Absorption and Biological Effects of Ionising Radiation
... genetic, and thermodynamic terms. Of these, the thermodynamics seems to be less complicated than the rest, at least from the scientific point of view. The second law of thermodynamics states, that in a closed system, no process can occur, which will result in increase of the net order (that is in de ...
... genetic, and thermodynamic terms. Of these, the thermodynamics seems to be less complicated than the rest, at least from the scientific point of view. The second law of thermodynamics states, that in a closed system, no process can occur, which will result in increase of the net order (that is in de ...
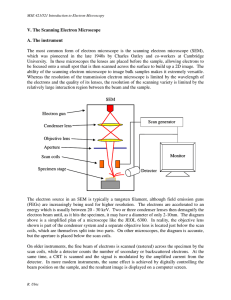
V. The Scanning Electron Microscope A. The instrument The most
... 2. Backscatter electron (BEI) detectors Bakcscattered electrons travelling in the appropriate direction will also hit the Everhart-Thornely detector and contribute to the secondary electron image; therefore, the secondary electron signal always contains some backscattered component as well. If the s ...
... 2. Backscatter electron (BEI) detectors Bakcscattered electrons travelling in the appropriate direction will also hit the Everhart-Thornely detector and contribute to the secondary electron image; therefore, the secondary electron signal always contains some backscattered component as well. If the s ...
Reflection of a Ray of Light Introduction: Purpose
... A "beam" of light is a collection of parallel rays. This activity requires a single ray of light but the ray box used allows too many rays to pass through the slit. The said ray cannot even be called a beam because often, these rays aren't parallel. So, when doing this activity, realize that ...
... A "beam" of light is a collection of parallel rays. This activity requires a single ray of light but the ray box used allows too many rays to pass through the slit. The said ray cannot even be called a beam because often, these rays aren't parallel. So, when doing this activity, realize that ...
G. Hall
... detectors which have been exploited for other particle physics applications, for example as scintillation light detectors, where miniaturization of the detectors has been another attraclive feature, as well as the wide spectral sensitivity. It has encouraged innovative individuals to produce novel a ...
... detectors which have been exploited for other particle physics applications, for example as scintillation light detectors, where miniaturization of the detectors has been another attraclive feature, as well as the wide spectral sensitivity. It has encouraged innovative individuals to produce novel a ...
Nonlinear Optical Methods to Study Condensed Phase
... information is often hidden behind a mask of spectral broadening resulting from these influences, and this makes linear spectroscopy (i.e. absorption spectra) of limited value for the study of condensed phase chemical and biological dynamics. ...
... information is often hidden behind a mask of spectral broadening resulting from these influences, and this makes linear spectroscopy (i.e. absorption spectra) of limited value for the study of condensed phase chemical and biological dynamics. ...
Perrot_1_ID15
... treatments to Silicon detector is a classical spectrometry electronic. We can study energy losses in CAVIAR and detected in the Silicon detector. Figure 6 present the energy spectra measured with the Silicon detector for CAVIAR off line, in line with and without gaz. We can observe that lose a ...
... treatments to Silicon detector is a classical spectrometry electronic. We can study energy losses in CAVIAR and detected in the Silicon detector. Figure 6 present the energy spectra measured with the Silicon detector for CAVIAR off line, in line with and without gaz. We can observe that lose a ...
HT-7上逃逸电子行为的研究进展
... make these interesting measurements, then since you have LHCD on HT-7, you might also consider measuring the runaway probability function by varying the rf phase velocity. To my knowledge, such a direct measurement has not yet been done, though much of the physics has been inferred from current (mag ...
... make these interesting measurements, then since you have LHCD on HT-7, you might also consider measuring the runaway probability function by varying the rf phase velocity. To my knowledge, such a direct measurement has not yet been done, though much of the physics has been inferred from current (mag ...
Discovery
... It is a great pleasure to write the foreword for this issue of Discovery highlighting the work of the national nuclear security field at AWE. The role of AWE and its technical experts to protect the UK is as important now as it has ever been. We have outstanding and internationally recognised scient ...
... It is a great pleasure to write the foreword for this issue of Discovery highlighting the work of the national nuclear security field at AWE. The role of AWE and its technical experts to protect the UK is as important now as it has ever been. We have outstanding and internationally recognised scient ...
Physics Research A
... Fig. 2(b). An application of mirrors (Fig. 2(c)) improves again somewhat the detected photon number but increases also the costs and causes additional complexity. Therefore, the detector geometry from Fig. 2(b), described in Section 2, was decided to be optimal for our purpose. An example of the sim ...
... Fig. 2(b). An application of mirrors (Fig. 2(c)) improves again somewhat the detected photon number but increases also the costs and causes additional complexity. Therefore, the detector geometry from Fig. 2(b), described in Section 2, was decided to be optimal for our purpose. An example of the sim ...
Chapter 7- Components of Optical Instruments
... ChemiluminescenceChemiluminescence occurs after excitation of a molecule or ion by the energy emitted during the chemical or biochemical reaction in which the excited species is a product. In many cases, the chemical excited energy level of a molecule is identical to the energy level that could be a ...
... ChemiluminescenceChemiluminescence occurs after excitation of a molecule or ion by the energy emitted during the chemical or biochemical reaction in which the excited species is a product. In many cases, the chemical excited energy level of a molecule is identical to the energy level that could be a ...
Gamma spectroscopy

Gamma-ray spectroscopy is the quantitative study of the energy spectra of gamma-ray sources, in such as the nuclear industry, geochemical investigation, and astrophysics. Most radioactive sources produce gamma rays, which are of various energies and intensities. When these emissions are detected and analyzed with a spectroscopy system, a gamma-ray energy spectrum can be produced. A detailed analysis of this spectrum is typically used to determine the identity and quantity of gamma emitters present in a gamma source, and is a vital tool in radiometric assay. The gamma spectrum is characteristic of the gamma-emitting nuclides contained in the source, just as in optical spectroscopy, the optical spectrum is characteristic of the material contained in a sample.