Microbial Diseases of the Respiratory System
... – This infection is caused by group A -hemolytic streptococci, the group that consists of the species Streptococcus pyogenes. – Symptoms of this infection are inflammation of the mucous membrane and fever, tonsillitis, and otitis media may also occur. At least half of pharyngitis cases are caused b ...
... – This infection is caused by group A -hemolytic streptococci, the group that consists of the species Streptococcus pyogenes. – Symptoms of this infection are inflammation of the mucous membrane and fever, tonsillitis, and otitis media may also occur. At least half of pharyngitis cases are caused b ...
Lower Respiratory System a. larynx (voice box)
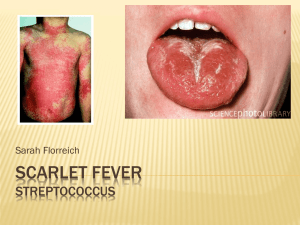
... scarlet fever; the toxin kills cells and causes intense inflammation; was once a life.)threatening illness; today's cases are mild (due to a decrease in virulence septicemia - bacteria spread to into the blood stream ).2 rheumatic fever - occurs after the infection is over (postinfection complicatio ...
... scarlet fever; the toxin kills cells and causes intense inflammation; was once a life.)threatening illness; today's cases are mild (due to a decrease in virulence septicemia - bacteria spread to into the blood stream ).2 rheumatic fever - occurs after the infection is over (postinfection complicatio ...
No. 12, 2003 - Statens Serum Institut
... The following case definition from WHO is also used in Denmark: Suspected cases A person presenting after 1 February 2003 with history of : - high fever (>38o C) and - one or more respiratory symptoms including cough, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing and one or more of the following: - clos ...
... The following case definition from WHO is also used in Denmark: Suspected cases A person presenting after 1 February 2003 with history of : - high fever (>38o C) and - one or more respiratory symptoms including cough, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing and one or more of the following: - clos ...
aspiration syndromes - Life in the Fast Lane
... includes gastric contents in the oropharynx, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, cyanosis, pulmonary edema, hypotension, and hypoxemia, which may progress rapidly to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and death. - Many patients may not develop signs or symptoms associated with as ...
... includes gastric contents in the oropharynx, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, cyanosis, pulmonary edema, hypotension, and hypoxemia, which may progress rapidly to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and death. - Many patients may not develop signs or symptoms associated with as ...
Answer Sheet
... 3. What is this sound and what does it indicate? a) Bronchial breathing b) Consolidation (Pneumonia) ...
... 3. What is this sound and what does it indicate? a) Bronchial breathing b) Consolidation (Pneumonia) ...
Streptococci
... 3. Pneumolysin: Intracellular membrane damaging toxin released by autolysis. Immunogenic overcomes host defense mechanisms. 4. Autolysin: Activated autolysin lyses the bacteria. Releases pneumolysin & large amounts of cell wall fragments which result in large inflamatory response. 5. Teichoic acid: ...
... 3. Pneumolysin: Intracellular membrane damaging toxin released by autolysis. Immunogenic overcomes host defense mechanisms. 4. Autolysin: Activated autolysin lyses the bacteria. Releases pneumolysin & large amounts of cell wall fragments which result in large inflamatory response. 5. Teichoic acid: ...
Pneumococcal and Influenza vaccine
... (including but not limited to asthma, cardiac disease, sickle cell disease, human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] and diabetes) handwashing, especially when exposed to individuals with ...
... (including but not limited to asthma, cardiac disease, sickle cell disease, human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] and diabetes) handwashing, especially when exposed to individuals with ...
Micro Chapter 13 [4-20
... o The most common local problem is pleural effusion – outpouring of fluid into the pleural space Usually the effusion exudate is sterile, but rarely it can have bacteria, and infect the pleural space, called empyema o Distal problems happen when strep pneumonia get into the blood In early pneumo ...
... o The most common local problem is pleural effusion – outpouring of fluid into the pleural space Usually the effusion exudate is sterile, but rarely it can have bacteria, and infect the pleural space, called empyema o Distal problems happen when strep pneumonia get into the blood In early pneumo ...
necrobacillosis_0
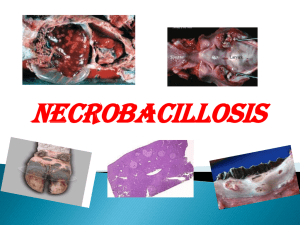
... Bronchopneumonia, purulent or necrotic pneumonia and pleurisy Acute catarrhal, ulcerative or necrotic enteritis Calf usually dies after 4-5 days due to pneumonia and toxemia ...
... Bronchopneumonia, purulent or necrotic pneumonia and pleurisy Acute catarrhal, ulcerative or necrotic enteritis Calf usually dies after 4-5 days due to pneumonia and toxemia ...
Causes of Death in 11 of 227 Patients with Traumatic
... rebellious reaction to all authority figures. His IQ was estimated at 94. His MMPI profile was described as one 'apt to be found among psychiatric patients carrying the diagnosis of hypomania'. It was suggested that management might be difficult because of over-activity, over-talkativeness and 'trul ...
... rebellious reaction to all authority figures. His IQ was estimated at 94. His MMPI profile was described as one 'apt to be found among psychiatric patients carrying the diagnosis of hypomania'. It was suggested that management might be difficult because of over-activity, over-talkativeness and 'trul ...
Sept2_Lecture3
... Respiratory infections, including pneumonia, are a big class of human pathogens ...
... Respiratory infections, including pneumonia, are a big class of human pathogens ...
Назва наукового напрямку (модуля): Семестр: 9 Step
... A 3-year-old child was playing in a playpen when he suddenly developed paroxysmal cough and shortness of breath. Objectively: dry cough, mixed dyspnea. Lung auscultation revealed some wheezes. Breathing sounds on the right are diminished. The child doesn't mix with other children. Immunization is ag ...
... A 3-year-old child was playing in a playpen when he suddenly developed paroxysmal cough and shortness of breath. Objectively: dry cough, mixed dyspnea. Lung auscultation revealed some wheezes. Breathing sounds on the right are diminished. The child doesn't mix with other children. Immunization is ag ...
Gram-Negative Rods
... Effective host defense depends primarily on cellmediated immunity. The host responses by granulomatous along with lymphocytes and epithelioid giant cells, which can progress to form focal abscesses and caseation. ...
... Effective host defense depends primarily on cellmediated immunity. The host responses by granulomatous along with lymphocytes and epithelioid giant cells, which can progress to form focal abscesses and caseation. ...
10 M301 Bacteria 2011 - Cal State LA
... When host defenses fail, mature tubercle form and bacilli multiply Tubercle eventually ruptures, releasing bacilli that disseminate throughout body This is progressive form of disease and symptoms include weight loss, coughing with blood, and loss of vigor ...
... When host defenses fail, mature tubercle form and bacilli multiply Tubercle eventually ruptures, releasing bacilli that disseminate throughout body This is progressive form of disease and symptoms include weight loss, coughing with blood, and loss of vigor ...
Respiratory System
... trachea and bronchial tubes, producing excessive mucous • May be acute or chronic • Acute bronchitis characterized by cough, fever, substernal pain and RALES (raspy sound) • Chronic bronchitis – middle or old age, cigarette smoking most common cause ...
... trachea and bronchial tubes, producing excessive mucous • May be acute or chronic • Acute bronchitis characterized by cough, fever, substernal pain and RALES (raspy sound) • Chronic bronchitis – middle or old age, cigarette smoking most common cause ...
Bacterial Diseases
... Color Plates 39 and 40 • S. aureus growth associated with the use of a new type of highly absorbent vaginal tampon • swell with menstrual fluids and adhere to the vagina • tears in the vaginal wall ...
... Color Plates 39 and 40 • S. aureus growth associated with the use of a new type of highly absorbent vaginal tampon • swell with menstrual fluids and adhere to the vagina • tears in the vaginal wall ...
Gram + Bacteria (Cocci): Staphylococcus & Streptococcus
... rheumatic carditis; changes in the ECG pattern; abnormal sedimentation rate or C-reactive protein (laboratory tests performed on blood) • Diagnosis - made when two of the major criteria, or one major criterion plus two minor criteria, are present along with evidence of a strep infection. ...
... rheumatic carditis; changes in the ECG pattern; abnormal sedimentation rate or C-reactive protein (laboratory tests performed on blood) • Diagnosis - made when two of the major criteria, or one major criterion plus two minor criteria, are present along with evidence of a strep infection. ...
Fever in Infants and Children: Sepsis, Meningitis, and Occult
... amoxicillin(80-100mg/dg/day), ceftriaxone Pneumococcemia: promptly reassess, if well, should at least treat with 1 dose ceftriaxone. ...
... amoxicillin(80-100mg/dg/day), ceftriaxone Pneumococcemia: promptly reassess, if well, should at least treat with 1 dose ceftriaxone. ...
Respiratory System
... Minutes: pulmonary thromboembolism, pneumothorax, asthma, inhaled forein body Hours to days: pneumonia, asthma. Weeks to months: Anemia, Pleural effuion, neruomuscular disease. Months to years: COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, ...
... Minutes: pulmonary thromboembolism, pneumothorax, asthma, inhaled forein body Hours to days: pneumonia, asthma. Weeks to months: Anemia, Pleural effuion, neruomuscular disease. Months to years: COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, ...
Gram (-) Bacteria: Neisseria, Enterobacteriaceae, etc.
... abdominal cramps, fever, diarrhea, and purulent bloody stools (severe form of dysentery) • Pathogenesis – fecal-oral route; enter the intestinal epith. cells and multiply; causes abscess and inflammation of intestinal mucosa; cause dysentery (loss of fluids/electrolytes) • Mortality 20% ...
... abdominal cramps, fever, diarrhea, and purulent bloody stools (severe form of dysentery) • Pathogenesis – fecal-oral route; enter the intestinal epith. cells and multiply; causes abscess and inflammation of intestinal mucosa; cause dysentery (loss of fluids/electrolytes) • Mortality 20% ...
Mycoplasma and Fastidious Gram Negative Bacteria
... • GI & renal manifestations • Risk factors – Older men with COPD – Immunosuppressed (transplant recipients) ...
... • GI & renal manifestations • Risk factors – Older men with COPD – Immunosuppressed (transplant recipients) ...
From, Dr. Swathi V Post Graduate in Department of Microbiology
... removal. VAP can be categorized into early onset VAP which occurs within first four days of mechanical ventilation and late onset VAP occurring after four days of mechanical ventilation.2 ...
... removal. VAP can be categorized into early onset VAP which occurs within first four days of mechanical ventilation and late onset VAP occurring after four days of mechanical ventilation.2 ...
Hot Topics in Pediatrics - VCU Department of Pediatrics
... Choosing an Anti-infective Most common organisms ...
... Choosing an Anti-infective Most common organisms ...
Infections of the respiratory tract
... during influenza epidemics as a result of cardiorespiratory failure or secondary bacterial pneumonia (caused by Staphylococcus aureus or S. pneumoniae). Diagnosis Diagnosis is usually clinical, with serology reserved for epidemiological studies and pandemic surveillance. Treatment Treatment is aimed ...
... during influenza epidemics as a result of cardiorespiratory failure or secondary bacterial pneumonia (caused by Staphylococcus aureus or S. pneumoniae). Diagnosis Diagnosis is usually clinical, with serology reserved for epidemiological studies and pandemic surveillance. Treatment Treatment is aimed ...
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung affecting primarily the microscopic air sacs known as alveoli. It is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria and less commonly other microorganisms, certain drugs and other conditions such as autoimmune diseases.Typical signs and symptoms include a cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. Diagnostic tools include x-rays and culture of the sputum. Vaccines to prevent certain types of pneumonia are available. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Pneumonia presumed to be bacterial is treated with antibiotics. If the pneumonia is severe, the affected person is generally hospitalized.Pneumonia affects approximately 450 million people globally per year (7% of the population) and results in about 4 million deaths. Although pneumonia was regarded by William Osler in the 19th century as ""the captain of the men of death,"" the advent of antibiotic therapy and vaccines in the 20th century has seen improvements in survival. Nevertheless, in developing countries, and among the very old, the very young, and the chronically ill, pneumonia remains a leading cause of death. In the terminally ill and elderly, especially those with other conditions, pneumonia is often the immediate cause of death. In such cases, particularly when it cuts short the suffering associated with lingering illness, pneumonia has often been called ""the old man's friend.""