Synthesis and Characterization of Optically Active Zn
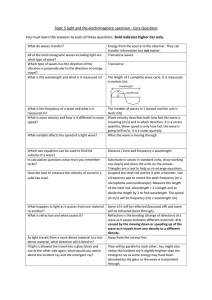
... to ~ 62% at wavelength of 550nm. Furthermore, the refractive indices for nonocomposites were calculated by the Fresnel equation. The dispersion of the refractive index is shown in Fig. 2(II). The calculated refractive index of silica-titania matrix is 1.33 at 550 nm, which is increased up to 1.39 at ...
... to ~ 62% at wavelength of 550nm. Furthermore, the refractive indices for nonocomposites were calculated by the Fresnel equation. The dispersion of the refractive index is shown in Fig. 2(II). The calculated refractive index of silica-titania matrix is 1.33 at 550 nm, which is increased up to 1.39 at ...
High Harmonic Generation
... barrier into the continuum. This is called first step. 2. The laser field accelerates the electron away from the parent ion and drives it back when the electric field sign is changed. During this process the electron gains kinetic energy from the laser electric field. This is step two. 3. In step th ...
... barrier into the continuum. This is called first step. 2. The laser field accelerates the electron away from the parent ion and drives it back when the electric field sign is changed. During this process the electron gains kinetic energy from the laser electric field. This is step two. 3. In step th ...
Topic 5 Core Questions
... Ritter also split visible light up but looked for wave energy at the other end of the spectrum (the other side of the violet light). He tried to detect the presence of wave energy using silver chloride that he knew reacted with violet light faster than red light. He found that an unseen energy at th ...
... Ritter also split visible light up but looked for wave energy at the other end of the spectrum (the other side of the violet light). He tried to detect the presence of wave energy using silver chloride that he knew reacted with violet light faster than red light. He found that an unseen energy at th ...
Word 97 Format
... RESULTS. For the theoretical curve, the normalized detected power is given by (see Figure 2 for definition of angles): ...
... RESULTS. For the theoretical curve, the normalized detected power is given by (see Figure 2 for definition of angles): ...
Light - Effingham County Schools
... transparent covering on your eyeball called the cornea. The cornea causes light rays to bend so that they converge. The light then passes through an opening called the pupil. Behind the pupil is a flexible convex lens. The lens helps focus light rays so that a sharp image is formed on your retina. T ...
... transparent covering on your eyeball called the cornea. The cornea causes light rays to bend so that they converge. The light then passes through an opening called the pupil. Behind the pupil is a flexible convex lens. The lens helps focus light rays so that a sharp image is formed on your retina. T ...
DOC - math for college
... towards the camera (i.e. towards the viewer). Assume a 3D coordinate system centered at the camera with x -direction along the horizontal direction, y -direction along the vertical direction, and z -direction is away from the camera into the scene. Then the actual surface normal of the middle of the ...
... towards the camera (i.e. towards the viewer). Assume a 3D coordinate system centered at the camera with x -direction along the horizontal direction, y -direction along the vertical direction, and z -direction is away from the camera into the scene. Then the actual surface normal of the middle of the ...
Universal Description of Spherical Aberration Free Lenses
... It was known to René Descartes as early as 1637 that aspherical surfaces are required to convert plane waves into spherical waves and vice versa. In the short wavelength limit of geometric optics, the right conic surface can bring all parallel incident light rays to a single common focus point. Mos ...
... It was known to René Descartes as early as 1637 that aspherical surfaces are required to convert plane waves into spherical waves and vice versa. In the short wavelength limit of geometric optics, the right conic surface can bring all parallel incident light rays to a single common focus point. Mos ...
Generalized Laws of Reflection and Refraction
... propagation to shape light beams. New degrees of freedom are attained by introducing abrupt phase changes over the scale of the wavelength. A two-dimensional array of optical resonators with spatially varying phase response and subwavelength separation can imprint such phase discontinuities on propa ...
... propagation to shape light beams. New degrees of freedom are attained by introducing abrupt phase changes over the scale of the wavelength. A two-dimensional array of optical resonators with spatially varying phase response and subwavelength separation can imprint such phase discontinuities on propa ...
Introduction to Light Microscopy Introduction Light microscopes are
... contrast microscope was the first contrast generating system readily available for the study of phase objects. Many kinds of microscopes are now available for generating contrast. We will be working with the phase contrast microscope in this lab. Light Waves and What Phase Objects Do to Them To unde ...
... contrast microscope was the first contrast generating system readily available for the study of phase objects. Many kinds of microscopes are now available for generating contrast. We will be working with the phase contrast microscope in this lab. Light Waves and What Phase Objects Do to Them To unde ...
Refractive index dispersion and related properties in fluorine doped
... of 0.2 have been achieved with only 3 wt. % addition of fluorine to the glass.2 Bulk measurement of refractive index dispersion continues to be of importance for accurate characterization of dispersion in glasses used in lightguides. Although techniques have been developed which measure the dispersi ...
... of 0.2 have been achieved with only 3 wt. % addition of fluorine to the glass.2 Bulk measurement of refractive index dispersion continues to be of importance for accurate characterization of dispersion in glasses used in lightguides. Although techniques have been developed which measure the dispersi ...
Document
... A reflecting surface is one that is highly polished, opaque and coated with special reflective materials. The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The incident ray is the line AO, the reflected ray is OB and ON is the normal to the reflecting surf ...
... A reflecting surface is one that is highly polished, opaque and coated with special reflective materials. The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The incident ray is the line AO, the reflected ray is OB and ON is the normal to the reflecting surf ...
On-chip gas detection in silicon optical microcavities
... Interaction of light with matter in a gaseous state is an important functionality for sensors as well as for addressing isolated atomic or molecular states for quantum optic applications [1]. The vast majority of room-temperature experiments involving light-matter interactions in integrated photonic ...
... Interaction of light with matter in a gaseous state is an important functionality for sensors as well as for addressing isolated atomic or molecular states for quantum optic applications [1]. The vast majority of room-temperature experiments involving light-matter interactions in integrated photonic ...
A. Menegolli
... it is present a strong asymmetry going from -45° to +45°, maybe due to the shadow from the support of the sample; the two contributions could not properly have been disentangled, so that it was possible just to have an estimate of the opening angle of the diffusive reflection (~ 30° - FWHM) IPRD06 - ...
... it is present a strong asymmetry going from -45° to +45°, maybe due to the shadow from the support of the sample; the two contributions could not properly have been disentangled, so that it was possible just to have an estimate of the opening angle of the diffusive reflection (~ 30° - FWHM) IPRD06 - ...
1 Optical Phenomena
... Above the ground are layers of air with different indexes of refraction. The light from the tree reaches the observer in a straight line path A. Other light rays directed toward the ground are bend because the hot air above the ground has a lower index of refraction and the light bend in the curved ...
... Above the ground are layers of air with different indexes of refraction. The light from the tree reaches the observer in a straight line path A. Other light rays directed toward the ground are bend because the hot air above the ground has a lower index of refraction and the light bend in the curved ...
Polarization Beam Splitter Based on Self
... 4. Conclusions We have proposed and numerically demonstrated a photonic crystal based polarization beam splitter with high splitting efficiency, large separation angle and low crosstalk at the optical communication wavelengths. The transmission and reflection efficiencies of the device for TE and TM ...
... 4. Conclusions We have proposed and numerically demonstrated a photonic crystal based polarization beam splitter with high splitting efficiency, large separation angle and low crosstalk at the optical communication wavelengths. The transmission and reflection efficiencies of the device for TE and TM ...
Intensity-dependent change in polarization state of light in normal
... by many authors. Maker et al [1,2] reported that when strong elliptically polarized light propagates through a lossless isotropic nonlinear medium, self-rotation of the polarization ellipse occurs. Prakash and Chandra [3] showed that if this Kerr medium is lossy, the ellipticity also changes; only p ...
... by many authors. Maker et al [1,2] reported that when strong elliptically polarized light propagates through a lossless isotropic nonlinear medium, self-rotation of the polarization ellipse occurs. Prakash and Chandra [3] showed that if this Kerr medium is lossy, the ellipticity also changes; only p ...
1.3.6 Electromagnetic radiation Name Symbol Definition SI
... The same information may be conveyed by quoting either the specific optical rotatory power α/γl, or the molar optical rotatory power α/cl, where γ is the mass concentration, c is the amount (of substance) concentration, and l is the path length. Most tabulations give the specific optical rotatory po ...
... The same information may be conveyed by quoting either the specific optical rotatory power α/γl, or the molar optical rotatory power α/cl, where γ is the mass concentration, c is the amount (of substance) concentration, and l is the path length. Most tabulations give the specific optical rotatory po ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.