a pedagogical / historical introduction (D. Downes)
... Regard the interferometer as a tuned, (phaselocked) resonant cavity, that allows travelingwave modes. A 1- photon excitation of a mode is distrubuted over the entire interferometer, including the two internal paths. ...
... Regard the interferometer as a tuned, (phaselocked) resonant cavity, that allows travelingwave modes. A 1- photon excitation of a mode is distrubuted over the entire interferometer, including the two internal paths. ...
Geant4: Electromagnetic Processes 1
... Geant4 Lowenergy package provide a possibility to apply toolkit to variety of applications for which atomic shell structure is essential Optical photons generation and tracking can be simulated inside the same geometry Geant4 ...
... Geant4 Lowenergy package provide a possibility to apply toolkit to variety of applications for which atomic shell structure is essential Optical photons generation and tracking can be simulated inside the same geometry Geant4 ...
Spectroscopic methods for biology and medicine
... Biological samples contain large numbers of different compounds in concentrations ranging from single molecules to millimolar concentrations. We therefore have to consider the sensitivity of spectroscopic methods (i.e. the ability to detect small quantities of a compound) and the selectivity (i.e. t ...
... Biological samples contain large numbers of different compounds in concentrations ranging from single molecules to millimolar concentrations. We therefore have to consider the sensitivity of spectroscopic methods (i.e. the ability to detect small quantities of a compound) and the selectivity (i.e. t ...
25.1 Nuclear Radiation
... of Becquerel’s associates were Marie Curie (1867–1934) and Pierre Curie (1859–1906). The Curies were able to show that rays emitted by the uranium atoms caused the fogging of the plates. Marie Curie named the process by which materials give off such rays radioactivity. The penetrating rays and parti ...
... of Becquerel’s associates were Marie Curie (1867–1934) and Pierre Curie (1859–1906). The Curies were able to show that rays emitted by the uranium atoms caused the fogging of the plates. Marie Curie named the process by which materials give off such rays radioactivity. The penetrating rays and parti ...
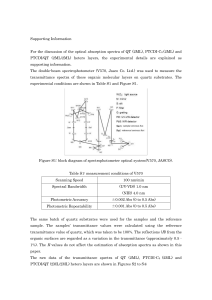
Supporting Information For the discussion of the optical absorption
... In contrast, the HOMO level is located around 5.9 eV, estimated by UPS measurements carried out by the authors [Figure S6] and Forker [18]. This result indicates that the ex-situ measurement reveals the QT HOMO level drops to a lower level or the optical band-gap expands after exposure to air. In an ...
... In contrast, the HOMO level is located around 5.9 eV, estimated by UPS measurements carried out by the authors [Figure S6] and Forker [18]. This result indicates that the ex-situ measurement reveals the QT HOMO level drops to a lower level or the optical band-gap expands after exposure to air. In an ...
Introduction to Radiation Physics, Quantities and Units
... • EM radiation is a pair of perpendicular, timevarying electric and magnetic fields traveling through space with the velocity of light (c). • The distance between maxima of the EM fields is the wavelength (λ). • The frequency (ν) of the wave is given by: ...
... • EM radiation is a pair of perpendicular, timevarying electric and magnetic fields traveling through space with the velocity of light (c). • The distance between maxima of the EM fields is the wavelength (λ). • The frequency (ν) of the wave is given by: ...
Silicon Detectors - Basic Concepts I
... If the energy required for excitation Ex is much smaller than required for ionization E i , sufficient degrees of freedom will exist for some combination of ionization and excitation processes to dissipate precisely the total energy. Hence, for a given energy deposited in the sample a fluctuation in ...
... If the energy required for excitation Ex is much smaller than required for ionization E i , sufficient degrees of freedom will exist for some combination of ionization and excitation processes to dissipate precisely the total energy. Hence, for a given energy deposited in the sample a fluctuation in ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... Go down two on periodic table Atomic number decreases by 2 Mass number decreases by 4 Beta: Go up one on periodic table Atomic number increases by 1 Mass number stays the same ...
... Go down two on periodic table Atomic number decreases by 2 Mass number decreases by 4 Beta: Go up one on periodic table Atomic number increases by 1 Mass number stays the same ...
anal chem II / IR spectrometry
... in a mull as well for comparison purposes. In addition, KBr is quite hygroscopic and the spectra obtained are difficult to ...
... in a mull as well for comparison purposes. In addition, KBr is quite hygroscopic and the spectra obtained are difficult to ...
Document
... • We apply following tests: Measurement of the surface resistance of cathode after the ...
... • We apply following tests: Measurement of the surface resistance of cathode after the ...
Gamma spectroscopy

Gamma-ray spectroscopy is the quantitative study of the energy spectra of gamma-ray sources, in such as the nuclear industry, geochemical investigation, and astrophysics. Most radioactive sources produce gamma rays, which are of various energies and intensities. When these emissions are detected and analyzed with a spectroscopy system, a gamma-ray energy spectrum can be produced. A detailed analysis of this spectrum is typically used to determine the identity and quantity of gamma emitters present in a gamma source, and is a vital tool in radiometric assay. The gamma spectrum is characteristic of the gamma-emitting nuclides contained in the source, just as in optical spectroscopy, the optical spectrum is characteristic of the material contained in a sample.