Document
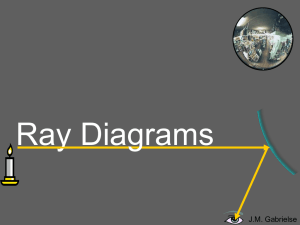
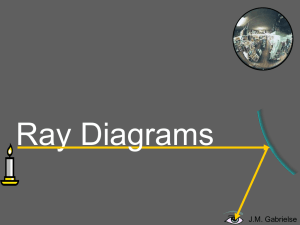
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (the incidence angle, θi) as it reflects off the mirror (the reflection angle, θr). ...
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (the incidence angle, θi) as it reflects off the mirror (the reflection angle, θr). ...
Fast-Fourier-domain delay line for in vivo optical coherence
... achievable delay. A further increase in scan rate can be achieved with a continuously rotating device. A spinning cube delay line8,9 uses internal reflections from the cube surfaces to produce angle-dependent group delay. Although scan rates up to 28.6 kHz have been reported,9 these systems suffer ...
... achievable delay. A further increase in scan rate can be achieved with a continuously rotating device. A spinning cube delay line8,9 uses internal reflections from the cube surfaces to produce angle-dependent group delay. Although scan rates up to 28.6 kHz have been reported,9 these systems suffer ...
Ray Diagrams Powerpoint
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (the incidence angle, θi) as it reflects off the mirror (the reflection angle, θr). ...
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (the incidence angle, θi) as it reflects off the mirror (the reflection angle, θr). ...
Detecting tissue optical and mechanical properties with an
... optical scatterers [4], and the intensity of the ultrasound modulated light is selectively detected, either through the spectral features of modulated light [1] or based on the temporal features of speckles [5], to measure the optical properties within the ultrasound focal region [6-8]. Since ultras ...
... optical scatterers [4], and the intensity of the ultrasound modulated light is selectively detected, either through the spectral features of modulated light [1] or based on the temporal features of speckles [5], to measure the optical properties within the ultrasound focal region [6-8]. Since ultras ...
Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy
... over a disc of scattering angles centered on the optic axis of the microscope, whereas the ADF detector collects over an annulus at higher angle where only scattered electrons are detected. The ADF imaging mode is important and unique to STEM in that it provides incoherent images of materials and ha ...
... over a disc of scattering angles centered on the optic axis of the microscope, whereas the ADF detector collects over an annulus at higher angle where only scattered electrons are detected. The ADF imaging mode is important and unique to STEM in that it provides incoherent images of materials and ha ...
Lecture 35: Holography.
... the visual information of the scene To view a hologram, the wavefront is reconstructed View what we would have seen if present at the original scene through the window defined by the hologram Provides depth perception and parallax ...
... the visual information of the scene To view a hologram, the wavefront is reconstructed View what we would have seen if present at the original scene through the window defined by the hologram Provides depth perception and parallax ...
Appendix B 2Spectral Decomposition of Diffracted Light
... where u O(x ,y) is the specified image in a plane at a distance z=zO from the hologram plane and U O(k x, k y) is the 2-D Fourier transform of the specified image38. This dissertation generally discusses horizontal-parallax-only (HPO) holograms. Because a single HPO holograms (hololine) diffracts li ...
... where u O(x ,y) is the specified image in a plane at a distance z=zO from the hologram plane and U O(k x, k y) is the 2-D Fourier transform of the specified image38. This dissertation generally discusses horizontal-parallax-only (HPO) holograms. Because a single HPO holograms (hololine) diffracts li ...
Modulation of spatial coherence of optical field by means of liquid
... liquid crystal placed between two polarizers (see, for example [8]). As has been shown in Ref. 9, depending on the mutual orientation of the main axes of polarizers, this modulator may produce to a good approximation either intensity-only or phase-only modulation of optical field. To demonstrate the ...
... liquid crystal placed between two polarizers (see, for example [8]). As has been shown in Ref. 9, depending on the mutual orientation of the main axes of polarizers, this modulator may produce to a good approximation either intensity-only or phase-only modulation of optical field. To demonstrate the ...
Controlling light-with-light without nonlinearity
... absorber. Indeed, in the total transmission regime, spectral components of the distorted pulse that have the same intensity and amplitude as the clock pulse will be transmitted with negligible loss, while distorted components are strongly absorbed, thereby restoring the temporal and spectral profile ...
... absorber. Indeed, in the total transmission regime, spectral components of the distorted pulse that have the same intensity and amplitude as the clock pulse will be transmitted with negligible loss, while distorted components are strongly absorbed, thereby restoring the temporal and spectral profile ...
Bi Imaging - MicroscopyU
... no background. The red and green intensities are very similar. The co-localization analysis gives coefficients of red = 0.8 and green = 0.48. This is expected because a greater proportion of the red pixels are co-localized in comparison to the proportion of co-localized green pixels. Because the int ...
... no background. The red and green intensities are very similar. The co-localization analysis gives coefficients of red = 0.8 and green = 0.48. This is expected because a greater proportion of the red pixels are co-localized in comparison to the proportion of co-localized green pixels. Because the int ...
A Coaxial Optical Scanner for Synchronous Acquisition of 3D
... previous designs often fail to correctly account for global illumination, such as interreflections and sub-surface scattering, which contaminate measurements of the desired local surface reflectance. We address many of these issues with a simple optical setup and processing pipeline that build on re ...
... previous designs often fail to correctly account for global illumination, such as interreflections and sub-surface scattering, which contaminate measurements of the desired local surface reflectance. We address many of these issues with a simple optical setup and processing pipeline that build on re ...
Extraordinary optical transmission by interference of diffracted
... interference) and a valley will be detected when these interfering beams are out of phase (destructive interference). In the infinite fringe mode condition (bright field) all the three waves will travel along the same line and the same optical paths, i.e., φ = ψ = 0 which means a is of the order of ...
... interference) and a valley will be detected when these interfering beams are out of phase (destructive interference). In the infinite fringe mode condition (bright field) all the three waves will travel along the same line and the same optical paths, i.e., φ = ψ = 0 which means a is of the order of ...
Understanding Polarization
... 2. A description of the polarization of light To understand the polarization of light, we must first recognize that light can be described as a classical wave. The most basic parameters that describe any wave are the amplitude and the wavelength. For example, the amplitude of a wave represents the l ...
... 2. A description of the polarization of light To understand the polarization of light, we must first recognize that light can be described as a classical wave. The most basic parameters that describe any wave are the amplitude and the wavelength. For example, the amplitude of a wave represents the l ...
CHAPTER 4 REFLECTED LIGHT OPTICS
... optically isotropic. A vacuum, all gases , most liquids, glasses, and cubic (isometric) crystalline substances are isotropic; other materials (chiefly nonisometric crystals) are optically anisotropic, and light rays may travel through them at different speeds, depending on the direction oflight vibr ...
... optically isotropic. A vacuum, all gases , most liquids, glasses, and cubic (isometric) crystalline substances are isotropic; other materials (chiefly nonisometric crystals) are optically anisotropic, and light rays may travel through them at different speeds, depending on the direction oflight vibr ...
YOUNG`S INTERFERENCE EXPERIMENT: THE LONG AND
... We emphasize that the surprising results expressed by Eqs. (20) and (28) also hold in the limiting case when each pinhole is illuminated by a separate laser. It is to be noted that taking obliquity factors into account does not alter the outcome of our analysis (for a proof of this, see [12]). Moreo ...
... We emphasize that the surprising results expressed by Eqs. (20) and (28) also hold in the limiting case when each pinhole is illuminated by a separate laser. It is to be noted that taking obliquity factors into account does not alter the outcome of our analysis (for a proof of this, see [12]). Moreo ...
... liquid crystal placed between two polarizers (see, for example [8]). As has been shown in Ref. 9, depending on the mutual orientation of the main axes of polarizers, this modulator may produce to a good approximation either intensity-only or phase-only modulation of optical field. To demonstrate the ...
Chapter15 - cloudfront.net
... • Waves must have a constant phase difference for interference to be observed. • Coherence is the correlation between the phases of two or more waves. ...
... • Waves must have a constant phase difference for interference to be observed. • Coherence is the correlation between the phases of two or more waves. ...
Extended depth-of-field iris recognition system for a
... field of view determines the spatial extent of the scene acquired by the sensor. Depth of field determines how far a planar object can move away from the best focus position and still be imaged without focus errors. The exposure period is defined as the detector integration time while acquiring an i ...
... field of view determines the spatial extent of the scene acquired by the sensor. Depth of field determines how far a planar object can move away from the best focus position and still be imaged without focus errors. The exposure period is defined as the detector integration time while acquiring an i ...
mm {0.84 M PASS
... rect-bandgap semiconductor having a thickness be wavelength wave energy detected by the silicon detec tween opposed faces thereof in a range of 50-400 mi tor of second detector 216 is insuf?cient to cause cross crometers, said direct bandgap exhibiting an energy talk. Third, the residual energy re?e ...
... rect-bandgap semiconductor having a thickness be wavelength wave energy detected by the silicon detec tween opposed faces thereof in a range of 50-400 mi tor of second detector 216 is insuf?cient to cause cross crometers, said direct bandgap exhibiting an energy talk. Third, the residual energy re?e ...
The Absolute Sensitivity of Lens and Compound Eyes
... pupil of the dark adapted human eye, however, can be as large as 7 mm, which makes its area larger by a factor of approxim ately 105 times. Due to this fact, it is generally accepted that the num ber of light quanta available to the photoreceptors in insects is small compared to that available to an ...
... pupil of the dark adapted human eye, however, can be as large as 7 mm, which makes its area larger by a factor of approxim ately 105 times. Due to this fact, it is generally accepted that the num ber of light quanta available to the photoreceptors in insects is small compared to that available to an ...
Ultra-thin plasmonic optical vortex plate based on phase
... plates,8 spatial light modulators,9 or holograms.10 This type of beam can also be directly generated by lasers as an intrinsic transverse mode11 or when an incident beam diffracts from fork-shaped intensity masks.10 Optical vortices are of great fundamental interest since they carry optical singular ...
... plates,8 spatial light modulators,9 or holograms.10 This type of beam can also be directly generated by lasers as an intrinsic transverse mode11 or when an incident beam diffracts from fork-shaped intensity masks.10 Optical vortices are of great fundamental interest since they carry optical singular ...
2. Spectral Stray Light
... The correction algorithm used here was taken from (Zong 2006) and will be described briefly in this section. The basic assumption for this correction algorithm is that stray light in one detector element originates is proportional to the signal of surrounding detector elements. The knowledge obtaine ...
... The correction algorithm used here was taken from (Zong 2006) and will be described briefly in this section. The basic assumption for this correction algorithm is that stray light in one detector element originates is proportional to the signal of surrounding detector elements. The knowledge obtaine ...
Bild 1
... Epoxy usually has the shape of a hemisphere so that the angle of incidence at the epoxy-air interface is always normal to the epoxy surface, the total reflection does not occur at the epoxy-air interface. Planar-surface LEDs are frequently used where the intended viewing angle is close to the normal ...
... Epoxy usually has the shape of a hemisphere so that the angle of incidence at the epoxy-air interface is always normal to the epoxy surface, the total reflection does not occur at the epoxy-air interface. Planar-surface LEDs are frequently used where the intended viewing angle is close to the normal ...
Click
... Now rotate the crystal slowly as shown in figure ii. It is found that one image remains stationary and the second image rotates with the rotation of the crystal. The stationary image is known as the ordinary image The second image is known as the extraordinary image. The retracted ray which produces ...
... Now rotate the crystal slowly as shown in figure ii. It is found that one image remains stationary and the second image rotates with the rotation of the crystal. The stationary image is known as the ordinary image The second image is known as the extraordinary image. The retracted ray which produces ...
Physically-Based Glare Effects for Digital Images
... and the real experience of looking at a small incandescent bulb. The real bulb differs from the digital image in two important ways. The first difference is a qualitative “brightness” that the bulb possesses. The second difference is the hazy glow that can be seen around the bulb. This glow not only ...
... and the real experience of looking at a small incandescent bulb. The real bulb differs from the digital image in two important ways. The first difference is a qualitative “brightness” that the bulb possesses. The second difference is the hazy glow that can be seen around the bulb. This glow not only ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.