Physics for Scientists & Geometric Optics
... ! We can further abstract these traveling planes by vectors or arrows perpendicular to the surface of these planes ...
... ! We can further abstract these traveling planes by vectors or arrows perpendicular to the surface of these planes ...
L4 INTERFERENCE
... source can normally be described as a superposition of a vast number of elementary waves, which have a continuous range of frequencies and wavelengths. These elementary waves can be related to photons emitted by atoms or molecules in the light source. Although each elementary wave has a fairly well- ...
... source can normally be described as a superposition of a vast number of elementary waves, which have a continuous range of frequencies and wavelengths. These elementary waves can be related to photons emitted by atoms or molecules in the light source. Although each elementary wave has a fairly well- ...
CHAPTER 3 Optical Components of Spectrometers
... normal to the interface, the reflectance () is given by Fresnel equation • The larger the difference in refractive indices, the larger the reflectance. • When 1 = 2, there is no reflection. • For an air-glass interface, where air = 1 and glass = 1.5, approximately 4% of the light incident pe ...
... normal to the interface, the reflectance () is given by Fresnel equation • The larger the difference in refractive indices, the larger the reflectance. • When 1 = 2, there is no reflection. • For an air-glass interface, where air = 1 and glass = 1.5, approximately 4% of the light incident pe ...
Chapter 7 Optical lattices and experiment design
... Lattices more exotic than the 1D standing wave can be created by the interference of multiple laser beams, see [161] for the crystallography of optical lattices. A N -dimensional lattice requires a minimum of N + 1 laser beams. One problem with the topography of lattices is that they can be changed ...
... Lattices more exotic than the 1D standing wave can be created by the interference of multiple laser beams, see [161] for the crystallography of optical lattices. A N -dimensional lattice requires a minimum of N + 1 laser beams. One problem with the topography of lattices is that they can be changed ...
Imaging and Measurement of Thermal Lensing in Glass
... and a photon of energy equal to the energy difference between the excited and the lower state hits the atom, then there is a probability that it will stimulate the emission of a photon of equal frequency, phase, and direction. There are two other process which we must look at. The first is spontane ...
... and a photon of energy equal to the energy difference between the excited and the lower state hits the atom, then there is a probability that it will stimulate the emission of a photon of equal frequency, phase, and direction. There are two other process which we must look at. The first is spontane ...
U-direction
... image produced by special light sensitive detectors, and employs rule-based knowledge about the light intensity profile of typical stars in order to identify the true stars and filter out other objects. Forward chaining is used initially to scan the light intensity in a given image searching for pix ...
... image produced by special light sensitive detectors, and employs rule-based knowledge about the light intensity profile of typical stars in order to identify the true stars and filter out other objects. Forward chaining is used initially to scan the light intensity in a given image searching for pix ...
Chapter 2 Optical fibers
... Optical fiber losses have been reduced from about 1000 dB/km before 1970, to around 20 dB/km in 1970, and 0.2 dB/km at 1.55-µm region in 1979. ...
... Optical fiber losses have been reduced from about 1000 dB/km before 1970, to around 20 dB/km in 1970, and 0.2 dB/km at 1.55-µm region in 1979. ...
The Basic Idea
... oscillation is to stretch and compress space along axes perpendicular to one another and to the direction of propagation of the waves. Typical modes of oscillation are shown in Figure 3.3. The two fundamental polarization modes for gravitational waves are depicted. In this perspective, the waves app ...
... oscillation is to stretch and compress space along axes perpendicular to one another and to the direction of propagation of the waves. Typical modes of oscillation are shown in Figure 3.3. The two fundamental polarization modes for gravitational waves are depicted. In this perspective, the waves app ...
Optical Studies of Materials for Spectral Design Christina ˚ Akerlind
... for lightness (L*), degree of red or green (+/-a*) and degree of yellow or blue(+/b*), respectively. The human eye has receptors for only red, green and blue color. By superposition of the signals from the three receptors almost any color can be perceived. An example is white light that is a combina ...
... for lightness (L*), degree of red or green (+/-a*) and degree of yellow or blue(+/b*), respectively. The human eye has receptors for only red, green and blue color. By superposition of the signals from the three receptors almost any color can be perceived. An example is white light that is a combina ...
Chapter2 Interaction Characteristics of Light
... If the light rays enter from optically denser medium to optically rare medium, it will move away from the normal. If the angle of incidence is increased so that the angle of refraction becomes 900 . The phenomena known as total internal reflection will occur ,if angle of incidence is further increas ...
... If the light rays enter from optically denser medium to optically rare medium, it will move away from the normal. If the angle of incidence is increased so that the angle of refraction becomes 900 . The phenomena known as total internal reflection will occur ,if angle of incidence is further increas ...
Prism Design
... where Ij and I′j are the angle’s incidence and reflection at surface “j”. The angles in these equations are measured with respect to the surface normal at the point of incidence of the ray on the surface. A change in algebraic sign of the ray angle occurs upon reflection. The algebraic signs of the ...
... where Ij and I′j are the angle’s incidence and reflection at surface “j”. The angles in these equations are measured with respect to the surface normal at the point of incidence of the ray on the surface. A change in algebraic sign of the ray angle occurs upon reflection. The algebraic signs of the ...
CP2: Optics Why study optics? The problem of teaching optics
... plane. If the object is not at infinity then must move lens away from detector or decrease its focal length ...
... plane. If the object is not at infinity then must move lens away from detector or decrease its focal length ...
The Microscope in a Computer: Image Synthesis from Three
... simply intensity for the radiated power per unit area. The light intensity is a direct measure of the signal collected by recording media that convert light energy to other forms of energy. Examples of these recording media include photoresists, CCD cameras, and the retina. We will assume non-magnet ...
... simply intensity for the radiated power per unit area. The light intensity is a direct measure of the signal collected by recording media that convert light energy to other forms of energy. Examples of these recording media include photoresists, CCD cameras, and the retina. We will assume non-magnet ...
Total internal reflection microscopy studies on colloidal particle
... “We must take care not to make intellect our God. It has, of course, powerful muscles, but has no personality. It cannot rule, only serve.” ...
... “We must take care not to make intellect our God. It has, of course, powerful muscles, but has no personality. It cannot rule, only serve.” ...
HOLO TEXT
... however, there is considerable interest in this field of optics with the effects which differing substances will have upon a ray of light as it interacts with them. In this regard there are essentially three common and well-known properties of physical materials that describe their effect upon light ...
... however, there is considerable interest in this field of optics with the effects which differing substances will have upon a ray of light as it interacts with them. In this regard there are essentially three common and well-known properties of physical materials that describe their effect upon light ...
File - Electrical Engineering
... In a short interval of time each end of the wavefront would move forward a set distance. If we look at a single ray of light moving through a clear material the distance advanced by the wavefront would be quite regular.There is a widely held view that light always travels at the same speed. Th ...
... In a short interval of time each end of the wavefront would move forward a set distance. If we look at a single ray of light moving through a clear material the distance advanced by the wavefront would be quite regular.There is a widely held view that light always travels at the same speed. Th ...
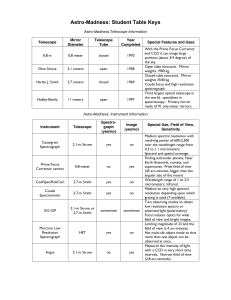
Astro-Madness: Student Table Keys
... (45 arc-minutes, bigger than the angular size of the moon) Wavelength range of 1 to 2.5 micrometers; infrared Medium to very high spectral resolution depending upon which grating is used (7 available). Two observing modes to obtain low resolution spectra or polarized light (polarimetry). Focal reduc ...
... (45 arc-minutes, bigger than the angular size of the moon) Wavelength range of 1 to 2.5 micrometers; infrared Medium to very high spectral resolution depending upon which grating is used (7 available). Two observing modes to obtain low resolution spectra or polarized light (polarimetry). Focal reduc ...
1 - High Point University
... 8) Click the “Clear Active” button to remove the source from the screen. Click on the “Object” button at the top of the workbench and then click on the screen to place the object there. Think of the object as a large arrow cut out of paper or wood. Move the object so that it is at x = 1. There are ...
... 8) Click the “Clear Active” button to remove the source from the screen. Click on the “Object” button at the top of the workbench and then click on the screen to place the object there. Think of the object as a large arrow cut out of paper or wood. Move the object so that it is at x = 1. There are ...
Dr. Stephan Landis Poster
... • Each white light post-debridement wound/periwound was deemed appropriately debrided by expert opinion • When compared to post-debridement BF, 41-88% of wound/periwound areas still showed presence of BF: i.e. no change in BF distribution, or more BF after debridement ...
... • Each white light post-debridement wound/periwound was deemed appropriately debrided by expert opinion • When compared to post-debridement BF, 41-88% of wound/periwound areas still showed presence of BF: i.e. no change in BF distribution, or more BF after debridement ...
Handbook of Optical Filters
... bright fluorescence and are used to selectively stain parts of a specimen. This method is called secondary or indirect fluorescence. These dyes are called fluorochromes, and when conjugated to other organically active substances, such as antibodies and nucleic acids, they are called fluorescent prob ...
... bright fluorescence and are used to selectively stain parts of a specimen. This method is called secondary or indirect fluorescence. These dyes are called fluorochromes, and when conjugated to other organically active substances, such as antibodies and nucleic acids, they are called fluorescent prob ...
COMPUTER GRAPHICS OPTIQUE Optical Superposition of
... find that n = 500 would be sufficient for a monochrome projector. Further, [3] says that humans are 3 4 times more sensitive to luminance differences in the presence of color. Thus, the problems arising from the low value of n offered by current projectors can be addressed to some extent by CGO. Fur ...
... find that n = 500 would be sufficient for a monochrome projector. Further, [3] says that humans are 3 4 times more sensitive to luminance differences in the presence of color. Thus, the problems arising from the low value of n offered by current projectors can be addressed to some extent by CGO. Fur ...
Coherence scanning interferometry: linear theory of surface
... the image of a point-like object, the PSF provides a direct measure of the 3D “resolution cell” of the imaging system while the TF describes how the phase and amplitude of the spatial frequencies present within the object are modified by the imaging system. For the case of CSI, the phase of the TF i ...
... the image of a point-like object, the PSF provides a direct measure of the 3D “resolution cell” of the imaging system while the TF describes how the phase and amplitude of the spatial frequencies present within the object are modified by the imaging system. For the case of CSI, the phase of the TF i ...
Chapter 9 Notes
... Since the wavelength of visible light is so small, diffraction is not noticeable through a window. You need a very narrow slight to see the diffraction of light. This figure shows the result of laser light after passing through a slit 0.008 cm wide. The screen was 10 meters from the slit. ...
... Since the wavelength of visible light is so small, diffraction is not noticeable through a window. You need a very narrow slight to see the diffraction of light. This figure shows the result of laser light after passing through a slit 0.008 cm wide. The screen was 10 meters from the slit. ...
Pixel level optical-transfer-function design based on the surface
... both phase and amplitude) into the Fourier plane of a 4f system [1], or by using a spatial light modulator (SLM) to modify the phase and amplitude in real time [2]. While these implementation methods allow for good control of OTF, they do come with the associated cost of sophisticated bulk optical a ...
... both phase and amplitude) into the Fourier plane of a 4f system [1], or by using a spatial light modulator (SLM) to modify the phase and amplitude in real time [2]. While these implementation methods allow for good control of OTF, they do come with the associated cost of sophisticated bulk optical a ...
Scattering and Polarization Properties of the Scarab Beetle Cyphochilus insulanus cuticle
... wavelength range 250 – 2500 nm at an angle of incidence of 10 and in the wavelength range 2.44 – 25 µm at an angle of incidence of 9. The instruments were calibrated against a Spectralon® diffuse reflectance standard with a reflectance of ~99 % (UV-NIR) and a diffusely reflecting gold surface with ...
... wavelength range 250 – 2500 nm at an angle of incidence of 10 and in the wavelength range 2.44 – 25 µm at an angle of incidence of 9. The instruments were calibrated against a Spectralon® diffuse reflectance standard with a reflectance of ~99 % (UV-NIR) and a diffusely reflecting gold surface with ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.