An introduction to Optics
... two media, or equivalently, to the opposite ratio of the indices of refraction (n2 / n1): In optics, refraction is a phenomenon that often occurs when waves travel from a medium with a given refractive index to a medium with another at an oblique angle. At the boundary between the media, the wave's ...
... two media, or equivalently, to the opposite ratio of the indices of refraction (n2 / n1): In optics, refraction is a phenomenon that often occurs when waves travel from a medium with a given refractive index to a medium with another at an oblique angle. At the boundary between the media, the wave's ...
SWIR (Short Wave Infrared) to Visible Image Up
... thus, full imaging capability is feasible. This wavelength up-conversion is carried out through a linear conversion and with relatively high conversion efficiency, where an external electric field is induced to supplement the energy difference between the SWIR energy absorbed and the visible light e ...
... thus, full imaging capability is feasible. This wavelength up-conversion is carried out through a linear conversion and with relatively high conversion efficiency, where an external electric field is induced to supplement the energy difference between the SWIR energy absorbed and the visible light e ...
PH 481 - Physics | Oregon State University
... To measure the reflected laser power, you will use a Thor Labs photodetector with a 10 kresistor at the output. You can then measure the voltage with the Fluke multimeter. A diagram of the detector circuit is shown below. The 22V battery reverse biases the photodiode and forces the photo-generated ...
... To measure the reflected laser power, you will use a Thor Labs photodetector with a 10 kresistor at the output. You can then measure the voltage with the Fluke multimeter. A diagram of the detector circuit is shown below. The 22V battery reverse biases the photodiode and forces the photo-generated ...
20170327_AH_Interference
... situation is similar to that which we saw in the previous Topic. If the path difference is a whole number of wavelengths (λ, 2λ, 3λ...) then the two waves will arrive in phase. If the path difference is an odd number of half wavelengths (λ/2, 3λ/2, 5λ/2...) then the two waves arrive out of phase at ...
... situation is similar to that which we saw in the previous Topic. If the path difference is a whole number of wavelengths (λ, 2λ, 3λ...) then the two waves will arrive in phase. If the path difference is an odd number of half wavelengths (λ/2, 3λ/2, 5λ/2...) then the two waves arrive out of phase at ...
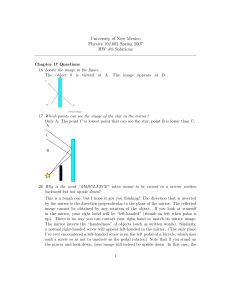
HW #8 Solutions
... (plus absorbed intensity, if any) is equal to the incident intensity. 15 Waves that are refracted towards the normal at a boundary have a shorter wavelength than the wave incident to the boundary. What does this say about the speed of light in glass versus air? Since the frequency is constant, the r ...
... (plus absorbed intensity, if any) is equal to the incident intensity. 15 Waves that are refracted towards the normal at a boundary have a shorter wavelength than the wave incident to the boundary. What does this say about the speed of light in glass versus air? Since the frequency is constant, the r ...
08-Michelson
... pattern. When 100 have disappeared, record the new micrometer reading and calculate the mean wavelength. Repeat the procedure a few times and calculate an average. (You will probably need some practice for this. It is very easy to miss a fringe.) [Hint: To find the average distance, be sure to remem ...
... pattern. When 100 have disappeared, record the new micrometer reading and calculate the mean wavelength. Repeat the procedure a few times and calculate an average. (You will probably need some practice for this. It is very easy to miss a fringe.) [Hint: To find the average distance, be sure to remem ...
Plane mirrors
... Reflection Reflection- occurs when an object or wave bounces back off a surface through which it cannot pass. Law of Reflection- all waves obey this law. 1. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. II. Mirrors 1. There are 3 types of mirrors: Plane, concave, and convex. A. Plane Mirror ...
... Reflection Reflection- occurs when an object or wave bounces back off a surface through which it cannot pass. Law of Reflection- all waves obey this law. 1. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. II. Mirrors 1. There are 3 types of mirrors: Plane, concave, and convex. A. Plane Mirror ...
Refractive Index Measurement Principle - K
... This ratio is the relative refractive index between the two media (n). As the absolute refractive indexes (relative to vacuum) of the media are: ...
... This ratio is the relative refractive index between the two media (n). As the absolute refractive indexes (relative to vacuum) of the media are: ...
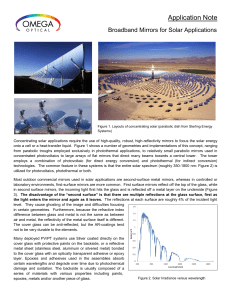
Broadband Mirrors for Solar Applications
... the light enters the mirror and again as it leaves. The reflections at each surface are roughly 4% of the incident light level. They cause ghosting of the image and difficulties focusing in certain geometries. Furthermore, because the refractive index difference between glass and metal is not the sa ...
... the light enters the mirror and again as it leaves. The reflections at each surface are roughly 4% of the incident light level. They cause ghosting of the image and difficulties focusing in certain geometries. Furthermore, because the refractive index difference between glass and metal is not the sa ...
Final Exam
... a) At what angle from the central axis will green light (550 nm) emerge in the first-order spectrum (m = 1)? b) Consider that 4,000 grating lines (N = 4,000) are used to disperse the incident light beam (for example, either the light beam width or the grating region is limited to 2-cm wide, whicheve ...
... a) At what angle from the central axis will green light (550 nm) emerge in the first-order spectrum (m = 1)? b) Consider that 4,000 grating lines (N = 4,000) are used to disperse the incident light beam (for example, either the light beam width or the grating region is limited to 2-cm wide, whicheve ...
ch.16_18 vocabulary
... Opaque-a material that absorbs or reflects light, not allowing objects to be seen through it Spectrum-the ordered arrangement of wavelengths Primary color-color from which other colors can be derived Secondary color-color formed by a pair of primary colors Complementary color-two colors of light tha ...
... Opaque-a material that absorbs or reflects light, not allowing objects to be seen through it Spectrum-the ordered arrangement of wavelengths Primary color-color from which other colors can be derived Secondary color-color formed by a pair of primary colors Complementary color-two colors of light tha ...
Human Vision: Electrophysiology and Psychophysics
... Several biological visual systems include one or several lenses ...
... Several biological visual systems include one or several lenses ...
Chapter 24
... higher index of refraction than the initial medium, the electromagnetic wave undergoes a phase change of 1800. See fig. 24.6 and 24.7 In figure 24.7 the two reflected beam interfere with each other. ...
... higher index of refraction than the initial medium, the electromagnetic wave undergoes a phase change of 1800. See fig. 24.6 and 24.7 In figure 24.7 the two reflected beam interfere with each other. ...
Design and Simulation of DPSS Laser with SHG for Material
... figures with optical thickness of 0.25 (above) and 0.5 (above) for both high and low coating layers, respectively ...
... figures with optical thickness of 0.25 (above) and 0.5 (above) for both high and low coating layers, respectively ...
Document
... Crown glass is type of optical glass used in lenses and other optical components. Crown glass is produced from alkali-lime silicates containing approximately 10% potassium oxide. It has low n (≈1.52) and low despersion (with Abbe Number around 60). Generally, this is any glass with Abbe numbers in t ...
... Crown glass is type of optical glass used in lenses and other optical components. Crown glass is produced from alkali-lime silicates containing approximately 10% potassium oxide. It has low n (≈1.52) and low despersion (with Abbe Number around 60). Generally, this is any glass with Abbe numbers in t ...
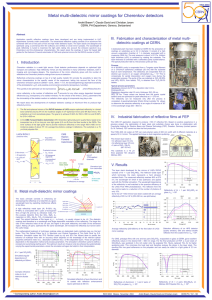
ppt
... Application specific reflective coatings have been developed and are being implemented in LHC experiments currently under construction. The broad-band reflective coating consists of an aluminum film combined with one or two pairs of low and high index dielectric layers. The layer stacks are designed ...
... Application specific reflective coatings have been developed and are being implemented in LHC experiments currently under construction. The broad-band reflective coating consists of an aluminum film combined with one or two pairs of low and high index dielectric layers. The layer stacks are designed ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.