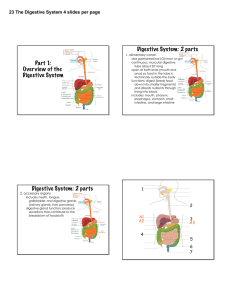
Part 1: Overview of the Digestive System Digestive System: 2 parts
... 4 The small intestine does peristalsis, chemical digestion, mechanical digestion, and absorption. ...
... 4 The small intestine does peristalsis, chemical digestion, mechanical digestion, and absorption. ...
Digestive System general review and Application
... Up to 99.5% of saliva is composed of water. It is slightly acidic and it’s solutes include electrolytes (such as sodium and potassium), salivary amylase – a digestive enzyme, mucin – which hydrates the food, and wastes such as urea. ...
... Up to 99.5% of saliva is composed of water. It is slightly acidic and it’s solutes include electrolytes (such as sodium and potassium), salivary amylase – a digestive enzyme, mucin – which hydrates the food, and wastes such as urea. ...
Digestion - UBC Zoology
... Up to 99.5% of saliva is composed of water. It is slightly acidic and it’s solutes include electrolytes (such as sodium and potassium), salivary amylase – a digestive enzyme, mucin – which hydrates the food, and wastes such as urea. ...
... Up to 99.5% of saliva is composed of water. It is slightly acidic and it’s solutes include electrolytes (such as sodium and potassium), salivary amylase – a digestive enzyme, mucin – which hydrates the food, and wastes such as urea. ...
9 Digestive Physiology
... Up to 99.5% of saliva is composed of water. It is slightly acidic and it’s solutes include electrolytes (such as sodium and potassium), salivary amylase – a digestive enzyme, mucin – which hydrates the food, and traces of waste products (such as urea). ...
... Up to 99.5% of saliva is composed of water. It is slightly acidic and it’s solutes include electrolytes (such as sodium and potassium), salivary amylase – a digestive enzyme, mucin – which hydrates the food, and traces of waste products (such as urea). ...
CHAPTER 51: FUELING BODY ACTIVITIES: DIGESTION
... digestion. Bile is stored in the gallbladder until it is needed. The remaining divisions of the small intestine, the jejunum, and the ileum, are specialized for absorption. The surface area is increased by finger-like projections called villi. The epithelium of each villus is covered with cytoplasmi ...
... digestion. Bile is stored in the gallbladder until it is needed. The remaining divisions of the small intestine, the jejunum, and the ileum, are specialized for absorption. The surface area is increased by finger-like projections called villi. The epithelium of each villus is covered with cytoplasmi ...
Chapters 22-24
... 7. Know the functions of the stomach. Know the anatomy of the stomach including the regions (cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus) and what is unique to each region of the stomach. What is distinctive to the histology of the stomach? 8. Know the purpose of the gastric glands in the stomach. What types ...
... 7. Know the functions of the stomach. Know the anatomy of the stomach including the regions (cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus) and what is unique to each region of the stomach. What is distinctive to the histology of the stomach? 8. Know the purpose of the gastric glands in the stomach. What types ...
Sarah Harney_AHS Digestion 2
... the mouth and stomach but mostly by pancreatic lipases in small intestine ...
... the mouth and stomach but mostly by pancreatic lipases in small intestine ...
Thomas
... http://www.allposters.com/-sp/This-Illustration-Depicts-the-Anatomy-of-the-Large-IntestineColon_Posters_i9013176_.htm http://www.sccollege.edu/studentservices/healthwellnesscenter/alcoholeffects/pages/liver.aspx http://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/picture-of-the-appendix ...
... http://www.allposters.com/-sp/This-Illustration-Depicts-the-Anatomy-of-the-Large-IntestineColon_Posters_i9013176_.htm http://www.sccollege.edu/studentservices/healthwellnesscenter/alcoholeffects/pages/liver.aspx http://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/picture-of-the-appendix ...
Digestive and absorptive functions of the gastrointestinal system
... Included with ingested dietary lipids in the micelles and absorbed via simple diffusion Water soluble vitamins and vitamin C Absorbed via simple diffusion Vitamin B12 combined with intrinsic factor ...
... Included with ingested dietary lipids in the micelles and absorbed via simple diffusion Water soluble vitamins and vitamin C Absorbed via simple diffusion Vitamin B12 combined with intrinsic factor ...
Chapter 3 Gastroenterology
... pouches in the wall of the large intestine that expand to accommodate the bulk of undigested materials weakness in the muscle of the diaphragm or abdominal wall. The intestine bulges through the defect. a 12‐foot segment of the small intestine where absorption of nutrients is completed abnormal ...
... pouches in the wall of the large intestine that expand to accommodate the bulk of undigested materials weakness in the muscle of the diaphragm or abdominal wall. The intestine bulges through the defect. a 12‐foot segment of the small intestine where absorption of nutrients is completed abnormal ...
Liver: Histology
... (brush border), containing at surface enzymes that finish digesting carbohydrates and proteins, estimating 200 million microvilli per mm2, greatly expanding surface area of the plasma membrane and thus greatly enhancing absorption. ...
... (brush border), containing at surface enzymes that finish digesting carbohydrates and proteins, estimating 200 million microvilli per mm2, greatly expanding surface area of the plasma membrane and thus greatly enhancing absorption. ...
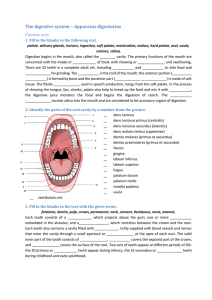
The digestive system – Apparatus digestorius
... Portions of moistened food are moved from the oral cavity toward the ____________ where swallowing reflexes push it into the ____________. ______________moves the food through the esophagus and into the stomach. At its distal end, where it joins the stomach, the esophagus has muscle tissue that cont ...
... Portions of moistened food are moved from the oral cavity toward the ____________ where swallowing reflexes push it into the ____________. ______________moves the food through the esophagus and into the stomach. At its distal end, where it joins the stomach, the esophagus has muscle tissue that cont ...
CHAPTER 17
... tells you that both your grandparents have had some bowel "irregularity" lately and asks you to recommend a laxative. Based on your knowledge of the alimentary tube, what information would you collect and what advice would you give her? ...
... tells you that both your grandparents have had some bowel "irregularity" lately and asks you to recommend a laxative. Based on your knowledge of the alimentary tube, what information would you collect and what advice would you give her? ...
Digestion Review Answer Key
... 6. What is responsible for heartburn and how is it normally prevented from occurring? 7. List the functions of the stomach. What is chyme? 8. What is the function of the gastric glands in the stomach? 9. What is an ulcer an why does it form? 10. List 4 functions of the small intestine. What molecule ...
... 6. What is responsible for heartburn and how is it normally prevented from occurring? 7. List the functions of the stomach. What is chyme? 8. What is the function of the gastric glands in the stomach? 9. What is an ulcer an why does it form? 10. List 4 functions of the small intestine. What molecule ...
Chapter 25 *Lecture PowerPoint The Digestive System
... • Greater omentum—hangs from the greater curvature of the stomach – Covers the small intestines like an apron – The inferior margin turns back on itself and passes ...
... • Greater omentum—hangs from the greater curvature of the stomach – Covers the small intestines like an apron – The inferior margin turns back on itself and passes ...
Document
... Lesser omentum – suspends stomach and duodenum from liver – passage for hepatic portal vein and artery and common bile duct Next two loosely hold the intestines allowing for movement. ...
... Lesser omentum – suspends stomach and duodenum from liver – passage for hepatic portal vein and artery and common bile duct Next two loosely hold the intestines allowing for movement. ...
the digestive system
... Saliva is a fluid that is continuously secreted by glands in or near the mouth. Ordinarily, just enough saliva is secreted to keep the mucous membranes of the mouth moist, but when food enters the mouth, secretion increases so the saliva can lubricate, dissolve, and begin the chemical breakdown of t ...
... Saliva is a fluid that is continuously secreted by glands in or near the mouth. Ordinarily, just enough saliva is secreted to keep the mucous membranes of the mouth moist, but when food enters the mouth, secretion increases so the saliva can lubricate, dissolve, and begin the chemical breakdown of t ...
View - Dr Falk
... lymphocytic colitis, the inflammation is thought to be caused by an increase in the white blood cells within the lining of the colon. These lymphocytes usually fight infection and can cause inflammation. In collagenous colitis the lining of the colon has a thicker than usual layer of collagen which ...
... lymphocytic colitis, the inflammation is thought to be caused by an increase in the white blood cells within the lining of the colon. These lymphocytes usually fight infection and can cause inflammation. In collagenous colitis the lining of the colon has a thicker than usual layer of collagen which ...
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
... esophagus. A small, flexible tube is passed into the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine. The tube has a light source and a camera that displays magnified images. Damage to the lining of these structures can be evaluated and a small sample of tissue (biopsy) can be taken to determine the extent ...
... esophagus. A small, flexible tube is passed into the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine. The tube has a light source and a camera that displays magnified images. Damage to the lining of these structures can be evaluated and a small sample of tissue (biopsy) can be taken to determine the extent ...
The Digestive System
... Gastric enzymes: Pepsin, from gastric glands – begins protein digestion. Lipase, from gastric glands – begins fat digestion. Pancreatic enzymes: Amylase, from pancreas – breaks down starch and glycogen into disaccharides. Lipase, from pancreas – breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol. Nuclea ...
... Gastric enzymes: Pepsin, from gastric glands – begins protein digestion. Lipase, from gastric glands – begins fat digestion. Pancreatic enzymes: Amylase, from pancreas – breaks down starch and glycogen into disaccharides. Lipase, from pancreas – breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol. Nuclea ...
Reticulum Honeycomb lining Formation of food bolus
... Small stomach in carnivores is related to high nutrient density of the diet Distribution and composition of epithelial lining varies between species and dietary ...
... Small stomach in carnivores is related to high nutrient density of the diet Distribution and composition of epithelial lining varies between species and dietary ...
L3 Small Intestine File
... ¤ The pancreas secretes enzymes to further break down fats, proteins and starches. Trypsin is produced here ¤ The liver secretes bile via the gall bladder to emulsify fats. ...
... ¤ The pancreas secretes enzymes to further break down fats, proteins and starches. Trypsin is produced here ¤ The liver secretes bile via the gall bladder to emulsify fats. ...
Bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Different molecular forms of bile acids can be synthesized in the liver by different species. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine in the liver, forming bile salts.Primary bile acids are those synthesized by the liver. Secondary bile acids result from bacterial actions in the colon. In humans, taurocholic acid and glycocholic acid (derivatives of cholic acid) and taurochenodeoxycholic acid and glycochenodeoxycholic acid (derivatives of chenodeoxycholic acid) are the major bile salts in bile and are roughly equal in concentration. The conjugated salts of their 7-alpha-dehydroxylated derivatives, deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid, are also found, with derivatives of cholic, chenodeoxycholic and deoxycholic acids accounting for over 90% of human biliary bile acids.Bile acids comprise about 80% of the organic compounds in bile (others are phospholipids and cholesterol). An increased secretion of bile acids produces an increase in bile flow. The main function of bile acids is to facilitate the formation of micelles, which promotes digestion and absorption of dietary fat, but they are increasingly being shown to have hormonal actions throughout the body.