File
... meaning “all the earth”), and over time have been drifting apart. Continental Drift gave an explanation to finding similar organisms, rock types and past glacial activity on several different continents – in Wegener’s time and today. ...
... meaning “all the earth”), and over time have been drifting apart. Continental Drift gave an explanation to finding similar organisms, rock types and past glacial activity on several different continents – in Wegener’s time and today. ...
Unit 11 Oceans Concepts of Earth Science Key Concepts and
... 2. Describe the two theories for how Earth’s oceans developed. 3. List the common dissolved gases that are found in the ocean according to abundance. List the common solids that are found in the ocean according to abundance. How does temperature impact the amount of dissolved gasses and salinity? 4. ...
... 2. Describe the two theories for how Earth’s oceans developed. 3. List the common dissolved gases that are found in the ocean according to abundance. List the common solids that are found in the ocean according to abundance. How does temperature impact the amount of dissolved gasses and salinity? 4. ...
Part 2 - cosee now
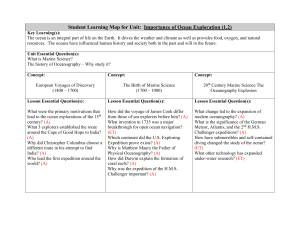
... The ocean is an integral part of life on the Earth. It drives the weather and climate as well as provides food, oxygen, and natural resources. The oceans have influenced human history and society both in the past and will in the future. Unit Essential Question(s): What is Marine Science? The history ...
... The ocean is an integral part of life on the Earth. It drives the weather and climate as well as provides food, oxygen, and natural resources. The oceans have influenced human history and society both in the past and will in the future. Unit Essential Question(s): What is Marine Science? The history ...
The Seafloor (69)
... • Mid-ocean ridges can be found at the bottom of all ocean basins. They form a continuous underwater ridge approximately 70,000 km long. • A mid-ocean ridge is the area in an ocean basin where new ocean floor is formed ...
... • Mid-ocean ridges can be found at the bottom of all ocean basins. They form a continuous underwater ridge approximately 70,000 km long. • A mid-ocean ridge is the area in an ocean basin where new ocean floor is formed ...
Free Flash Cards - MyClass at TheInspiredInstructor.com
... A tide in which the ocean water moves up the shore in areas where the moon is directly over that part of the ocean and in areas on the opposite side of the earth. ...
... A tide in which the ocean water moves up the shore in areas where the moon is directly over that part of the ocean and in areas on the opposite side of the earth. ...
sustained ocean observations from merchant marine vessels
... monitoring the interior of the ocean. While we do so to a limited extent today, with instrumentation and data management techniques designed and optimized for these platforms we could open up an entirely new dimension to ocean observation. The following material was presented to the US NSF last year ...
... monitoring the interior of the ocean. While we do so to a limited extent today, with instrumentation and data management techniques designed and optimized for these platforms we could open up an entirely new dimension to ocean observation. The following material was presented to the US NSF last year ...
Chapter 23
... In 1855 Matthew F. Murray published the first known textbook on the oceans with information that he collected from Navy records about the currents, winds, depths and weather conditions. In 1872 the scientists aboard the H.M.S. Challenger made some discoveries that we still use today. In WWII scienti ...
... In 1855 Matthew F. Murray published the first known textbook on the oceans with information that he collected from Navy records about the currents, winds, depths and weather conditions. In 1872 the scientists aboard the H.M.S. Challenger made some discoveries that we still use today. In WWII scienti ...
Oceans: Chapters 19, 20, and 21
... 7. Gases dissolve most easily in water that is ____. 8. Ocean water temperature depends on two things: the solar energy an area receives and ____. 9. As deep ocean water becomes colder, it also becomes ____. 10. What two factors affect the salinity of ocean water? 11. How do marine organisms help ba ...
... 7. Gases dissolve most easily in water that is ____. 8. Ocean water temperature depends on two things: the solar energy an area receives and ____. 9. As deep ocean water becomes colder, it also becomes ____. 10. What two factors affect the salinity of ocean water? 11. How do marine organisms help ba ...
The Ocean
... • Average depth=3720 meters • Found at border of continental crust and oceanic crust • Sometimes slope is more like a steep cliff ...
... • Average depth=3720 meters • Found at border of continental crust and oceanic crust • Sometimes slope is more like a steep cliff ...
The Ocean Floor
... 4000 meters (3-25k ft)below the surface. Brrrr, you wouldn't want to visit the midnight zone. Temperatures are close to freezing The water is pitch-black Food is scarce ...
... 4000 meters (3-25k ft)below the surface. Brrrr, you wouldn't want to visit the midnight zone. Temperatures are close to freezing The water is pitch-black Food is scarce ...
mb3ech02-a - Chaparral Star Academy
... The Ocean and Marginal Seas • The world’s oceans: oceans and marginal seas • Oceans cover 71% of earth’s surface • Southern hemisphere 80%, Northern hemisphere 61% • 84% deeper than 2000m • Greatest depth ~ 11,000 m in Marianas Trench ...
... The Ocean and Marginal Seas • The world’s oceans: oceans and marginal seas • Oceans cover 71% of earth’s surface • Southern hemisphere 80%, Northern hemisphere 61% • 84% deeper than 2000m • Greatest depth ~ 11,000 m in Marianas Trench ...
Map Skills Using Globes
... Latitude lines run east and west just like the equator. They are also called parallel lines. Latitude is measured in degrees similar to the degrees for measuring temperature. () Latitude lines are used to measure how far north or south of the equator a location is. The equator is located at 0 line ...
... Latitude lines run east and west just like the equator. They are also called parallel lines. Latitude is measured in degrees similar to the degrees for measuring temperature. () Latitude lines are used to measure how far north or south of the equator a location is. The equator is located at 0 line ...
Slide 1
... The Growing Human Footprint on Coastal and Open-Ocean Biogeochemistry Science 328, 1512 ...
... The Growing Human Footprint on Coastal and Open-Ocean Biogeochemistry Science 328, 1512 ...
Ocean Topography
... known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. It is usually an oceanic spreading center, which is responsible for seafloor spreading. ...
... known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. It is usually an oceanic spreading center, which is responsible for seafloor spreading. ...
Here is an example formatted abstract
... Decadal change of the deep and upper ocean heat content of the north-east Atlantic KING, MCDONAGH, GARRY We examine the vertical distribution of trends in heat content of the north-east basin of the Atlantic Ocean since the late 1980s. The 2010 analysis of Purkey and Johnson identified this basin as ...
... Decadal change of the deep and upper ocean heat content of the north-east Atlantic KING, MCDONAGH, GARRY We examine the vertical distribution of trends in heat content of the north-east basin of the Atlantic Ocean since the late 1980s. The 2010 analysis of Purkey and Johnson identified this basin as ...
Seafloor Spreading Notes - mrs. villarreal`s orange team science
... • WHO: Discovered by Harry Hess- U.S. Geologist at Princeton, Navy Reservist • WHEN: 1950’s • WHERE: Pacific Ocean • WHAT: – The process by which new ocean crust is formed by the upwelling of magma at mid-ocean ridges. – Cause: Convection currents in the mantle. – Result: Existing/older ocean crust ...
... • WHO: Discovered by Harry Hess- U.S. Geologist at Princeton, Navy Reservist • WHEN: 1950’s • WHERE: Pacific Ocean • WHAT: – The process by which new ocean crust is formed by the upwelling of magma at mid-ocean ridges. – Cause: Convection currents in the mantle. – Result: Existing/older ocean crust ...
Changes in Ocean Geometry Over the Past Billion Years
... A Plate tectonic model tracing the evolution of the Arctic Ocean from 500 Ma to present A major Ocean—the Iapetus—existed roughly where the Arctic is now relative to other plates from 482-438 Ma. Up to 200 Ma, the ocean then closed up—reappearing around the same time as the Atlantic (~163 Ma) at the ...
... A Plate tectonic model tracing the evolution of the Arctic Ocean from 500 Ma to present A major Ocean—the Iapetus—existed roughly where the Arctic is now relative to other plates from 482-438 Ma. Up to 200 Ma, the ocean then closed up—reappearing around the same time as the Atlantic (~163 Ma) at the ...
Intro to Oceanography - pams
... • Oceanography is the study of the composition of the water, temperature/life zones, and ...
... • Oceanography is the study of the composition of the water, temperature/life zones, and ...
Landforms of the Ocean
... • The ocean floor contains all of the geographic features that can be found on the continents: Mountains, volcanoes, plains, valleys, and canyons. • These underwater landforms are many times taller, deeper, longer, and wider than those on dry land. ...
... • The ocean floor contains all of the geographic features that can be found on the continents: Mountains, volcanoes, plains, valleys, and canyons. • These underwater landforms are many times taller, deeper, longer, and wider than those on dry land. ...
Adjectives Using Ocean Facts
... deepest waters in the world. The Marianas Trench is 36,198 feet deep! That’s almost seven miles! The Indian Ocean usually has gentle breezes. However, during the months from April to October, there is a chance that a monsoon will form over the ocean. Monsoons carry a lot of rain into India, sometime ...
... deepest waters in the world. The Marianas Trench is 36,198 feet deep! That’s almost seven miles! The Indian Ocean usually has gentle breezes. However, during the months from April to October, there is a chance that a monsoon will form over the ocean. Monsoons carry a lot of rain into India, sometime ...
History of Oceanography
... Created map of Earth that showed a portion of the Earth as a sphere on flat paper. Produced first world atlas Improved longitude/latitude system ...
... Created map of Earth that showed a portion of the Earth as a sphere on flat paper. Produced first world atlas Improved longitude/latitude system ...
The Southern Ocean Observing System (SOOS)
... of the ice sheets to sea level rise 3. The role of the ocean in the stability of the Antarctic ice sheet Southern Ocean overturning shapes the global ocean and its contribution to sea-level rise; circulation and climate 4. The future and consequences of Southern Ocean carbon uptake; 5. The future of ...
... of the ice sheets to sea level rise 3. The role of the ocean in the stability of the Antarctic ice sheet Southern Ocean overturning shapes the global ocean and its contribution to sea-level rise; circulation and climate 4. The future and consequences of Southern Ocean carbon uptake; 5. The future of ...
Seafloor notes
... When the lava hits the water, it cools quickly into solid rock, forming new___________________. ...
... When the lava hits the water, it cools quickly into solid rock, forming new___________________. ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 7 – Oceans Review Test Details
... 6. Where are the flattest regions on Earth located? 7. What is a trench? 8. Why is Earth called the water planet? 9. What is the largest ocean? How much water does it contain? 10. How would a glacial period during an ice age affect the continental shelf? 11. Review your “What is the Mystery Object” ...
... 6. Where are the flattest regions on Earth located? 7. What is a trench? 8. Why is Earth called the water planet? 9. What is the largest ocean? How much water does it contain? 10. How would a glacial period during an ice age affect the continental shelf? 11. Review your “What is the Mystery Object” ...
Unit 7 Chapter 23 Powerpoint
... In 1855 Matthew F. Murray published the first known textbook on the oceans with information that he collected from Navy records about the currents, winds, depths and weather conditions. In 1872 the scientists aboard the H.M.S. Challenger made some discoveries that we still use today. In WWII scienti ...
... In 1855 Matthew F. Murray published the first known textbook on the oceans with information that he collected from Navy records about the currents, winds, depths and weather conditions. In 1872 the scientists aboard the H.M.S. Challenger made some discoveries that we still use today. In WWII scienti ...
Indian Ocean

The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia on the north, on the west by Africa, on the east by Australia, and on the south by the Southern Ocean or, depending on definition, by Antarctica. It is named after India.The Indian Ocean is known as Ratnakara, ""the mine of gems"", in ancient Sanskrit literature and as Hind Mahasagar in Hindi and other Indian languages.