Accelerating Light Beams along Arbitrary Convex
... Eq. (6), the curve x ¼ fðzÞ is the envelope of rays tangent to all members of the ray family leaving the mask, and therefore a caustic [15]. Since a caustic is a manifold on which rays focus to a maximum extent, it is not surprising that the optical intensity juðx; zÞj2 has a global maximum there. T ...
... Eq. (6), the curve x ¼ fðzÞ is the envelope of rays tangent to all members of the ray family leaving the mask, and therefore a caustic [15]. Since a caustic is a manifold on which rays focus to a maximum extent, it is not surprising that the optical intensity juðx; zÞj2 has a global maximum there. T ...
Optical Fiber Communication
... On the basis of number of modes:on the basis of number of modes of propagation the optical fiber are classified into two types: (i) Single mode fiber (SMF) and (ii) Multi-mode fiber (MMF) • Single-mode fibers – in single mode fiber only one mode can propagate through the fiber. This type of fiber h ...
... On the basis of number of modes:on the basis of number of modes of propagation the optical fiber are classified into two types: (i) Single mode fiber (SMF) and (ii) Multi-mode fiber (MMF) • Single-mode fibers – in single mode fiber only one mode can propagate through the fiber. This type of fiber h ...
Physical Optics and Diffraction
... When any of the above assumptions fail, the image quality is degraded Useful to define the Strehl ratio as the ratio between the peak amplitude of the actual PSF and the peak amplitude expected in the presence of diffraction only Looking through the atmosphere, the Strehl ratio will be very low, eve ...
... When any of the above assumptions fail, the image quality is degraded Useful to define the Strehl ratio as the ratio between the peak amplitude of the actual PSF and the peak amplitude expected in the presence of diffraction only Looking through the atmosphere, the Strehl ratio will be very low, eve ...
guide to thin section microscopy - Mineralogical Society of America
... When using a polarized-light microscope, communicating directions in an unequivocal way is important. The cross-hairs in the ocular, the directions of light polarization and the microscope axis are the main reference directions. The four cardinal points (and intermediate directions derived from thos ...
... When using a polarized-light microscope, communicating directions in an unequivocal way is important. The cross-hairs in the ocular, the directions of light polarization and the microscope axis are the main reference directions. The four cardinal points (and intermediate directions derived from thos ...
Vision and Optical Instruments
... Refractive indices are crucial to image formation using lenses. Table 26.1 shows refractive indices relevant to the eye. The biggest change in the refractive index, and bending of rays, occurs at the cornea rather than the lens. The ray diagram in Figure 26.3 shows image formation by the cornea and ...
... Refractive indices are crucial to image formation using lenses. Table 26.1 shows refractive indices relevant to the eye. The biggest change in the refractive index, and bending of rays, occurs at the cornea rather than the lens. The ray diagram in Figure 26.3 shows image formation by the cornea and ...
chapter 6—light and telescopes
... ____ 31. Light with a wavelength of 300 nm has a lower frequency than light with a wavelength of 500 nm. ____ 32. The largest optical telescope ever constructed was a refracting telescope. ____ 33. X-rays easily penetrate Earth's atmosphere and reach the ground from space. ____ 34. Light can behave ...
... ____ 31. Light with a wavelength of 300 nm has a lower frequency than light with a wavelength of 500 nm. ____ 32. The largest optical telescope ever constructed was a refracting telescope. ____ 33. X-rays easily penetrate Earth's atmosphere and reach the ground from space. ____ 34. Light can behave ...
CHAPTER 6—LIGHT AND TELESCOPES
... ____ 31. Light with a wavelength of 300 nm has a lower frequency than light with a wavelength of 500 nm. ____ 32. The largest optical telescope ever constructed was a refracting telescope. ____ 33. X-rays easily penetrate Earth's atmosphere and reach the ground from space. ____ 34. Light can behave ...
... ____ 31. Light with a wavelength of 300 nm has a lower frequency than light with a wavelength of 500 nm. ____ 32. The largest optical telescope ever constructed was a refracting telescope. ____ 33. X-rays easily penetrate Earth's atmosphere and reach the ground from space. ____ 34. Light can behave ...
Optics - Frederiksen
... This Plexiglas tank is supplied with plane parallel sides. One of the corners in the bottom is cut off at a 45° angle to facilitate the entry of light rays. It is ideal for optical experiments with refraction and (total) reflection. To make the light rays visible in the water, a small amount of chal ...
... This Plexiglas tank is supplied with plane parallel sides. One of the corners in the bottom is cut off at a 45° angle to facilitate the entry of light rays. It is ideal for optical experiments with refraction and (total) reflection. To make the light rays visible in the water, a small amount of chal ...
Acoustooptic interaction of two light beams in a paratellurite crystal
... f* = 188.4 MHz, which had been predicted theoretically. The transducer’s electric voltage determined by the condition ql = 2 π reached the value U = 6 V, which corresponded to an ultrasonic power of 0.8 W. The dots in Fig. 4 show the experimental values of double-diffraction efficiency I21 as a func ...
... f* = 188.4 MHz, which had been predicted theoretically. The transducer’s electric voltage determined by the condition ql = 2 π reached the value U = 6 V, which corresponded to an ultrasonic power of 0.8 W. The dots in Fig. 4 show the experimental values of double-diffraction efficiency I21 as a func ...
Kuhnke Laser Shutter DS200X8 - Kendrion Kuhnke Automation GmbH
... The deflection mirror is also available with coaings for different wave lengths, the Kuhnke Laser Shutter also features redundant NTC temperature monitoring in order to continuously monitor the ...
... The deflection mirror is also available with coaings for different wave lengths, the Kuhnke Laser Shutter also features redundant NTC temperature monitoring in order to continuously monitor the ...
How can I tell what the polarization axis is for a linear polarizer? The
... What does the wavelength designation mean for quartz retarders and how does this relate to the film specifications? To achieve the phase shift designated for any given retarder, the optical thickness of the material is selected to give the desired shift at a specific wavelength. Retarders are very w ...
... What does the wavelength designation mean for quartz retarders and how does this relate to the film specifications? To achieve the phase shift designated for any given retarder, the optical thickness of the material is selected to give the desired shift at a specific wavelength. Retarders are very w ...
Imaging optical singularities; Understanding the duality of C-points and optical vortices
... of points with elliptical polarization. The semi-major axis of the ellipses rotates about the C-point. Two of the three fundamental types of C-points are the lemon and the star. They occur when the semi-major axis of the ellipses rotates around the C-point in a counter-clockwise or clockwise fashion ...
... of points with elliptical polarization. The semi-major axis of the ellipses rotates about the C-point. Two of the three fundamental types of C-points are the lemon and the star. They occur when the semi-major axis of the ellipses rotates around the C-point in a counter-clockwise or clockwise fashion ...
Optical coherence tomography (OCT): a review
... width of the point-spread function; therefore, in this onedimensional model the coherence length is an appropriate measure of the axial resolution of the OCT system. In the more general situation in which a two-dimensional cross-sectional image is built up from multiple axial scans, the optical tran ...
... width of the point-spread function; therefore, in this onedimensional model the coherence length is an appropriate measure of the axial resolution of the OCT system. In the more general situation in which a two-dimensional cross-sectional image is built up from multiple axial scans, the optical tran ...
Optical Broadband Angular Selectivity Yichen Shen, Dexin Ye, Ivan Celanovic,
... and its propagation direction. The ability to select light according to each of these separate properties would be an essential step in achieving control over light (Fig. 1). Tremendous progress has been made toward both frequency selectivity and polarization selectivity. Frequency selectivity (Fig. ...
... and its propagation direction. The ability to select light according to each of these separate properties would be an essential step in achieving control over light (Fig. 1). Tremendous progress has been made toward both frequency selectivity and polarization selectivity. Frequency selectivity (Fig. ...
LABORATORY MANUAL (Modern Physics & General Optics) PL – 402 (2013-2014)
... cathode temperature and kB is the Boltzmann’s constant. In the steady stated with the grid at a positive potential relative to cathode the emitted electrons form a cloud of negative charges. This created an electric field forcing lower energy electrons back to the cathode and suppress the current to ...
... cathode temperature and kB is the Boltzmann’s constant. In the steady stated with the grid at a positive potential relative to cathode the emitted electrons form a cloud of negative charges. This created an electric field forcing lower energy electrons back to the cathode and suppress the current to ...
Research on the Design of an Optical Information Storage Sensing
... beam focuses on the servo layer for focusing and tracking, while the first-order diffraction beams focuses on the recording layer. The two beams are controlled and focus on the corresponding layers independently when changing the positions of the objective lens and the DOE. Therefore, the zeroth-ord ...
... beam focuses on the servo layer for focusing and tracking, while the first-order diffraction beams focuses on the recording layer. The two beams are controlled and focus on the corresponding layers independently when changing the positions of the objective lens and the DOE. Therefore, the zeroth-ord ...
CHAPTER 5: LIGHT
... ii) The object must be placed at a distance (more than f / same as f / less than f / between f and 2f / more than 2f) in order for the lens to act as a magnifying glass. iii) The characteristics of the image formed by a magnifying glass are yang (real / virtual) ; (inverted / upright) ; (magnified / ...
... ii) The object must be placed at a distance (more than f / same as f / less than f / between f and 2f / more than 2f) in order for the lens to act as a magnifying glass. iii) The characteristics of the image formed by a magnifying glass are yang (real / virtual) ; (inverted / upright) ; (magnified / ...
Sorting by Periodic Potential Energy Landscapes: Optical
... dimensions. Colloidal particles flowing through arrays of optical tweezers [2, 3] provide a uniquely accessible experimental archetype for this class of problems. Experiments on transport through square arrays have revealed a Devil’s staircase hierarchy of kinetically locked-in states as a function ...
... dimensions. Colloidal particles flowing through arrays of optical tweezers [2, 3] provide a uniquely accessible experimental archetype for this class of problems. Experiments on transport through square arrays have revealed a Devil’s staircase hierarchy of kinetically locked-in states as a function ...
Diffraction
... In addition to the diffraction at a slit, in this experiment, the diffraction grating is also observed. The diffraction grating is a generalization of the diffraction at a double slit, which is an experiment with extreme importance in physics because of the transition from classical physics to quant ...
... In addition to the diffraction at a slit, in this experiment, the diffraction grating is also observed. The diffraction grating is a generalization of the diffraction at a double slit, which is an experiment with extreme importance in physics because of the transition from classical physics to quant ...
Bending What is Optical Fiber Dispersion?
... Since each mode ray travels a different distance as it propagates, the ray arrive at different times at the fiber output. So the light pulse spreads out in time which can cause signal overlapping so seriously that you cannot distinguish them any more.. ...
... Since each mode ray travels a different distance as it propagates, the ray arrive at different times at the fiber output. So the light pulse spreads out in time which can cause signal overlapping so seriously that you cannot distinguish them any more.. ...
Roger`s Descriptions
... COURSE: OPTICAL PHYSICS FOR IMAGING II - SIMG yyy, SPSP-455 1.1 One-quarter course: Four credit hours. 1.2 Three 50-minute lectures and one 3-hour lab per week. 1.3 Prerequisites: Credit in SPSP-313 (University Physics III) SIMG-??? (Linear Mathematics for Imaging) ...
... COURSE: OPTICAL PHYSICS FOR IMAGING II - SIMG yyy, SPSP-455 1.1 One-quarter course: Four credit hours. 1.2 Three 50-minute lectures and one 3-hour lab per week. 1.3 Prerequisites: Credit in SPSP-313 (University Physics III) SIMG-??? (Linear Mathematics for Imaging) ...
Photonics Workshop Program and Worksheets
... Fibre optics is the most rapidly growing portion of optics study in the world. It has grown so dramatically that some people may not think of it as even being part of the optics field. In terms of data communications they could be right, because fibre optic communications utilizes electronic and las ...
... Fibre optics is the most rapidly growing portion of optics study in the world. It has grown so dramatically that some people may not think of it as even being part of the optics field. In terms of data communications they could be right, because fibre optic communications utilizes electronic and las ...
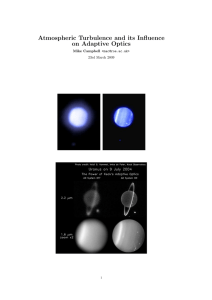
Atmospheric Turbulence and its Influence on Adaptive Optics
... Adaptive Optics (AO) is still a relatively young branch of astronomical instrumentation. Different technologies are developing all the time and it can be difficult keeping up with all the different acronyms (e.g. GLAO, MOAO, MCAO, SLGS, RLGS, etc..) never mind the technologies themselves. It is easy ...
... Adaptive Optics (AO) is still a relatively young branch of astronomical instrumentation. Different technologies are developing all the time and it can be difficult keeping up with all the different acronyms (e.g. GLAO, MOAO, MCAO, SLGS, RLGS, etc..) never mind the technologies themselves. It is easy ...
ABSTRACT Dissertation: STUDIES OF
... 10 cm to the earth’s diameter. In the past, optical behavior has been studied down to the micrometer scale, which is in the visible light range. We know that scattering and diffraction happen when the object size is on the same order of the impinging light wavelength. However, when the dimension of ...
... 10 cm to the earth’s diameter. In the past, optical behavior has been studied down to the micrometer scale, which is in the visible light range. We know that scattering and diffraction happen when the object size is on the same order of the impinging light wavelength. However, when the dimension of ...
Press Release Product Developed under CSIR
... A humble beginning towards Prime Minister’s “Made in India and Reach Global” Strategy ...
... A humble beginning towards Prime Minister’s “Made in India and Reach Global” Strategy ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.