Nutrition - Cloudfront.net
... Calories are how we measure how much energy a food has. How many do each of the following nutrients have per gram? ...
... Calories are how we measure how much energy a food has. How many do each of the following nutrients have per gram? ...
PS2_Chapter_2_Notes_Framework_half_already_answered
... Minerals are inorganic elements needed for life and balanced nutrition. Minerals are classified as major or trace. People need larger amounts of major minerals and only very small amount of trace minerals. Minerals are part of body structures (like calcium in bones). They also help the body regulate ...
... Minerals are inorganic elements needed for life and balanced nutrition. Minerals are classified as major or trace. People need larger amounts of major minerals and only very small amount of trace minerals. Minerals are part of body structures (like calcium in bones). They also help the body regulate ...
How do living things take in nutrients, breathe, and
... for fighting infection and for using the stored energy in your body. It is generally found in citrus fruits and other vegetables like tomatoes and peppers. The B vitamins are important for building blood cells, nerve cells, and are vital for many of your body’s chemical reactions. These are present ...
... for fighting infection and for using the stored energy in your body. It is generally found in citrus fruits and other vegetables like tomatoes and peppers. The B vitamins are important for building blood cells, nerve cells, and are vital for many of your body’s chemical reactions. These are present ...
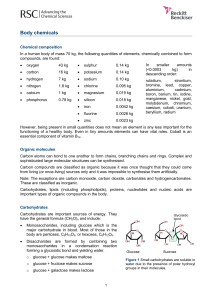
Body chemicals
... and a phosphate group. ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy carrier in cells has three phosphates. Nucleic acids are formed from nucleotides. Phosphates and pentoses link through condensation reactions to form long chains. ...
... and a phosphate group. ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy carrier in cells has three phosphates. Nucleic acids are formed from nucleotides. Phosphates and pentoses link through condensation reactions to form long chains. ...
Biochemistry: the study of the chemical reactions of life
... Cell membranes are composed of a double layer of lipid molecules. In the diagram below, the "head" of a lipid molecule is a phosphate group and the "tail" is composed of two carbon chains. The middle part of the membrane composed of the "tails" is highly hydrophobic (lacking affinity for water) as o ...
... Cell membranes are composed of a double layer of lipid molecules. In the diagram below, the "head" of a lipid molecule is a phosphate group and the "tail" is composed of two carbon chains. The middle part of the membrane composed of the "tails" is highly hydrophobic (lacking affinity for water) as o ...
Nutritional Needs Name__________________________________
... included both fats and oils. 9. All lipids contain chemical chains called ______________ -______________ which contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. 10. Fatty acids that have as many hydrogen atoms as they can hold are called _______________ fatty acids. 11. Fatty acids that are missing one hydrogen ...
... included both fats and oils. 9. All lipids contain chemical chains called ______________ -______________ which contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. 10. Fatty acids that have as many hydrogen atoms as they can hold are called _______________ fatty acids. 11. Fatty acids that are missing one hydrogen ...
Why do we eat
... made up of amino acids. We need proteins in our diet because we break them down and use the amino acids to build various proteins that our bodies need -- hormone, enzyme, muscle fiber. We can use protein as a source of energy, but this is inefficient. Usually the body does not use proteins as an ene ...
... made up of amino acids. We need proteins in our diet because we break them down and use the amino acids to build various proteins that our bodies need -- hormone, enzyme, muscle fiber. We can use protein as a source of energy, but this is inefficient. Usually the body does not use proteins as an ene ...
unit-review-key
... substituted for animal fats in the diet. v. A common lipid that contains fatty acids is a triglyceride. Triglycerides (referred to as neutral fats) are glycerol linked to three fatty acids (in the shape of an “E”) by condensation reaction. III. Proteins i. Proteins are organic compounds composed mai ...
... substituted for animal fats in the diet. v. A common lipid that contains fatty acids is a triglyceride. Triglycerides (referred to as neutral fats) are glycerol linked to three fatty acids (in the shape of an “E”) by condensation reaction. III. Proteins i. Proteins are organic compounds composed mai ...
BIOCHEMISTRY
... • contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen • composed of MANY amino acid subunits • It is the arrangement of the amino acid that forms the primary structure of proteins. • The basic amino acid form has a carboxyl group on one end, a methyl group that only has one hydrogen in the m ...
... • contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen • composed of MANY amino acid subunits • It is the arrangement of the amino acid that forms the primary structure of proteins. • The basic amino acid form has a carboxyl group on one end, a methyl group that only has one hydrogen in the m ...
Essential Nutrients Overview Handout
... such as glucose, fructose, dextrose, and sucrose. Sugars are found naturally in fruits, milk, and some vegetables such as peas. Refined sugars from sugar beets and sugarcane are used for table sugar and as sweeteners in processed foods and home recipes. Starches are more complex carbohydrates. They ...
... such as glucose, fructose, dextrose, and sucrose. Sugars are found naturally in fruits, milk, and some vegetables such as peas. Refined sugars from sugar beets and sugarcane are used for table sugar and as sweeteners in processed foods and home recipes. Starches are more complex carbohydrates. They ...
NUTRITION You are what you eat!
... • LDL – bad: primary risk factor for heart attack (clog arteries) ...
... • LDL – bad: primary risk factor for heart attack (clog arteries) ...
English
... fats, vitamins, and minerals. 2. A good diet must include all six of these nutrients in proper amounts. 3. If any are insufficient then growth, reproduction, eggshell quality, egg production, egg size and other factors may be affected. ...
... fats, vitamins, and minerals. 2. A good diet must include all six of these nutrients in proper amounts. 3. If any are insufficient then growth, reproduction, eggshell quality, egg production, egg size and other factors may be affected. ...
How do living things take in nutrients, breathe, and
... for fighting infection and for using the stored energy in your body. It is generally found in citrus fruits and other vegetables like tomatoes and peppers. The B vitamins are important for building blood cells, nerve cells, and are vital for many of your body’s chemical reactions. These are present ...
... for fighting infection and for using the stored energy in your body. It is generally found in citrus fruits and other vegetables like tomatoes and peppers. The B vitamins are important for building blood cells, nerve cells, and are vital for many of your body’s chemical reactions. These are present ...
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Chapter Vocabulary
... 17. Sugars and starches are the two kinds of a. fats. c. carbohydrates. b. proteins. d. minerals. 18. What nutrients are made up of fatty acids and glycerol? a. carbohydrates c. fats b. proteins d. minerals 19. Inorganic nutrients that the body usually needs in small amounts are called a. minerals. ...
... 17. Sugars and starches are the two kinds of a. fats. c. carbohydrates. b. proteins. d. minerals. 18. What nutrients are made up of fatty acids and glycerol? a. carbohydrates c. fats b. proteins d. minerals 19. Inorganic nutrients that the body usually needs in small amounts are called a. minerals. ...
Answer Sheet
... The body uses simple sugar called glucose. Complex carbs are called starches. The body has to break complex carbs into simple carbs to be able to use them. 5. What does our body do with extra glucose? It is turned into glycogen and saved in the muscles and liver or turned to fat. 6. Why does our bod ...
... The body uses simple sugar called glucose. Complex carbs are called starches. The body has to break complex carbs into simple carbs to be able to use them. 5. What does our body do with extra glucose? It is turned into glycogen and saved in the muscles and liver or turned to fat. 6. Why does our bod ...
Nutrients Outline
... 1. Definition: _____________ that your body needs to keep going 2. Uses: fuel, _________________, repair, fights diseases 3. Types: carbs, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, water II. Carbohydrates A. Sugar 1. _________________ – simple sugar a. Simplest carb b. 1st choice for fuel c. Extra Glucose ...
... 1. Definition: _____________ that your body needs to keep going 2. Uses: fuel, _________________, repair, fights diseases 3. Types: carbs, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, water II. Carbohydrates A. Sugar 1. _________________ – simple sugar a. Simplest carb b. 1st choice for fuel c. Extra Glucose ...
Biology Chapter 6 Section 4 Test-The Building Blocks of Life
... 1. Examples of these large molecules that are formed by joining smaller organic molecules are carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. 2. All organic compounds contain ______________________. 3. These macromolecules provide energy and provide structural support in plants and other cells. 4. These ...
... 1. Examples of these large molecules that are formed by joining smaller organic molecules are carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. 2. All organic compounds contain ______________________. 3. These macromolecules provide energy and provide structural support in plants and other cells. 4. These ...
student-notes-copy-unit-review
... 1. ________________: a common storage form of glucose in plants (breads, pasta, potatoes) 2. ________________: a polysaccharide contained in the cell walls of ________________; gives strength and rigidity to plant cells. 3. ________________: a common storage form of glucose in animals (stored in the ...
... 1. ________________: a common storage form of glucose in plants (breads, pasta, potatoes) 2. ________________: a polysaccharide contained in the cell walls of ________________; gives strength and rigidity to plant cells. 3. ________________: a common storage form of glucose in animals (stored in the ...
Biochemistry power point
... CELLULOSE – A polysaccharide in the cell walls of plants -Cellulose we eat comes from vegetables, fruits, whole grain breads and cereals -Your body CANNOT break down, no nutritional value (fiber) ...
... CELLULOSE – A polysaccharide in the cell walls of plants -Cellulose we eat comes from vegetables, fruits, whole grain breads and cereals -Your body CANNOT break down, no nutritional value (fiber) ...
Chapter 2 Nutrition Study Questions
... fatty acids (90) • These are the result of taking a liquid fat and making it a solid through a process called hydrogenation. Hydrogenation of fat alters its physical properties and makes it stay fresh longer. • The disadvantage of hydrogenation is that it may be more harmful to a person’s health tha ...
... fatty acids (90) • These are the result of taking a liquid fat and making it a solid through a process called hydrogenation. Hydrogenation of fat alters its physical properties and makes it stay fresh longer. • The disadvantage of hydrogenation is that it may be more harmful to a person’s health tha ...
CARBOHYDRATES
... • If not immediately needed for ATP synthesis, they are converted into glycogen or fat ...
... • If not immediately needed for ATP synthesis, they are converted into glycogen or fat ...
Food: Our Body`s Source of Energy and Structural Materials
... Nothing but salted carrots last year, which meant that from September to Jun the skilly was plain carrot. This year it was black cabbage. The most nourishing time of the year June: then all vegetables came to an end and were replaced by groats (hulled and crushed oats or wheat). The worst time was J ...
... Nothing but salted carrots last year, which meant that from September to Jun the skilly was plain carrot. This year it was black cabbage. The most nourishing time of the year June: then all vegetables came to an end and were replaced by groats (hulled and crushed oats or wheat). The worst time was J ...
Nutritional requirements
... Lactose is called Milk sugar Sucrose is called cane sugar. Sports persons take glucose to get instant energy If we eat only rice, only carbohydrates are supplied to the body and body building materials (proteins) will be deficient. If we eat only proteins, body will be built up but for dai ...
... Lactose is called Milk sugar Sucrose is called cane sugar. Sports persons take glucose to get instant energy If we eat only rice, only carbohydrates are supplied to the body and body building materials (proteins) will be deficient. If we eat only proteins, body will be built up but for dai ...
Nutritional Requirements
... Lactose is called Milk sugar Sucrose is called cane sugar. Sports persons take glucose to get instant energy If we eat only rice, only carbohydrates are supplied to the body and body building materials (proteins) will be deficient. If we eat only proteins, body will be built up but for dai ...
... Lactose is called Milk sugar Sucrose is called cane sugar. Sports persons take glucose to get instant energy If we eat only rice, only carbohydrates are supplied to the body and body building materials (proteins) will be deficient. If we eat only proteins, body will be built up but for dai ...
Animal nutrition

Animal nutrition focuses on the dietary needs of domesticated animals, primarily those in agriculture and food production.