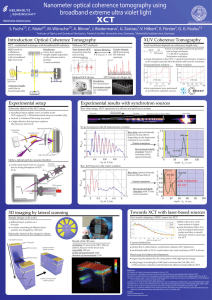
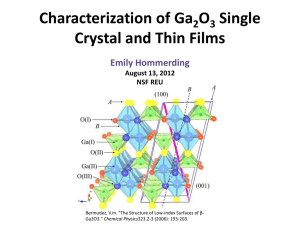
25.7 The Photon Model of Electromagnetic Waves
... bottom, shows a perfectly normal photograph of a woman. But with very faint illumination (top), the picture is not just a dim version of the properly exposed photo. Instead, it is a collection of dots. A few points on the detector have registered the presence of light, but most have not. As the illu ...
... bottom, shows a perfectly normal photograph of a woman. But with very faint illumination (top), the picture is not just a dim version of the properly exposed photo. Instead, it is a collection of dots. A few points on the detector have registered the presence of light, but most have not. As the illu ...
Chapter 5 - UniMAP Portal
... Therefore, as well as the depletion region where most of the photons are absorbed and the primary carrier pairs generated there is a high field region in which holes and electrons can acquire sufficient energy to excite new electron-hole pairs. The process is known as impact ionization and is th ...
... Therefore, as well as the depletion region where most of the photons are absorbed and the primary carrier pairs generated there is a high field region in which holes and electrons can acquire sufficient energy to excite new electron-hole pairs. The process is known as impact ionization and is th ...
Nuclear Decay
... Gamma Decay - after a nuclear reaction such as alpha or beta decay has occurred, the daughter nucleus is in high-energy, or excited state. As a result the nucleus spontaneously releases energy in the form of a gamma ray to return to a lower more stable energy state. gamma ray - a highly energetic fo ...
... Gamma Decay - after a nuclear reaction such as alpha or beta decay has occurred, the daughter nucleus is in high-energy, or excited state. As a result the nucleus spontaneously releases energy in the form of a gamma ray to return to a lower more stable energy state. gamma ray - a highly energetic fo ...
Slow Photoelectron Imaging
... Rydberg electron with the core, which implies the image only weakly depends on the M of the initial state. Hence Xe behaves like an atom with a 1 S core in this experiment, and the images can be qualitatively reproduced by a model without multichannel couplings in zero field. The full quantum calcul ...
... Rydberg electron with the core, which implies the image only weakly depends on the M of the initial state. Hence Xe behaves like an atom with a 1 S core in this experiment, and the images can be qualitatively reproduced by a model without multichannel couplings in zero field. The full quantum calcul ...
CHM111 Lab – Atomic Emission Spectroscopy – Grading Rubric
... Atomic emission spectra can be thought of as atomic fingerprints. ...
... Atomic emission spectra can be thought of as atomic fingerprints. ...
Topic 6 Radioactivity Core Questions
... A few mm of a metal like aluminium What stops gamma rays? A few cm of a dense metal like lead will significantly reduce the amount of gamma rays getting through. What is meant by background Radiation that is around us all the time. radiation? Why are there regional variations in the 50% of the backg ...
... A few mm of a metal like aluminium What stops gamma rays? A few cm of a dense metal like lead will significantly reduce the amount of gamma rays getting through. What is meant by background Radiation that is around us all the time. radiation? Why are there regional variations in the 50% of the backg ...
File
... are too many protons in a nucleus. In this case the element will emit radiation in the form of positively charged particles called alpha particles. Alpha particles are considered not dangerous as it can be stopped by a sheet of paper Beta decay - Beta decay is caused when there are too many neutrons ...
... are too many protons in a nucleus. In this case the element will emit radiation in the form of positively charged particles called alpha particles. Alpha particles are considered not dangerous as it can be stopped by a sheet of paper Beta decay - Beta decay is caused when there are too many neutrons ...
Chapter 29: Nuclear Physics
... Gamma rays were determined to be high energy photons. A gamma ray will be emitted when a nucleus is an excited state when making a transition to a lower energy level. For example, ...
... Gamma rays were determined to be high energy photons. A gamma ray will be emitted when a nucleus is an excited state when making a transition to a lower energy level. For example, ...
Gamma spectroscopy

Gamma-ray spectroscopy is the quantitative study of the energy spectra of gamma-ray sources, in such as the nuclear industry, geochemical investigation, and astrophysics. Most radioactive sources produce gamma rays, which are of various energies and intensities. When these emissions are detected and analyzed with a spectroscopy system, a gamma-ray energy spectrum can be produced. A detailed analysis of this spectrum is typically used to determine the identity and quantity of gamma emitters present in a gamma source, and is a vital tool in radiometric assay. The gamma spectrum is characteristic of the gamma-emitting nuclides contained in the source, just as in optical spectroscopy, the optical spectrum is characteristic of the material contained in a sample.