Reflection and Mirrors
... Have you ever seen a large, round mirror high in the corner of a store? The mirror enables workers at the store to see places they cannot see with a plane mirror. A mirror that curves outward, like the back of a spoon, is called a convex mirror. Light rays diverge, or spread apart, after they strike ...
... Have you ever seen a large, round mirror high in the corner of a store? The mirror enables workers at the store to see places they cannot see with a plane mirror. A mirror that curves outward, like the back of a spoon, is called a convex mirror. Light rays diverge, or spread apart, after they strike ...
6.1 Electromagnetic Waves
... propagation is given by E×H. The radiant flux density transmitted in the z-direction is given by ExHy in units of W m-2. When intensity is used the flux is given by photons s-1 m-2. ...
... propagation is given by E×H. The radiant flux density transmitted in the z-direction is given by ExHy in units of W m-2. When intensity is used the flux is given by photons s-1 m-2. ...
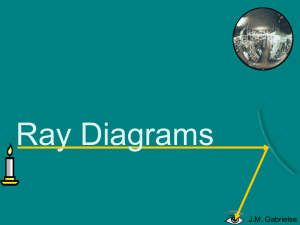
Mirrors form images by reflecting light.
... You have read that when light waves strike an object, they either pass through it or they bounce off its surface. Objects are made visible by light waves, or rays, bouncing off their surfaces. In section 3 you will see how the light waves create images inside the human eye. Light rays bounce off obj ...
... You have read that when light waves strike an object, they either pass through it or they bounce off its surface. Objects are made visible by light waves, or rays, bouncing off their surfaces. In section 3 you will see how the light waves create images inside the human eye. Light rays bounce off obj ...
Martti Kauranen , 1182 (2013); DOI: 10.1126/science.1247622
... ing problem, a closer look at frequency dou- for forward SH generation is typically on the ones (6). Nonlinear experiments on metamabling, or second harmonic (SH) generation, is order of 10 µm, but is only about 100 nm in the terials in the optical regime have mainly been helpful. A wave at the fund ...
... ing problem, a closer look at frequency dou- for forward SH generation is typically on the ones (6). Nonlinear experiments on metamabling, or second harmonic (SH) generation, is order of 10 µm, but is only about 100 nm in the terials in the optical regime have mainly been helpful. A wave at the fund ...
Is the speed of light in free
... • Delay exists for any form of structuring (inc OAM) • The delay is proportional to the square of the numerical aperture, therefore small at long (low NA) range ...
... • Delay exists for any form of structuring (inc OAM) • The delay is proportional to the square of the numerical aperture, therefore small at long (low NA) range ...
Transparent mirrors: rays, waves and localization
... 1994, Erdös 1982). It is a well known consequence of the theory of products of random matrices (Furstenberg 1963) that for large N the exponential describes not only the average decay but also the decay for almost all individual stacks. Many studies have explored the application of this theory to t ...
... 1994, Erdös 1982). It is a well known consequence of the theory of products of random matrices (Furstenberg 1963) that for large N the exponential describes not only the average decay but also the decay for almost all individual stacks. Many studies have explored the application of this theory to t ...
4 Lab 1: Scattering and Reflection of Polarized Light
... When θi > θc , there is no real (in the mathematical sense) solution for the angle of refraction and all of the incident light is reflected into the medium with index n1 . The phenomenon of total internal reflection is important for fiber optic communication technology because one would like the lig ...
... When θi > θc , there is no real (in the mathematical sense) solution for the angle of refraction and all of the incident light is reflected into the medium with index n1 . The phenomenon of total internal reflection is important for fiber optic communication technology because one would like the lig ...
A simple method for Bragg diffraction in volume holographic gratings Heifetz,
... processing systems based on volume gratings are currently under development.1–5 Other applications include polarization optics,6–8 beam splitters and combiners,9,10 narrowband spectral filters for optical communications,11–13 and intracavity Bragg gratings for various types of lasers.14–16 A rigorou ...
... processing systems based on volume gratings are currently under development.1–5 Other applications include polarization optics,6–8 beam splitters and combiners,9,10 narrowband spectral filters for optical communications,11–13 and intracavity Bragg gratings for various types of lasers.14–16 A rigorou ...
Chapter 4 Many properties of light can be understood using a wave
... The process in which light or another type of wave interacts with a surface and is sent back from the surface. ...
... The process in which light or another type of wave interacts with a surface and is sent back from the surface. ...
Highly transmissive luminescent down
... production of transparent layers with tunable absorption and emission bands [9, 10]. Such layers can be adjusted to specific photovoltaic devices and raise their overall efficiency. However, both material types share such disadvantages as high re-absorption, followed by luminescence efficiency drop ...
... production of transparent layers with tunable absorption and emission bands [9, 10]. Such layers can be adjusted to specific photovoltaic devices and raise their overall efficiency. However, both material types share such disadvantages as high re-absorption, followed by luminescence efficiency drop ...
File - SPHS Devil Physics
... Brewster found that the degree to which reflected light was polarized was dependent on the angle of incidence and angle of refraction He also found that reflected light was 100% polarized when the angle between reflected light and refracted light was 90° ...
... Brewster found that the degree to which reflected light was polarized was dependent on the angle of incidence and angle of refraction He also found that reflected light was 100% polarized when the angle between reflected light and refracted light was 90° ...
doc
... broad range of different colors. So, when white light strikes an object, it causes a multiplicity of responses. By contrast laser light provokes a far more limited set of reactions. This allows scientists to use it to measure the physical properties of materials with great precision. Ordinary lasers ...
... broad range of different colors. So, when white light strikes an object, it causes a multiplicity of responses. By contrast laser light provokes a far more limited set of reactions. This allows scientists to use it to measure the physical properties of materials with great precision. Ordinary lasers ...
Light and optics
... satellite, which, from time to time, sweeps the ground below it with radio waves, penetrating fog, haze, clouds and rain. Their reflection back to the satellite give scientists information they can use in their studies of the Earth. Monitoring ice flows, which can endanger ships Search possible ...
... satellite, which, from time to time, sweeps the ground below it with radio waves, penetrating fog, haze, clouds and rain. Their reflection back to the satellite give scientists information they can use in their studies of the Earth. Monitoring ice flows, which can endanger ships Search possible ...
X-ray Optics - Studentportalen
... An interesting recent development in this context is that one can modify the structures in detail to influence the ‘diffraction pattern’. Here, more of the primary intensity is lost, but one can reduce effects of higher order diffraction. The idea is suggested in……. ...
... An interesting recent development in this context is that one can modify the structures in detail to influence the ‘diffraction pattern’. Here, more of the primary intensity is lost, but one can reduce effects of higher order diffraction. The idea is suggested in……. ...
Wireless Communications and Networks
... Fiber-optic cables are substantially lighter in weight and occupy much less volume than copper cables with the same information capacity. Fiberoptic cables are being used to relieve congested underground ducts in metropolitan and suburban areas. For example, a 3-in. diameter telephone cable consisti ...
... Fiber-optic cables are substantially lighter in weight and occupy much less volume than copper cables with the same information capacity. Fiberoptic cables are being used to relieve congested underground ducts in metropolitan and suburban areas. For example, a 3-in. diameter telephone cable consisti ...
Effect of Macroscopic Structure in Iridescent Color
... periodicity comparable with the wavelength of visible light and are thought to be the origin of optical interference. The spongy medullary structure responsible for the structural color was also found in many kinds of birds and analyzed with 2D Fourier transformation (AUBER , 1957; DYCK, 1971; P RUM ...
... periodicity comparable with the wavelength of visible light and are thought to be the origin of optical interference. The spongy medullary structure responsible for the structural color was also found in many kinds of birds and analyzed with 2D Fourier transformation (AUBER , 1957; DYCK, 1971; P RUM ...
Physics116_L22
... Covers material in Chs. 25 - 27 (not including material from ch. 28 yesterday) ...
... Covers material in Chs. 25 - 27 (not including material from ch. 28 yesterday) ...
Mirrors form images by reflecting light.
... You have read that when light waves strike an object, they either pass through it or they bounce off its surface. Objects are made visible by light waves, or rays, bouncing off their surfaces. In section 3 you will see how the light waves create images inside the human eye. Light rays bounce off obj ...
... You have read that when light waves strike an object, they either pass through it or they bounce off its surface. Objects are made visible by light waves, or rays, bouncing off their surfaces. In section 3 you will see how the light waves create images inside the human eye. Light rays bounce off obj ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.