in Fig. 2 have the same initial detuning but different bias currents: one is biased at 95% of its lasing threshold and the other at 98%. Experimentally, the input power in order to achieve optical switching is reduced fro ...
Observation of modulational instability in Bose
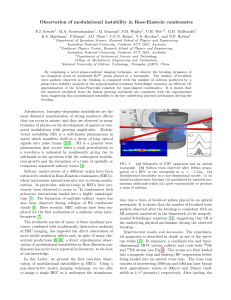
... nature of the humps observed in the experiments and represents a truly distinctive signature of a MI regime. Figure 4 displays the evolution of a simulated BEC undergoing MI, which resembles the typical evolution observed in experiments. Condensate breakup gives rise to the formation of spatial comp ...
... nature of the humps observed in the experiments and represents a truly distinctive signature of a MI regime. Figure 4 displays the evolution of a simulated BEC undergoing MI, which resembles the typical evolution observed in experiments. Condensate breakup gives rise to the formation of spatial comp ...
Image reconstruction in diffuse optical tomography based on
... µa is the absorption coefficient. Whilst these conditions are generally applicable in most soft tissue, the presence of non-scattering regions, such as the cerebrospinal fluid found within the brain, or small source-detector separation, as encountered in small animal imaging, can mean that the DA is ...
... µa is the absorption coefficient. Whilst these conditions are generally applicable in most soft tissue, the presence of non-scattering regions, such as the cerebrospinal fluid found within the brain, or small source-detector separation, as encountered in small animal imaging, can mean that the DA is ...
Pulsar scintillations from corrugated reconnection sheets in the ISM
... mani, Blandford, & Cordes (1987), mostly in the context of the so-called extreme-scattering events observed by Fiedler et al. Recently, Goldreich and Sridhar (2006) proposed that the image of the SgrA* radio-source is strongly scattered by several reconnection sheets that are closely aligned with th ...
... mani, Blandford, & Cordes (1987), mostly in the context of the so-called extreme-scattering events observed by Fiedler et al. Recently, Goldreich and Sridhar (2006) proposed that the image of the SgrA* radio-source is strongly scattered by several reconnection sheets that are closely aligned with th ...
2 Pulsed Optics
... and the sun. With such low-intensity sources the reaction of matter to light can be characterized by a set of parameters such as the index of refraction, the absorption and reflection coefficients and the orientation of the medium with respect to the polarization of the light. These parameters depend o ...
... and the sun. With such low-intensity sources the reaction of matter to light can be characterized by a set of parameters such as the index of refraction, the absorption and reflection coefficients and the orientation of the medium with respect to the polarization of the light. These parameters depend o ...
Initial demonstration of a local, evanescent, array coupled biosensor concept
... is about ∆P/P=81%. Noise in the measured intensity originates from the scattered light due to the surface roughness. The average noise level is approximately Pn=26 counts and therefore the estimated optical SNR is 55:1. This important result supports the potential application of this waveguide senso ...
... is about ∆P/P=81%. Noise in the measured intensity originates from the scattered light due to the surface roughness. The average noise level is approximately Pn=26 counts and therefore the estimated optical SNR is 55:1. This important result supports the potential application of this waveguide senso ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... (Electronics and Telecommunication, Babasaheb Gawde Institute of Technology/MSBTE, India) (Electronics and Telecommunication, Babasaheb Gawde Institute of Technology/MSBTE, India) ...
... (Electronics and Telecommunication, Babasaheb Gawde Institute of Technology/MSBTE, India) (Electronics and Telecommunication, Babasaheb Gawde Institute of Technology/MSBTE, India) ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... in the acoustical case [10, 14] which shows the relationship between the asymmetry in the scattering and the direction of the radiation force. There have been related theoretical discussions of momentum projection in optics [15] followed by a demonstration of negative optical forces in a beam closel ...
... in the acoustical case [10, 14] which shows the relationship between the asymmetry in the scattering and the direction of the radiation force. There have been related theoretical discussions of momentum projection in optics [15] followed by a demonstration of negative optical forces in a beam closel ...
Special-Effect Pigments
... involves tilting the sample panel backwards and fonvards to produce a shift. However, this tilting sirnply simulates changes from a fixed light source and does not account for color shifts produced through interference. It simply mimics the classical way of testing metallics. To allow interference s ...
... involves tilting the sample panel backwards and fonvards to produce a shift. However, this tilting sirnply simulates changes from a fixed light source and does not account for color shifts produced through interference. It simply mimics the classical way of testing metallics. To allow interference s ...
10_Lenses - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... As with mirrors, once the principal focus, (a.k.a.: focal point), has been located, three key rays passing through the lens, close to the principal axis are chosen, to locate the image: Ray 1: starts at the top of the object, (usually a solid, erect arrow), travels parallel to the principal axis and ...
... As with mirrors, once the principal focus, (a.k.a.: focal point), has been located, three key rays passing through the lens, close to the principal axis are chosen, to locate the image: Ray 1: starts at the top of the object, (usually a solid, erect arrow), travels parallel to the principal axis and ...
Influence of structural disorder on Raman scattering in amorphous
... The intensity of Raman scattering is sensitive to the degree of the structural disorder in solids, so this method can be used to measure relative fractions of the amorphous and the crystalline phases. However, there are problems in accurate estimation of such a fraction using experimental Raman spec ...
... The intensity of Raman scattering is sensitive to the degree of the structural disorder in solids, so this method can be used to measure relative fractions of the amorphous and the crystalline phases. However, there are problems in accurate estimation of such a fraction using experimental Raman spec ...
Imaging and Non-imaging System Modeling in ASAP
... final design. There are many different and sometimes industry-specific performance requirements for systems using imaging and illumination systems. The primary optical performance requirements for the LCD projector include requirements for both the imaging and illumination systems. The requirements ...
... final design. There are many different and sometimes industry-specific performance requirements for systems using imaging and illumination systems. The primary optical performance requirements for the LCD projector include requirements for both the imaging and illumination systems. The requirements ...
Shedding Light on Hybrid Optics: A Tutorial in
... Having chosen the collimating and focusing optics to use in a hybrid system, the issue becomes how to align the optics to minimize losses. The standard industry technique is to first focus the light from a device to a spot about the same size as the waveguide MFD. The waveguide is then precisely pos ...
... Having chosen the collimating and focusing optics to use in a hybrid system, the issue becomes how to align the optics to minimize losses. The standard industry technique is to first focus the light from a device to a spot about the same size as the waveguide MFD. The waveguide is then precisely pos ...
BEST OF - Edmund Optics
... the index of refraction of the coating, the thickness of the coating, and the angle of the incident light. The coating is designed so that the relative phase shift between the beam reflected at the upper and lower boundary of the thin film is 180°. Destructive interference between the two reflected ...
... the index of refraction of the coating, the thickness of the coating, and the angle of the incident light. The coating is designed so that the relative phase shift between the beam reflected at the upper and lower boundary of the thin film is 180°. Destructive interference between the two reflected ...
Optical phase measurement emphasized
... laser beam to a prism such that light is polarized at 45° with the horizontal. If we place and rotate a polarizer in the path of the beam right before the beam enters into the prism, we can reduce transmission to almost zero, which occurs when polarization axis of the polarizer makes 90° with the po ...
... laser beam to a prism such that light is polarized at 45° with the horizontal. If we place and rotate a polarizer in the path of the beam right before the beam enters into the prism, we can reduce transmission to almost zero, which occurs when polarization axis of the polarizer makes 90° with the po ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.