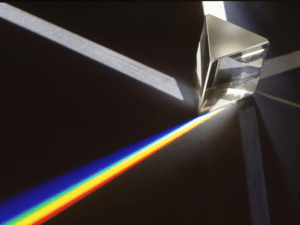
Monomolecular Layers and Light
... Equation 2 is the general wave function for the transmitted electric field (the evanescent wave we are interested in) where k is the propagation vector for the electric field and ω is the angular frequency. Equation 3 is the condition that arises when sinθi > nti by which our evanescent wave exists. ...
... Equation 2 is the general wave function for the transmitted electric field (the evanescent wave we are interested in) where k is the propagation vector for the electric field and ω is the angular frequency. Equation 3 is the condition that arises when sinθi > nti by which our evanescent wave exists. ...
Multispectral Optical Coatings Are Tough, Versatile for IR
... led to some technical challenges. At issue were the grid tension between the substrate and the coating (stress resulting from the different thermal coefficients of expansion between the substrate and the coating), the “eggshell effect” of the layer system, the tension between the dielectric and the ...
... led to some technical challenges. At issue were the grid tension between the substrate and the coating (stress resulting from the different thermal coefficients of expansion between the substrate and the coating), the “eggshell effect” of the layer system, the tension between the dielectric and the ...
Optics01
... described the law of reflection. He believed that vision involves rays going from the eyes to the object seen 965-1020Ibn-al-Haitham ~1267Roger Bacon (England) speed of light is finite and that it is propagated through a medium in a manner analogous to the propagation of sound 1303Bernard of Gordon ...
... described the law of reflection. He believed that vision involves rays going from the eyes to the object seen 965-1020Ibn-al-Haitham ~1267Roger Bacon (England) speed of light is finite and that it is propagated through a medium in a manner analogous to the propagation of sound 1303Bernard of Gordon ...
Topic 16: Geometric Optics
... Then, by using phonetics, Young gave sound values to each of the symbols. Applying this strategy to another inscription confirmed he was on the right track. However, after cracking the code, he ceased further work, calling his achievement the amusement of a few hours’ work. Young often left work unf ...
... Then, by using phonetics, Young gave sound values to each of the symbols. Applying this strategy to another inscription confirmed he was on the right track. However, after cracking the code, he ceased further work, calling his achievement the amusement of a few hours’ work. Young often left work unf ...
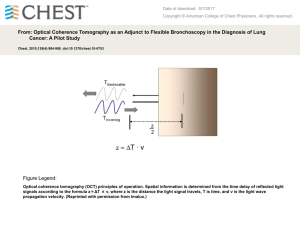
Experimental method for reliably establishing the refractive index of
... C. raja, a buprestid beetle, has an iridescent green colour over the whole of its body except for a red stripe on each elytral wing (Fig. 1). It displays the normal iridescence associated with conventional multilayers; its peak reflected colour reduces in wavelength as the angle of incidence increas ...
... C. raja, a buprestid beetle, has an iridescent green colour over the whole of its body except for a red stripe on each elytral wing (Fig. 1). It displays the normal iridescence associated with conventional multilayers; its peak reflected colour reduces in wavelength as the angle of incidence increas ...
RAY OPTICS notes
... The angle of reflection (i.e., the angle between reflected ray and the normal to the reflecting surface or the mirror) equals the angle of incidence (angle between incident ray and the normal). ...
... The angle of reflection (i.e., the angle between reflected ray and the normal to the reflecting surface or the mirror) equals the angle of incidence (angle between incident ray and the normal). ...
Total Internal Reflection Microscopy
... mounting in the TIRM apparatus. Similarly, dilution of surfactant-stabilized particles might cause desorption of the ionic surfactant, loss of charge, and sticking of the particles. This can be avoided by using sulfonated or carboxylated latexes having covalently attached charges; or the particles m ...
... mounting in the TIRM apparatus. Similarly, dilution of surfactant-stabilized particles might cause desorption of the ionic surfactant, loss of charge, and sticking of the particles. This can be avoided by using sulfonated or carboxylated latexes having covalently attached charges; or the particles m ...
Chapter 7 – Lecture Example Problems 1. A Wavelength of violet
... 8. Integrative Exercise: How many photons would be absorbed by 325mL of coffee that is heated from 22.3oC to 45.5oC in a microwave oven? The microwave operates at 12.4 cm, the density of the coffee is 0.997g/mL, and the specific heat of the coffee is 4.184 J/goC. ...
... 8. Integrative Exercise: How many photons would be absorbed by 325mL of coffee that is heated from 22.3oC to 45.5oC in a microwave oven? The microwave operates at 12.4 cm, the density of the coffee is 0.997g/mL, and the specific heat of the coffee is 4.184 J/goC. ...
Part 1
... (a) How far is the lens from the bug if you get the maximum useful angular mag? (b) What is the maximum useful mag? (c) What is the lateral mag? (d) How long does the bug look to you? Suppose you now move the lens so that it is 4.8 cm from the bug. (e) How far is the image of the bug from you? (f) W ...
... (a) How far is the lens from the bug if you get the maximum useful angular mag? (b) What is the maximum useful mag? (c) What is the lateral mag? (d) How long does the bug look to you? Suppose you now move the lens so that it is 4.8 cm from the bug. (e) How far is the image of the bug from you? (f) W ...
Integrated Optics: Guiding and manipulating light for device
... curiosity. The light behaves as wave and also as particle called photon. It has four primary parameters namely intensity, frequency or wavelength, polarisation and phase. It travels in a straight line unless the space-time itself is curved or the path is altered by means of external optical componen ...
... curiosity. The light behaves as wave and also as particle called photon. It has four primary parameters namely intensity, frequency or wavelength, polarisation and phase. It travels in a straight line unless the space-time itself is curved or the path is altered by means of external optical componen ...
chapter35
... light makes with the normal ( 2 in the diagram) is called the angle of refraction. The incident ray, the reflected ray, the refracted ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane. The reason for this bent is because light travels at different speeds in different medium: ...
... light makes with the normal ( 2 in the diagram) is called the angle of refraction. The incident ray, the reflected ray, the refracted ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane. The reason for this bent is because light travels at different speeds in different medium: ...
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Grating Interference by Thin
... incident ray • Ray 2, which is reflected from the lower surface, undergoes no phase change with respect to the incident wave ...
... incident ray • Ray 2, which is reflected from the lower surface, undergoes no phase change with respect to the incident wave ...
1 Macleod ‐ Thin Film Optics
... Now let the thickness of the film be increased by one half wave. The first beam returning to the front surface now has an increase in its path of one wavelength and so the earlier phase condition is undisturbed. The next beam will acquire an extra two wavelengths and so on It is easy to see that ...
... Now let the thickness of the film be increased by one half wave. The first beam returning to the front surface now has an increase in its path of one wavelength and so the earlier phase condition is undisturbed. The next beam will acquire an extra two wavelengths and so on It is easy to see that ...
Student Checklist
... ALL mastery checks should be completed, demonstrating mastery (≥ 80%), by the dates indicated. If they are not completed by this time they must be completed after school. Check-Ins must also be completed by the dates indicated. ...
... ALL mastery checks should be completed, demonstrating mastery (≥ 80%), by the dates indicated. If they are not completed by this time they must be completed after school. Check-Ins must also be completed by the dates indicated. ...
Facts About Ultra Violet (UV) Lights
... that, it falls steadily even though it is giving off a soft UV glow. An average life expectancy for an UV bulb is 7,500 hours. Turning the fixture on and off more than once every 8 hours will diminish the longevity of the bulb. There are factors that will influence sensitivity of bacteria to UV. Hig ...
... that, it falls steadily even though it is giving off a soft UV glow. An average life expectancy for an UV bulb is 7,500 hours. Turning the fixture on and off more than once every 8 hours will diminish the longevity of the bulb. There are factors that will influence sensitivity of bacteria to UV. Hig ...
Optics and Optoelectronics
... ray and wave optics, physical optics phenomena, as well as raise understanding about the close connection between optics and electronics (1) Understanding of ray and and wave approximation used for description of optical phenomenon (2) Ability to solve problems in optics and optoelectronics using ma ...
... ray and wave optics, physical optics phenomena, as well as raise understanding about the close connection between optics and electronics (1) Understanding of ray and and wave approximation used for description of optical phenomenon (2) Ability to solve problems in optics and optoelectronics using ma ...
File
... 1. A light wave enters from air into glass. How will1the following be affected? i) energy of the wave & ii) frequency of the wave. 2. A man is looking vertically down a tank full of water. The depth of tank appears to be 9m to him. What is the real depth of the tank? The ref. Index of water is 4/3. ...
... 1. A light wave enters from air into glass. How will1the following be affected? i) energy of the wave & ii) frequency of the wave. 2. A man is looking vertically down a tank full of water. The depth of tank appears to be 9m to him. What is the real depth of the tank? The ref. Index of water is 4/3. ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.