Sherbert
... including combustion and the reactions of acids, are important in both nonliving and living systems and involve energy transfer ...
... including combustion and the reactions of acids, are important in both nonliving and living systems and involve energy transfer ...
Section 1 Sulfuric Acid, 50% v/v (1:1) Product
... IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing. IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. DO NOT induce vomiting. Call a POISON CENTER or doctor if you feel unwell. IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. Store in corro ...
... IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing. IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. DO NOT induce vomiting. Call a POISON CENTER or doctor if you feel unwell. IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. Store in corro ...
Spring 2001 Key
... (Correct choice is d) 24. In which of the pairs listed below both compounds are strong electrolytes? I. CH3COOH and HClO4 II. HF and NH3 III. NaCl and Sr(OH)2 IV. HCl and C6H13OH a. III only b. I and II only c. II and IV only d. I and III only e. II and III only ------------------------------------- ...
... (Correct choice is d) 24. In which of the pairs listed below both compounds are strong electrolytes? I. CH3COOH and HClO4 II. HF and NH3 III. NaCl and Sr(OH)2 IV. HCl and C6H13OH a. III only b. I and II only c. II and IV only d. I and III only e. II and III only ------------------------------------- ...
AQA GCSE Chemistry My Revision Notes
... (d) A weak acid does not ionise completely in aqueous solution . This is simply the definition; nothing more is needed. ...
... (d) A weak acid does not ionise completely in aqueous solution . This is simply the definition; nothing more is needed. ...
makeup6
... (B) C2H2 (g) + 2 H2 (g) ---> C2H6 (g) (C) NH4Cl (s) + H2O ---> NH4Cl (aq) (D) H2 (g) + Cl2 ---> 2 HCl 35. Trouton's Rule, which states that font face="Symbol">DHvap / Tbp = 85 J mol¯1 K¯1 (a constant) for nonpolar liquids, relates to the entropy change for the vaporization process, Svap. Knowing th ...
... (B) C2H2 (g) + 2 H2 (g) ---> C2H6 (g) (C) NH4Cl (s) + H2O ---> NH4Cl (aq) (D) H2 (g) + Cl2 ---> 2 HCl 35. Trouton's Rule, which states that font face="Symbol">DHvap / Tbp = 85 J mol¯1 K¯1 (a constant) for nonpolar liquids, relates to the entropy change for the vaporization process, Svap. Knowing th ...
S4 Standard Grade Revision Booklet
... Ionic Equation:H+(aq)Cl - (aq) + Na+(aq)OH- (aq) Na+ (aq)Cl - (aq) + H2O(l) The Na+(aq) ion and Cl- (aq) ion can be crossed out, as they are on both sides of the equation, so DO NOT ACTUALLY TAKE PART IN THE REACTION. They are SPECTATOR IONS. H+(aq)Cl (aq) + Na+(aq)OH (aq) Na+(aq)Cl (aq) + H2O(l ...
... Ionic Equation:H+(aq)Cl - (aq) + Na+(aq)OH- (aq) Na+ (aq)Cl - (aq) + H2O(l) The Na+(aq) ion and Cl- (aq) ion can be crossed out, as they are on both sides of the equation, so DO NOT ACTUALLY TAKE PART IN THE REACTION. They are SPECTATOR IONS. H+(aq)Cl (aq) + Na+(aq)OH (aq) Na+(aq)Cl (aq) + H2O(l ...
AGE article for Sept 2013
... Being an exothermic redox reaction, electrical energy can be obtained directly from chemical energy if the two half reactions can be separated, with oxidation of hydrogen occurring at an anode and reduction of oxygen at a cathode. The fuel cell can operate with either an acid or an alkaline electrol ...
... Being an exothermic redox reaction, electrical energy can be obtained directly from chemical energy if the two half reactions can be separated, with oxidation of hydrogen occurring at an anode and reduction of oxygen at a cathode. The fuel cell can operate with either an acid or an alkaline electrol ...
Unit 5 • What Do Atoms Look Like
... great examples of a Brønsted-Lowry acid and base. Arrhenius only dealt with aqueous solutions. When NH3 and HCl meet in the air, a proton (H+) is transferred from the HCl to the NH3. The two resulting ions immediately are attracted to each other to form the solid, NH4Cl(s) which we see as smoke. HCl ...
... great examples of a Brønsted-Lowry acid and base. Arrhenius only dealt with aqueous solutions. When NH3 and HCl meet in the air, a proton (H+) is transferred from the HCl to the NH3. The two resulting ions immediately are attracted to each other to form the solid, NH4Cl(s) which we see as smoke. HCl ...
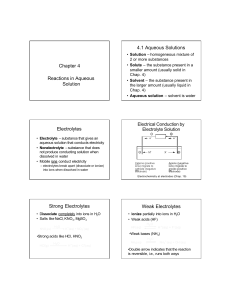
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solution 4.1 Aqueous Solutions
... aqueous solution that conducts electricity • Nonelectrolyte – substance that does not produce conducting solution when dissolved in water • Mobile ions conduct electricity – electrolytes break apart (dissociate or ionize) into ions when dissolved in water ...
... aqueous solution that conducts electricity • Nonelectrolyte – substance that does not produce conducting solution when dissolved in water • Mobile ions conduct electricity – electrolytes break apart (dissociate or ionize) into ions when dissolved in water ...
AP Chemistry - School Webmasters
... Answer the following questions in your own pen! You may alter the document to fit your work so that the answer and work are together. When you do NOT understand a question make a note of what you do NOT understand or what is stopping you from answering the question. DO NOT COPY ANSWERS FROM THE INT ...
... Answer the following questions in your own pen! You may alter the document to fit your work so that the answer and work are together. When you do NOT understand a question make a note of what you do NOT understand or what is stopping you from answering the question. DO NOT COPY ANSWERS FROM THE INT ...
X1-1 - murov.info
... possible using only the atomic number and atomic mass. 1. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in a.* F b. Al c. Mn d. Au 2. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in a.* Cl b. Cu 3. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in a.* H b. C c. N d. O e. Br 4. How many protons, neutron ...
... possible using only the atomic number and atomic mass. 1. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in a.* F b. Al c. Mn d. Au 2. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in a.* Cl b. Cu 3. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in a.* H b. C c. N d. O e. Br 4. How many protons, neutron ...
Question Paper - Revision Science
... 9 This question is about magnesium chloride, MgCl2. It can be formed by burning magnesium in chlorine. Mg(s) + Cl2(g) o MgCl2(s) ...
... 9 This question is about magnesium chloride, MgCl2. It can be formed by burning magnesium in chlorine. Mg(s) + Cl2(g) o MgCl2(s) ...
No Slide Title
... 2. Ammonium sulfide reacts with hydrochloric acid. 3. Cobalt(II) chloride combines with silver nitrate. 4. Solid calcium carbonate reacts with sulfuric acid. 5. Potassium sulfite reacts with hydrobromic acid. 6. Potassium sulfide reacts with nitric acid. 7. Ammonium iodide mixes with magnesium sulfa ...
... 2. Ammonium sulfide reacts with hydrochloric acid. 3. Cobalt(II) chloride combines with silver nitrate. 4. Solid calcium carbonate reacts with sulfuric acid. 5. Potassium sulfite reacts with hydrobromic acid. 6. Potassium sulfide reacts with nitric acid. 7. Ammonium iodide mixes with magnesium sulfa ...
Safety Data Sheet - Fisher Scientific
... Persistence and degradability: Not applicable for test method. Bioaccumulative potential: Not Bioaccumulative. Mobility in soil: Aqueous solution has high mobility in soil. Created by Global Safety Management, Inc. -Tel: 1-813-435-5161 - www.gsmsds.com ...
... Persistence and degradability: Not applicable for test method. Bioaccumulative potential: Not Bioaccumulative. Mobility in soil: Aqueous solution has high mobility in soil. Created by Global Safety Management, Inc. -Tel: 1-813-435-5161 - www.gsmsds.com ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... 1. If a compound ends in –ide, what does it tell you about the compound? 2. If a compound ends in –ate what does it tell you about the compound? 3. If a compound ends in –ite what does it tell you about the compound? 4. How does a cation form? What charge does it form? What type of element forms the ...
... 1. If a compound ends in –ide, what does it tell you about the compound? 2. If a compound ends in –ate what does it tell you about the compound? 3. If a compound ends in –ite what does it tell you about the compound? 4. How does a cation form? What charge does it form? What type of element forms the ...
Chemistry 40S – Exam Review
... 19. A base added to a neutral solution will: a) decrease [OH-] b) decrease [H3O+] c) decrease the pH of the solution d) donate protons to another substance in the solution 20. A 0.10 M solution containing a single dissolved substance is a very good conductor of electricity and turns blue litmus pape ...
... 19. A base added to a neutral solution will: a) decrease [OH-] b) decrease [H3O+] c) decrease the pH of the solution d) donate protons to another substance in the solution 20. A 0.10 M solution containing a single dissolved substance is a very good conductor of electricity and turns blue litmus pape ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
Practice Test 2
... The correct complete ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of Ca(NO3)2 and Na2CO3 are mixed is A) Ca(NO3)2(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) ----> CaCO3(s) + 2 NaNO3(aq) B) Ca2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) + 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) ----> CaCO3(s) + 2 Na+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) C) Ca2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) + 2 ...
... The correct complete ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of Ca(NO3)2 and Na2CO3 are mixed is A) Ca(NO3)2(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) ----> CaCO3(s) + 2 NaNO3(aq) B) Ca2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) + 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) ----> CaCO3(s) + 2 Na+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) C) Ca2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) + 2 ...
- Cypress HS
... Obtain approximately 100 mL of standard 0.10 M NaOH solution in a clean, dry beaker. Rinse the buret several times with small portions of NaOH solution (discard the rinsings); then fill the buret with NaOH solution. Keep the remainder of the NaOH solution in the beaker covered until it is needed. Cl ...
... Obtain approximately 100 mL of standard 0.10 M NaOH solution in a clean, dry beaker. Rinse the buret several times with small portions of NaOH solution (discard the rinsings); then fill the buret with NaOH solution. Keep the remainder of the NaOH solution in the beaker covered until it is needed. Cl ...
CHAPTER-7 EQUILIBRIUM Equilibrium state- When
... The acid-base pair thatdiffers only by one proton is called a conjugateacidbase pair. IfBrönsted acid is a strong acid then itsconjugate base is a weak base and viceversa. Ionic product of water.Kw = [H+][OH–] pH = -log [H+] ; here[H+] is molar concentration of hydrogen ion. pH + pOH =14 p ...
... The acid-base pair thatdiffers only by one proton is called a conjugateacidbase pair. IfBrönsted acid is a strong acid then itsconjugate base is a weak base and viceversa. Ionic product of water.Kw = [H+][OH–] pH = -log [H+] ; here[H+] is molar concentration of hydrogen ion. pH + pOH =14 p ...