Removal of trapped charge in selenium detectors
... understand this material, many of its electrical and imaging properties are still not completely understood. With the absorption of an energetic x-ray photon (mostly via the photoelectric effect), electron-hole pairs (ehp’s) are generated. For x-ray energy in the medical imaging range, (less than 15 ...
... understand this material, many of its electrical and imaging properties are still not completely understood. With the absorption of an energetic x-ray photon (mostly via the photoelectric effect), electron-hole pairs (ehp’s) are generated. For x-ray energy in the medical imaging range, (less than 15 ...
Document
... Why not 3N-6/3N-5 bands in IR spectrum? • The theoretical number of fundamental vibrations (absorption frequencies) will seldom be observed –> overtones (multiples of a given frequency), combination (sum of two other vibrations) or difference (the difference of two other vibrations) tones increase ...
... Why not 3N-6/3N-5 bands in IR spectrum? • The theoretical number of fundamental vibrations (absorption frequencies) will seldom be observed –> overtones (multiples of a given frequency), combination (sum of two other vibrations) or difference (the difference of two other vibrations) tones increase ...
31.1 Nuclear Structure
... remaining vs. number of tosses would result in an exponential graph, like the one on the right. Tossing a single coin is a random process, but doing so repeatedly shows a definite pattern. Radioactive decay shows this same pattern. ...
... remaining vs. number of tosses would result in an exponential graph, like the one on the right. Tossing a single coin is a random process, but doing so repeatedly shows a definite pattern. Radioactive decay shows this same pattern. ...
fulltext ver 2
... for neutron spallation sources that require higher resolution and larger sensors. In this thesis a novel material and clean room compatible process for neutron conversion are discussed. Simulations and fabrication have been executed and analysed in measurements. It has been proven that such a device ...
... for neutron spallation sources that require higher resolution and larger sensors. In this thesis a novel material and clean room compatible process for neutron conversion are discussed. Simulations and fabrication have been executed and analysed in measurements. It has been proven that such a device ...
introduction - Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource
... Table 9.0.4 summarizes the possible materials that can be used, if there is no FEL radiation attenuation. In Hall B the increased spot size reduced the energy density by a factor ~15, and more standard materials are possible at all photon energies. For example, W, M and Au have doses < 0.3 eV/atom f ...
... Table 9.0.4 summarizes the possible materials that can be used, if there is no FEL radiation attenuation. In Hall B the increased spot size reduced the energy density by a factor ~15, and more standard materials are possible at all photon energies. For example, W, M and Au have doses < 0.3 eV/atom f ...
Single-shot Detection of Wavepacket Evolution
... A second application of the imaging detector is the direct observation of wave packet momentum evolution using impulsive momentum retrieval.[8] As in the previ ously described experiment, Ca atoms are excited to the 4s4p intermediate state to facilitate the creation of a 4snd wavepacket using a 500 ...
... A second application of the imaging detector is the direct observation of wave packet momentum evolution using impulsive momentum retrieval.[8] As in the previ ously described experiment, Ca atoms are excited to the 4s4p intermediate state to facilitate the creation of a 4snd wavepacket using a 500 ...
Unit 2: The Atom
... •Alpha decay is how elements greater than atomic #83 try to become stable. •They will emit an alpha particle (2 neutrons and 2 protons) to try to become stable. •Alpha reactions will always have He on the right side! •To balance: write the upper and lower equations! ...
... •Alpha decay is how elements greater than atomic #83 try to become stable. •They will emit an alpha particle (2 neutrons and 2 protons) to try to become stable. •Alpha reactions will always have He on the right side! •To balance: write the upper and lower equations! ...
A lightning discharge producing a beam of
... presented here. The fourteen scintillation detectors of GBM provide full‐sky coverage between ∼8 keV and ∼40 MeV. Observations of TGFs with the GBM instrument are reported by Briggs et al. [2010]. [13] Fermi follows a nearly circular orbit at an altitude of ∼560 km and an inclination of 25.6°. Data ...
... presented here. The fourteen scintillation detectors of GBM provide full‐sky coverage between ∼8 keV and ∼40 MeV. Observations of TGFs with the GBM instrument are reported by Briggs et al. [2010]. [13] Fermi follows a nearly circular orbit at an altitude of ∼560 km and an inclination of 25.6°. Data ...
Decay Mechanisms - High Energy Physics Research at Minnesota
... matter and then combine with an atomic electron in the material (making ‘positroniuim’). The positron-electron pair then annihilates, giving rise to two photons, each having energy 0.511 MeV and travelling in opposite directions. This phenomenon (which we’ll investigate in more detail later in the c ...
... matter and then combine with an atomic electron in the material (making ‘positroniuim’). The positron-electron pair then annihilates, giving rise to two photons, each having energy 0.511 MeV and travelling in opposite directions. This phenomenon (which we’ll investigate in more detail later in the c ...
Infrared Spectroscopy_03
... Why not 3N-6/3N-5 bands in IR spectrum? • The theoretical number of fundamental vibrations (absorption frequencies) will seldom be observed –> overtones (multiples of a given frequency), combination (sum of two other vibrations) or difference (the difference of two other vibrations) tones increase ...
... Why not 3N-6/3N-5 bands in IR spectrum? • The theoretical number of fundamental vibrations (absorption frequencies) will seldom be observed –> overtones (multiples of a given frequency), combination (sum of two other vibrations) or difference (the difference of two other vibrations) tones increase ...
Chapter 2
... Energy loss by heavy particles A massive particle that collides with an electron loses relatively small quantity of energy at each collision. For example, a slow alpha particle hitting an electron transfers a maximum of only 0.05% of its energy to the electron. Since head-on collisions are rare, usu ...
... Energy loss by heavy particles A massive particle that collides with an electron loses relatively small quantity of energy at each collision. For example, a slow alpha particle hitting an electron transfers a maximum of only 0.05% of its energy to the electron. Since head-on collisions are rare, usu ...
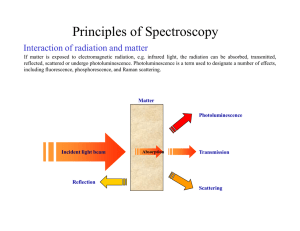
Principles of Spectroscopy
... Origin of the interferogram Spectrometers are equipped with a broadband light source, which yields a continuous, infinite number, of wavelengths, as shown in the figure on the left. The interferogram is the continuous sum, i.e. the integral, of all the interference patterns produced by each wavelen ...
... Origin of the interferogram Spectrometers are equipped with a broadband light source, which yields a continuous, infinite number, of wavelengths, as shown in the figure on the left. The interferogram is the continuous sum, i.e. the integral, of all the interference patterns produced by each wavelen ...
ppt
... Signature for particle/hole pairs Evidence for n>1 shell formation ? Implications for the fidelity of entanglement schemes in a lattice ...
... Signature for particle/hole pairs Evidence for n>1 shell formation ? Implications for the fidelity of entanglement schemes in a lattice ...
Gamma spectroscopy

Gamma-ray spectroscopy is the quantitative study of the energy spectra of gamma-ray sources, in such as the nuclear industry, geochemical investigation, and astrophysics. Most radioactive sources produce gamma rays, which are of various energies and intensities. When these emissions are detected and analyzed with a spectroscopy system, a gamma-ray energy spectrum can be produced. A detailed analysis of this spectrum is typically used to determine the identity and quantity of gamma emitters present in a gamma source, and is a vital tool in radiometric assay. The gamma spectrum is characteristic of the gamma-emitting nuclides contained in the source, just as in optical spectroscopy, the optical spectrum is characteristic of the material contained in a sample.