Chapter 1
... system takes place is known as process such as isobaric (constant pressure) process, isochoric (constant volume) process, ...
... system takes place is known as process such as isobaric (constant pressure) process, isochoric (constant volume) process, ...
Chapter 1 - All Made Easy
... system takes place is known as process such as isobaric (constant pressure) process, isochoric (constant volume) process, ...
... system takes place is known as process such as isobaric (constant pressure) process, isochoric (constant volume) process, ...
Changing Energy Energy is the ability to do work. The many forms of
... heat our homes, and still another to send TV pictures. People use large amounts of energy to help them perform work. Scientists are always looking for new energy sources. Where does energy go when it is used? Energy doesn’t actually “get used,” it turns into another form of energy! For example, when ...
... heat our homes, and still another to send TV pictures. People use large amounts of energy to help them perform work. Scientists are always looking for new energy sources. Where does energy go when it is used? Energy doesn’t actually “get used,” it turns into another form of energy! For example, when ...
17.7 Measuring mechanical energy and power
... 17.7 MEASURING MECHANICAL ENERGY AND POWER Before you continue, review Modules 14.1 to 14.4 and 16.2 which provide information about energy. Energy is defined by scientists as the capacity to do ‘work’. Anything that does work can be called a machine and a machine either transfers energy from one pl ...
... 17.7 MEASURING MECHANICAL ENERGY AND POWER Before you continue, review Modules 14.1 to 14.4 and 16.2 which provide information about energy. Energy is defined by scientists as the capacity to do ‘work’. Anything that does work can be called a machine and a machine either transfers energy from one pl ...
CHAPTER 10 INTRODUCTION TO COMPRESSIBLE FLOW
... measured by temperature, cannot affect the mechanical fields such as velocity and pressure. Energy can still shift from mechanical to thermal, via irreversible processes such as viscous dissipation, but this is determined entirely by the mechanical field4 . We must, however, determine when it is val ...
... measured by temperature, cannot affect the mechanical fields such as velocity and pressure. Energy can still shift from mechanical to thermal, via irreversible processes such as viscous dissipation, but this is determined entirely by the mechanical field4 . We must, however, determine when it is val ...
notes09
... 1.1 Mass Fraction, Mole Fraction and Average Molecular Weight. Consider the following box of “humid air” filled with a total mass, m, of a mixture of air and water vapor: ...
... 1.1 Mass Fraction, Mole Fraction and Average Molecular Weight. Consider the following box of “humid air” filled with a total mass, m, of a mixture of air and water vapor: ...
P - School of Chemical Sciences
... Every quadratic term in the Hamiltonian of a system contributes ½ kBT to the internal energy U and ½ kB to the heat capacity cv at high temperature. ...
... Every quadratic term in the Hamiltonian of a system contributes ½ kBT to the internal energy U and ½ kB to the heat capacity cv at high temperature. ...
Review of Engineering Thermodynamics - Part A
... a body could not contain any more caloric, much the same way as when a glass of water could not dissolve any more salt or sugar, the body was said to be saturated with caloric. The interpretation gives rise to the terms saturated liquid, saturated vapor, and heat flow that are still in use today.” [ ...
... a body could not contain any more caloric, much the same way as when a glass of water could not dissolve any more salt or sugar, the body was said to be saturated with caloric. The interpretation gives rise to the terms saturated liquid, saturated vapor, and heat flow that are still in use today.” [ ...
Lecture 3 - Fluid Dynamics and Balance Equations
... has been used for each reaction. • The second term on the right hand side may be neglected, if one assumes that all specific heats cpi are equal. • This assumption is very often justified since this term does not contribute as much to the change of temperature as the other terms in the equation, in ...
... has been used for each reaction. • The second term on the right hand side may be neglected, if one assumes that all specific heats cpi are equal. • This assumption is very often justified since this term does not contribute as much to the change of temperature as the other terms in the equation, in ...
The First, Second, and Third Law of Thermodynamics (ThLaws05.tex)
... The laws of thermodynamics apply to well-de…ned systems. First we will discuss a quite general form of the …rst and second law. I.e. we consider a system which is inhomogeneous, we allow mass transfer across the boundaries (open system), and we allow the boundaries to move. Fig.1 is a general repres ...
... The laws of thermodynamics apply to well-de…ned systems. First we will discuss a quite general form of the …rst and second law. I.e. we consider a system which is inhomogeneous, we allow mass transfer across the boundaries (open system), and we allow the boundaries to move. Fig.1 is a general repres ...
1. Energy - KSU Web Home
... is associated with the motion of particles. Adding heat to food increases the motion of the particles, which makes the food hot. ...
... is associated with the motion of particles. Adding heat to food increases the motion of the particles, which makes the food hot. ...
notes01
... Most real engineering systems are quite complicated and consist of many sub-systems. Each of these sub-systems (as well as the entire system) can be analyzed as either control volumes or closed systems. Choosing the appropriate system model is one of the most important tricks of the trade! Example 1 ...
... Most real engineering systems are quite complicated and consist of many sub-systems. Each of these sub-systems (as well as the entire system) can be analyzed as either control volumes or closed systems. Choosing the appropriate system model is one of the most important tricks of the trade! Example 1 ...
Fundamental Concepts, Definitions and Zeroth
... surrounding. All adiabatic systems are thermally insulated from their surroundings. Example is Thermos flask containing a liquid. 2. Homogeneous System: A system, which consists of a single phase, is termed as homogeneous system. For example, Mi×ture of air and water vapour, water plus nitric acid a ...
... surrounding. All adiabatic systems are thermally insulated from their surroundings. Example is Thermos flask containing a liquid. 2. Homogeneous System: A system, which consists of a single phase, is termed as homogeneous system. For example, Mi×ture of air and water vapour, water plus nitric acid a ...
4. Classical Thermodynamics
... than just extract heat from a hot reservoir. It also, by necessity, deposits some heat elsewhere. The energy available for work is the di↵erence between the heat extracted and the heat lost. To illustrate this, it’s very useful to consider a particular kind of reversible cycle called a Carnot engine ...
... than just extract heat from a hot reservoir. It also, by necessity, deposits some heat elsewhere. The energy available for work is the di↵erence between the heat extracted and the heat lost. To illustrate this, it’s very useful to consider a particular kind of reversible cycle called a Carnot engine ...
Different levels of reversibility
... change. For a system in a cyclical process (initial and final states the same) the change in the entropy of the system is ___________. (Fill in the blank.) In these notes we are using Q as the thermodynamic heat transfer with the sign convention that heat added to the system is positive and heat rej ...
... change. For a system in a cyclical process (initial and final states the same) the change in the entropy of the system is ___________. (Fill in the blank.) In these notes we are using Q as the thermodynamic heat transfer with the sign convention that heat added to the system is positive and heat rej ...
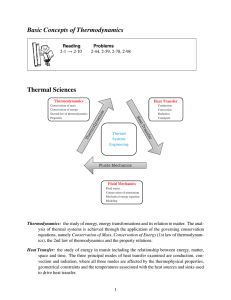
Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics Thermal Sciences
... 1. one can often find u1 and u2 in the thermodynamic tables (like those examined for the states of water). 2. we can also explicitly relate ΔU to ΔT (as a mathematical expression) by using the thermodynamic properties Cp and Cv . ...
... 1. one can often find u1 and u2 in the thermodynamic tables (like those examined for the states of water). 2. we can also explicitly relate ΔU to ΔT (as a mathematical expression) by using the thermodynamic properties Cp and Cv . ...