Catalytic decomposition of N2O over Rh/Zn–Al2O3 catalysts
... lead to more active catalysts due to the improved dispersion of Rh species.28 Parres-Esclapez et al. found that Sr can promote the activity of Rh/Al2O3 due to the improved dispersion and reducibility of Rh species.29 Zhao et al. reported that Rh/SiO2–Al2O3 shows high activity, because oxygen desorpt ...
... lead to more active catalysts due to the improved dispersion of Rh species.28 Parres-Esclapez et al. found that Sr can promote the activity of Rh/Al2O3 due to the improved dispersion and reducibility of Rh species.29 Zhao et al. reported that Rh/SiO2–Al2O3 shows high activity, because oxygen desorpt ...
СУМСЬКИЙ ДЕРЖАВНИЙ УНІВЕРСИТЕТ
... Review the definition of an acid (page 4). Hydrogen atoms in the acid molecules can be replaced by the metal atoms, as a result the salts are formed: Replacement of H atoms ...
... Review the definition of an acid (page 4). Hydrogen atoms in the acid molecules can be replaced by the metal atoms, as a result the salts are formed: Replacement of H atoms ...
Solutions for Chapter 8 End-of-Chapter Problems
... dripping on the outside of the cone, onto your hands, and possibly onto your clothes as well. (b) Students entering a classroom with fixed seating are about to undergo an increase in organization. The chairs are permanently arranged so that a specified order will be maintained. (c) A shrub forming s ...
... dripping on the outside of the cone, onto your hands, and possibly onto your clothes as well. (b) Students entering a classroom with fixed seating are about to undergo an increase in organization. The chairs are permanently arranged so that a specified order will be maintained. (c) A shrub forming s ...
Chemistry 134 Problem Set Introduction
... 14.38 (a) What is the difference between a sapphire and a ruby? (b) Why might aluminum be present with silicon in many minerals? 14.39 (a) List the stable oxidation states for each member of the boron family. (b) For any element that may have more than one stable oxidation state, identify the more s ...
... 14.38 (a) What is the difference between a sapphire and a ruby? (b) Why might aluminum be present with silicon in many minerals? 14.39 (a) List the stable oxidation states for each member of the boron family. (b) For any element that may have more than one stable oxidation state, identify the more s ...
The Process of Chemical Reactions
... Thus, as the reaction begins, an input of energy is necessary to produce the activated complex; as the reaction proceeds, and the system shifts from the activated complex to products, energy is released. In a chemical reaction, the minimum energy necessary for reaching the activated complex and proc ...
... Thus, as the reaction begins, an input of energy is necessary to produce the activated complex; as the reaction proceeds, and the system shifts from the activated complex to products, energy is released. In a chemical reaction, the minimum energy necessary for reaching the activated complex and proc ...
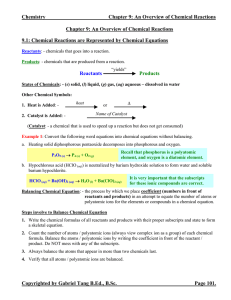
Chapter 09 An Overview of Chemical Reactions Notes
... Precipitation Reaction: - a reaction where a precipitate (new solid) is formed as a product. Neutralization Reaction: - a reaction between an acid and a base where water is formed as a product. To Predict Products and Balance Chemical Equations: 1. Write the correct chemical formulas for all product ...
... Precipitation Reaction: - a reaction where a precipitate (new solid) is formed as a product. Neutralization Reaction: - a reaction between an acid and a base where water is formed as a product. To Predict Products and Balance Chemical Equations: 1. Write the correct chemical formulas for all product ...
Chemistry II - Mr. Dougan`s Wonderful World of Chemistry
... physical changes. The flow of energy in a chemical reaction can be traced by allowing a measured amount of a chemical to react with another while the temperature of the reaction is monitored. As the reaction progresses, the rise or fall of temperature of the reacting mixture and the immediate enviro ...
... physical changes. The flow of energy in a chemical reaction can be traced by allowing a measured amount of a chemical to react with another while the temperature of the reaction is monitored. As the reaction progresses, the rise or fall of temperature of the reacting mixture and the immediate enviro ...
The Process of Chemical Reactions
... Thus, as the reaction begins, an input of energy is necessary to produce the activated complex; as the reaction proceeds, and the system shifts from the activated complex to products, energy is released. In a chemical reaction, the minimum energy necessary for reaching the activated complex and proc ...
... Thus, as the reaction begins, an input of energy is necessary to produce the activated complex; as the reaction proceeds, and the system shifts from the activated complex to products, energy is released. In a chemical reaction, the minimum energy necessary for reaching the activated complex and proc ...
Thermal Decomposition of Polymers - Marcelo Hirschler
... achieve a viscous state since they begin undergoing thermal decomposition before the polymer melts. Some typical glass transition temperatures are given in Table 1-7.1. As this type of physical transformation is less well defined than a phase transformation, it is known as a second order transition. ...
... achieve a viscous state since they begin undergoing thermal decomposition before the polymer melts. Some typical glass transition temperatures are given in Table 1-7.1. As this type of physical transformation is less well defined than a phase transformation, it is known as a second order transition. ...
Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Notice that in Interactive Figure 4.2.1 the water molecules orient themselves so that the oxygen atoms are near the Na+ cations and the hydrogen atoms are near the Cl− anions. This is due to the polar nature of water, a result of uneven electron distribution in water molecules. ( Flashforward to Se ...
... Notice that in Interactive Figure 4.2.1 the water molecules orient themselves so that the oxygen atoms are near the Na+ cations and the hydrogen atoms are near the Cl− anions. This is due to the polar nature of water, a result of uneven electron distribution in water molecules. ( Flashforward to Se ...
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Chemical Reactions
... and products in our equation. The balanced chemical equation tells what is happening on the molecular level, but it also tells what is happening on the “real world” level, through the use of gram ...
... and products in our equation. The balanced chemical equation tells what is happening on the molecular level, but it also tells what is happening on the “real world” level, through the use of gram ...
Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry
... Combustion analysis (which we saw in the previous chapter) employs a chemical reaction, a process in which one or more substances are converted into one or more different ones. Compounds form and change through chemical reactions. Water can be made by the reaction of hydrogen with oxygen. A combusti ...
... Combustion analysis (which we saw in the previous chapter) employs a chemical reaction, a process in which one or more substances are converted into one or more different ones. Compounds form and change through chemical reactions. Water can be made by the reaction of hydrogen with oxygen. A combusti ...
CHEM 1411 – STUDY-GUIDE-for-TEST-2
... 56. During volcanic eruptions, hydrogen sulfide gas is given off and oxidized by air according to the following chemical equation: 2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) 2SO2(g) + 2H2O(g) Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the above reaction given: 3S(s) + 2H2O(g) 2H2S(g) + SO2(g) H° = 146.9 kJ/mol S(s) + O2 ...
... 56. During volcanic eruptions, hydrogen sulfide gas is given off and oxidized by air according to the following chemical equation: 2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) 2SO2(g) + 2H2O(g) Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the above reaction given: 3S(s) + 2H2O(g) 2H2S(g) + SO2(g) H° = 146.9 kJ/mol S(s) + O2 ...
4 Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... However, before we can understand solution reactions, we need to discuss the nature of solutions in which water is the dissolving medium, or solvent. These solutions are called aqueous solutions. In this chapter we will study the nature of materials after they are dissolved in water and various type ...
... However, before we can understand solution reactions, we need to discuss the nature of solutions in which water is the dissolving medium, or solvent. These solutions are called aqueous solutions. In this chapter we will study the nature of materials after they are dissolved in water and various type ...
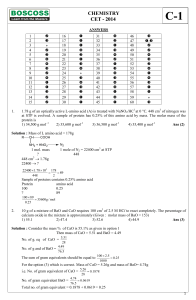
CHEMISTRY CET
... 'Z' is slowly passed into an aqueous solution of Y, colloidal sulphur is obtained. X and Z could be, respectively 1) Na2SO4, H2S 2) Na2SO4, SO2 3) Na2S, SO3 4) Na2SO3, H2S Ans (4) ...
... 'Z' is slowly passed into an aqueous solution of Y, colloidal sulphur is obtained. X and Z could be, respectively 1) Na2SO4, H2S 2) Na2SO4, SO2 3) Na2S, SO3 4) Na2SO3, H2S Ans (4) ...
Supplementary Exercise 1B Topic 5
... For the first two chemical cells, metal W is the positive electrode while metals X and Y are the negative electrodes. Therefore metals X and Y form ions more readily than metal W. The Y/W couple gives a higher voltage than the X/W couple. Therefore the difference in the tendency to form ions between ...
... For the first two chemical cells, metal W is the positive electrode while metals X and Y are the negative electrodes. Therefore metals X and Y form ions more readily than metal W. The Y/W couple gives a higher voltage than the X/W couple. Therefore the difference in the tendency to form ions between ...
Cyclam ``capa` POT.4` to ``capa` POT.3` denticity change
... or carboxy functional groups. These groups are versatile linkers because they can form amide bonds with a desired material or relevant biomolecules such as proteins or antibodies. Whereas complex-modified solid materials may lead, for example, to sensors with potential analytical applications, the a ...
... or carboxy functional groups. These groups are versatile linkers because they can form amide bonds with a desired material or relevant biomolecules such as proteins or antibodies. Whereas complex-modified solid materials may lead, for example, to sensors with potential analytical applications, the a ...
Solubility and Reactions
... occur between the cleaning chemicals and the dirty deposit, whereas a pure gas or solid would not react well with a solid. Thirdly, the manufacturer can control the rate of the reaction (and thus the safety) by choosing the ideal concentration of the cleaning solution. Having the chemical in solutio ...
... occur between the cleaning chemicals and the dirty deposit, whereas a pure gas or solid would not react well with a solid. Thirdly, the manufacturer can control the rate of the reaction (and thus the safety) by choosing the ideal concentration of the cleaning solution. Having the chemical in solutio ...
Here
... Covalent forces hold the carbon and hydrogen atoms together within a methane molecule. Weak dispersion forces – a type of intermolecular or non‐bonding force – hold neighboring methane molecules together The CFCs do not have H atoms bonded to C. Such H atoms readily react with hydroxyl radicals. ...
... Covalent forces hold the carbon and hydrogen atoms together within a methane molecule. Weak dispersion forces – a type of intermolecular or non‐bonding force – hold neighboring methane molecules together The CFCs do not have H atoms bonded to C. Such H atoms readily react with hydroxyl radicals. ...
EFFECT OF LEWIS ACID IN TiCl4/MgCl2/THF/AlCl3 CATALYST
... The total element content in catalysts such as Ti, Mg, Ca, Fe, Zn and Al upon various mixed metal chlorides is listed in Table 2. The external surface compositions of all catalyst also were approximated by EDX technique, as shown in Table 2. The results showed that None-Al exhibited the highest of T ...
... The total element content in catalysts such as Ti, Mg, Ca, Fe, Zn and Al upon various mixed metal chlorides is listed in Table 2. The external surface compositions of all catalyst also were approximated by EDX technique, as shown in Table 2. The results showed that None-Al exhibited the highest of T ...
File - Junior College Chemistry tuition
... Electrophoresis is a technique of separating and identifying amino acids. A solution of amino acids is absorbed into the paper that is moistened with a buffer solution and stretched between two electrodes. Positively charged species move towards the cathode, negatively charged towards the anode. At ...
... Electrophoresis is a technique of separating and identifying amino acids. A solution of amino acids is absorbed into the paper that is moistened with a buffer solution and stretched between two electrodes. Positively charged species move towards the cathode, negatively charged towards the anode. At ...
DOE Chemistry 1
... for use by DOE category A reactors. The subject areas, subject matter content, and level of detail of the Reactor Operator Fundamentals Manuals were determined from several sources. DOE Category A reactor training managers determined which materials should be included, and served as a primary refere ...
... for use by DOE category A reactors. The subject areas, subject matter content, and level of detail of the Reactor Operator Fundamentals Manuals were determined from several sources. DOE Category A reactor training managers determined which materials should be included, and served as a primary refere ...
Water splitting

Water splitting is the general term for a chemical reaction in which water is separated into oxygen and hydrogen. Efficient and economical water splitting would be a key technology component of a hydrogen economy. Various techniques for water splitting have been issued in water splitting patents in the United States. In photosynthesis, water splitting donates electrons to power the electron transport chain in photosystem II.