small intestine
... Bile Production by the Liver • Bile is contains bile salts which act as detergents that aid in digestion and absorption of lipids in small intestine. • Bile is made in the liver and stored and concentrated in the gallbladder • Liver breaks down toxins and helps balance nutrient utilization • Bile i ...
... Bile Production by the Liver • Bile is contains bile salts which act as detergents that aid in digestion and absorption of lipids in small intestine. • Bile is made in the liver and stored and concentrated in the gallbladder • Liver breaks down toxins and helps balance nutrient utilization • Bile i ...
Introduction to the Digestive System
... Stomach performs preliminary digestion of proteins by pepsin Some digestion of carbohydrates (by salivary amylase) Lipids (by lingual lipase) ...
... Stomach performs preliminary digestion of proteins by pepsin Some digestion of carbohydrates (by salivary amylase) Lipids (by lingual lipase) ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... The respiratory system is to carry out the gas exchanges -- supply of oxygen for living cells and remove of carbon dioxide resulting from cell metabolism. The primary function of urinary system is to keep the body in homeostasis by removing and restoring selected amount of water and solutes, excreti ...
... The respiratory system is to carry out the gas exchanges -- supply of oxygen for living cells and remove of carbon dioxide resulting from cell metabolism. The primary function of urinary system is to keep the body in homeostasis by removing and restoring selected amount of water and solutes, excreti ...
Digestive PPT
... 1. Store Food, so it can be slowly released into the small intestine. Your whole Thanksgiving dinner can take your stomach from 2” to 8” in diameter. 2. Mechanically Churns food. Secretions from the stomach are added, turns everything into a gooey paste. When you throw up, you can see the enzyme sec ...
... 1. Store Food, so it can be slowly released into the small intestine. Your whole Thanksgiving dinner can take your stomach from 2” to 8” in diameter. 2. Mechanically Churns food. Secretions from the stomach are added, turns everything into a gooey paste. When you throw up, you can see the enzyme sec ...
Unit B3-1
... On average, cattle chew their cud about six to eight times per day. A total of five to seven hours each day are spent in rumination. ...
... On average, cattle chew their cud about six to eight times per day. A total of five to seven hours each day are spent in rumination. ...
Digestion
... On average, cattle chew their cud about six to eight times per day. A total of five to seven hours each day are spent in rumination. ...
... On average, cattle chew their cud about six to eight times per day. A total of five to seven hours each day are spent in rumination. ...
Digestive System Summary Ch24 2014
... 1. Absorption is the passage of the end products of digestion from the GI tract into blood or lymph and occurs by diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. 2. Absorption of monosaccharides: Essentially all carbohydrates are absorbed as monosaccharides into blood capillaries. 3 ...
... 1. Absorption is the passage of the end products of digestion from the GI tract into blood or lymph and occurs by diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. 2. Absorption of monosaccharides: Essentially all carbohydrates are absorbed as monosaccharides into blood capillaries. 3 ...
Digestive System Self Study
... compound and list the monomeric units; The last three you may need to reference other materials. 1. Protein ______________________________________________________ 2. Starch _______________________________________________________ 3. Fats__________________________________________________________ 4. Ma ...
... compound and list the monomeric units; The last three you may need to reference other materials. 1. Protein ______________________________________________________ 2. Starch _______________________________________________________ 3. Fats__________________________________________________________ 4. Ma ...
Chapter 17: Digestive System
... 3. The common bile duct is formed from the cystic duct and common hepatic duct and opens into duodenum. 4. Gallstones form when bile is too concentrated, hepatic cells secrete too much cholesterol, or if the gallbladder is inflamed. V. Regulation of Bile Release 1. Cholecystokinin triggers the gall ...
... 3. The common bile duct is formed from the cystic duct and common hepatic duct and opens into duodenum. 4. Gallstones form when bile is too concentrated, hepatic cells secrete too much cholesterol, or if the gallbladder is inflamed. V. Regulation of Bile Release 1. Cholecystokinin triggers the gall ...
Chapter 3 - HCC Learning Web
... neck cells (secrete mucus), chief or zymogenic cells (secrete pepsinogen and gastric lipase), and parietal or oxyntic cells (secrete HCl). Gastric glands also contain enteroendocrine cells which are hormone producing cells. G cells secrete the hormone gastrin into the bloodstream. Zollinger-Elli ...
... neck cells (secrete mucus), chief or zymogenic cells (secrete pepsinogen and gastric lipase), and parietal or oxyntic cells (secrete HCl). Gastric glands also contain enteroendocrine cells which are hormone producing cells. G cells secrete the hormone gastrin into the bloodstream. Zollinger-Elli ...
Digestion
... Ruminant Stomach • The liquid part goes into reticulum, then the omasum and on into the abomasum. • In the rumen, the solid feed is mixed and partially broken down by bacteria. • When the rumen is full, the animal lies down. • The feed is then forced back into the mouth rumination occurs. ...
... Ruminant Stomach • The liquid part goes into reticulum, then the omasum and on into the abomasum. • In the rumen, the solid feed is mixed and partially broken down by bacteria. • When the rumen is full, the animal lies down. • The feed is then forced back into the mouth rumination occurs. ...
Digestion and Absorption
... non-carbohydrate sources (i.e., gluconeogenesis), fats (from glucose and amino acids), vitamin A, heparin (anticoagulant) and some enzymes. However, its main role in digestion is in the production of bile and metabolism of nutrients. The bile produced by cells of the liver, enters the intestine at t ...
... non-carbohydrate sources (i.e., gluconeogenesis), fats (from glucose and amino acids), vitamin A, heparin (anticoagulant) and some enzymes. However, its main role in digestion is in the production of bile and metabolism of nutrients. The bile produced by cells of the liver, enters the intestine at t ...
2 Practical Nutrition
... Average life span for a human without water and food is 3 days (1-7 days). Average life span for a human without food (but having water) is 61 days. Average life spans: male - 71 years; female - 79 years (female lives longer because of a lower metabolic rate). ...
... Average life span for a human without water and food is 3 days (1-7 days). Average life span for a human without food (but having water) is 61 days. Average life spans: male - 71 years; female - 79 years (female lives longer because of a lower metabolic rate). ...
19 Digestive System
... 1. Store Food, so it can be slowly released into the small intestine. Your whole Thanksgiving dinner can take your stomach from 2” to 8” in diameter. 2. Mechanically Churns food. Secretions from the stomach are added, turns everything into a gooey paste. When you throw up, you can see the enzyme sec ...
... 1. Store Food, so it can be slowly released into the small intestine. Your whole Thanksgiving dinner can take your stomach from 2” to 8” in diameter. 2. Mechanically Churns food. Secretions from the stomach are added, turns everything into a gooey paste. When you throw up, you can see the enzyme sec ...
The digestive system
... simple sugar made by the body from food, which is used by cells to make energy in respiration.] molecules joined together. The digestion of starch is a two-stage process: 1. it is first digested to form maltose (each maltose molecule consists of two glucose molecules joined together) 2. the maltose ...
... simple sugar made by the body from food, which is used by cells to make energy in respiration.] molecules joined together. The digestion of starch is a two-stage process: 1. it is first digested to form maltose (each maltose molecule consists of two glucose molecules joined together) 2. the maltose ...
PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE
... 41. Disbacteriosis is accompanied by the following bacterial shifts in small intestine: 1. increased total content of microbes 2. eschericia coli, clebciellas, lactobacillus, and enterococci prevalure 3. loss of bifidbacteria 4. escherichia, staphilococci,streptococci, clebciellas, proteus, and yeas ...
... 41. Disbacteriosis is accompanied by the following bacterial shifts in small intestine: 1. increased total content of microbes 2. eschericia coli, clebciellas, lactobacillus, and enterococci prevalure 3. loss of bifidbacteria 4. escherichia, staphilococci,streptococci, clebciellas, proteus, and yeas ...
Digestive System Notes (PPT)
... _______________________ before entering the small intestine Scattered among the acini are clusters of endocrine cells called the _____________________ _______________________, which contain the cells that produce the hormones _________ _________________________________ and release them right into th ...
... _______________________ before entering the small intestine Scattered among the acini are clusters of endocrine cells called the _____________________ _______________________, which contain the cells that produce the hormones _________ _________________________________ and release them right into th ...
pdf - Open Assembly
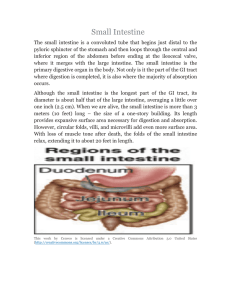
... duodenum. The jejunum is the next portion (3.5 - 5.5 ft or 110-170 cm) of the small intestine and is responsible for the absorption of a majority of nutrients. In the last section of the small intestine, the ileum, vitamin B12 and bile salts are absorbed as well as materials not absorbed by the jeju ...
... duodenum. The jejunum is the next portion (3.5 - 5.5 ft or 110-170 cm) of the small intestine and is responsible for the absorption of a majority of nutrients. In the last section of the small intestine, the ileum, vitamin B12 and bile salts are absorbed as well as materials not absorbed by the jeju ...
Nutrition & Digestion Review Power Point
... 6. Identify the nutrient being described: d. Made of amino acids • proteins e. Stores energy • Lipids/fat f. Makes up most of the body • water ...
... 6. Identify the nutrient being described: d. Made of amino acids • proteins e. Stores energy • Lipids/fat f. Makes up most of the body • water ...
The Digestive System
... Gastric enzymes: Pepsin, from gastric glands – begins protein digestion. Lipase, from gastric glands – begins fat digestion. Pancreatic enzymes: Amylase, from pancreas – breaks down starch and glycogen into disaccharides. Lipase, from pancreas – breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol. Nuclea ...
... Gastric enzymes: Pepsin, from gastric glands – begins protein digestion. Lipase, from gastric glands – begins fat digestion. Pancreatic enzymes: Amylase, from pancreas – breaks down starch and glycogen into disaccharides. Lipase, from pancreas – breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol. Nuclea ...
INTRODUCTION TO THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... proteins), and converts the gastric contents to a semiliquid mass called chyme, thus preparing it for further digestion in the small intestine. Gastric juice is a variable mixture of water, hydrochloric acid, electrolytes (sodium, potassium, calcium, phosphate, sulfate, and bicarbonate), and organic ...
... proteins), and converts the gastric contents to a semiliquid mass called chyme, thus preparing it for further digestion in the small intestine. Gastric juice is a variable mixture of water, hydrochloric acid, electrolytes (sodium, potassium, calcium, phosphate, sulfate, and bicarbonate), and organic ...
Part 1: Overview of the Digestive System Digestive System: 2 parts
... 9 MATA: Helps breakdown lipids. A pepsin B bile C lipase D trypsin ...
... 9 MATA: Helps breakdown lipids. A pepsin B bile C lipase D trypsin ...
Bio 20 6.2 6.3 notes
... The material that remains in the small intestine after nutrients are absorbed enters the last part of the digestive system : the large intestine. 1. Why is it called LARGE if it is so much smaller that the small intestine? 2. Does digestion occur in the large intestine? 3. What is the main function ...
... The material that remains in the small intestine after nutrients are absorbed enters the last part of the digestive system : the large intestine. 1. Why is it called LARGE if it is so much smaller that the small intestine? 2. Does digestion occur in the large intestine? 3. What is the main function ...
Bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Different molecular forms of bile acids can be synthesized in the liver by different species. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine in the liver, forming bile salts.Primary bile acids are those synthesized by the liver. Secondary bile acids result from bacterial actions in the colon. In humans, taurocholic acid and glycocholic acid (derivatives of cholic acid) and taurochenodeoxycholic acid and glycochenodeoxycholic acid (derivatives of chenodeoxycholic acid) are the major bile salts in bile and are roughly equal in concentration. The conjugated salts of their 7-alpha-dehydroxylated derivatives, deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid, are also found, with derivatives of cholic, chenodeoxycholic and deoxycholic acids accounting for over 90% of human biliary bile acids.Bile acids comprise about 80% of the organic compounds in bile (others are phospholipids and cholesterol). An increased secretion of bile acids produces an increase in bile flow. The main function of bile acids is to facilitate the formation of micelles, which promotes digestion and absorption of dietary fat, but they are increasingly being shown to have hormonal actions throughout the body.