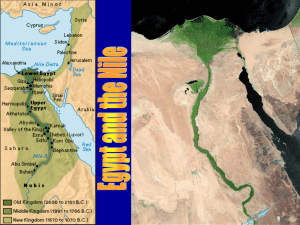
Social, Political, and Military History of Ancient Egypt
... few elite at the top of the society and the widening out down through the classes to the lowest of the low, slaves. For Egypt, that social diagram is particularly poignant. Without straying too far into either politics or economics, an examination of Egyptian society reveals a rigid system aimed at ...
... few elite at the top of the society and the widening out down through the classes to the lowest of the low, slaves. For Egypt, that social diagram is particularly poignant. Without straying too far into either politics or economics, an examination of Egyptian society reveals a rigid system aimed at ...
Egypt and the Nile River Valley System
... Citizens were now able to work in other occupations and become artisans, merchants, and traders. – The need for organized government became increasingly important as trade and farming increased. – Governments were needed for: • Overseeing construction and repairs • Developing a process for storing a ...
... Citizens were now able to work in other occupations and become artisans, merchants, and traders. – The need for organized government became increasingly important as trade and farming increased. – Governments were needed for: • Overseeing construction and repairs • Developing a process for storing a ...
File
... of the Nile and stretches all the way to the Red Sea. To the far south, the Nile’s dangerous cataracts blocked enemy boats from reaching Egypt. Early Egyptians were able to use the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea to trade with people outside Egypt. The Nile was also heavily used by Egyptians for t ...
... of the Nile and stretches all the way to the Red Sea. To the far south, the Nile’s dangerous cataracts blocked enemy boats from reaching Egypt. Early Egyptians were able to use the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea to trade with people outside Egypt. The Nile was also heavily used by Egyptians for t ...
Chapter 3 - Canadian Museum of History
... 2. Use Activity Sheet 6 to learn how to read the symbols on Narmer’s palette. King Narmer united Upper and Lower Egypt in 3000 B.C. (late pre-dynastic period). Ask your students why Narmer had such a palette made. Consider the importance of creating visual images in a society that was largely illite ...
... 2. Use Activity Sheet 6 to learn how to read the symbols on Narmer’s palette. King Narmer united Upper and Lower Egypt in 3000 B.C. (late pre-dynastic period). Ask your students why Narmer had such a palette made. Consider the importance of creating visual images in a society that was largely illite ...
Third Reading Civilization Egypt Pharaohs and Pyramids
... To the west of the Fertile Crescent in Africa, another river makes its way to the sea. While Sumerian civilization was on the rise, a similar process took place along the banks of this river, the Nile in Egypt. Yet the Egyptian civilization turned out to be very different from the collection of city ...
... To the west of the Fertile Crescent in Africa, another river makes its way to the sea. While Sumerian civilization was on the rise, a similar process took place along the banks of this river, the Nile in Egypt. Yet the Egyptian civilization turned out to be very different from the collection of city ...
Ancient Egypt 2015
... reign of Khufu (Cheops in Greek) at Giza. (All built between 2550-2490 B.C.) ...
... reign of Khufu (Cheops in Greek) at Giza. (All built between 2550-2490 B.C.) ...
Ancient Egypt*s Daily Life
... • The Rosetta Stone is a text written by a group of priests in Egypt to honour the Egyptian pharaoh. It lists all of the things that the pharaoh had done that were good for the priests and the people of Egypt. ...
... • The Rosetta Stone is a text written by a group of priests in Egypt to honour the Egyptian pharaoh. It lists all of the things that the pharaoh had done that were good for the priests and the people of Egypt. ...
2016 egyptian civ
... The Nile River - heart of Egyptian civilization - longest in world - magnet for life ...
... The Nile River - heart of Egyptian civilization - longest in world - magnet for life ...
HW/ Social Studies Chapter Four/ Section One – Egypt Under the
... 25. Explain the mummification process. Why was it important to the Egyptians? What was important about preserving the body correctly? ...
... 25. Explain the mummification process. Why was it important to the Egyptians? What was important about preserving the body correctly? ...
Main Idea 1 - Cloudfront.net
... Civilization developed after people began farming along the Nile. • The Nile provided both water and fertile soil for farming. • Egypt’s location offered another advantage because it had natural barriers that made it hard to invade. ...
... Civilization developed after people began farming along the Nile. • The Nile provided both water and fertile soil for farming. • Egypt’s location offered another advantage because it had natural barriers that made it hard to invade. ...
Document
... Civilization developed after people began farming along the Nile. • The Nile provided both water and fertile soil for farming. • Egypt’s location offered another advantage because it had natural barriers that made it hard to invade. ...
... Civilization developed after people began farming along the Nile. • The Nile provided both water and fertile soil for farming. • Egypt’s location offered another advantage because it had natural barriers that made it hard to invade. ...
Chapter 11 section 1 Power Point Notes
... Menes wanted to unify the kingdoms of Upper and Lower Egypt. Menes wore both the white and red crown to symbolize his leadership over both kingdoms. Many consider Menes to be the first pharaoh of Egypt. Menes also founded Egypt’s first dynasty, or series of rulers from the same family. Egypt’s First ...
... Menes wanted to unify the kingdoms of Upper and Lower Egypt. Menes wore both the white and red crown to symbolize his leadership over both kingdoms. Many consider Menes to be the first pharaoh of Egypt. Menes also founded Egypt’s first dynasty, or series of rulers from the same family. Egypt’s First ...
Egypt Study Ques
... outside by a shaft, which provided the ka with access to the tomb The form prob was developed from mounds of earth or stone that had covered earlier tombs Originally housed single burials, during latter Old Kingdom they were used for multiple family burialsand became more complex Central, undergroun ...
... outside by a shaft, which provided the ka with access to the tomb The form prob was developed from mounds of earth or stone that had covered earlier tombs Originally housed single burials, during latter Old Kingdom they were used for multiple family burialsand became more complex Central, undergroun ...
WH_3.1 Notes
... Powerful local nobles asserted their power which rivaled the pharaohs power, which caused order and stability to decline Old Kingdom government collapsed in 2100 BCE leading to economic problems, invasions, civil war, famine, disease, and chaos Middle Kingdom begins in 2055 BCE with a new dynasty Ne ...
... Powerful local nobles asserted their power which rivaled the pharaohs power, which caused order and stability to decline Old Kingdom government collapsed in 2100 BCE leading to economic problems, invasions, civil war, famine, disease, and chaos Middle Kingdom begins in 2055 BCE with a new dynasty Ne ...
Egypt and the Nile River Valley System
... settled near a river because of the benefits and contributions it gave. • Do you remember some of the reasons? ...
... settled near a river because of the benefits and contributions it gave. • Do you remember some of the reasons? ...
Nile River Valley Civilization
... A scribe's job was highly regarded in Ancient Egypt. Although being a scribe was rewarding, the training could take as long as twelve years. This statue of a Scribe was found in his tomb ...
... A scribe's job was highly regarded in Ancient Egypt. Although being a scribe was rewarding, the training could take as long as twelve years. This statue of a Scribe was found in his tomb ...
Egypt - S14
... (Egyptian’s chief god) at Karnak. The buildings were huge and impressive, but they are not as skillfully built as those of the Old Kingdom. ...
... (Egyptian’s chief god) at Karnak. The buildings were huge and impressive, but they are not as skillfully built as those of the Old Kingdom. ...
Egypt NAPLAN Test 1A
... Read the sentences below. Which word correctly completes the sentence? Pyramids were built as tombs for Pharaohs and their families. However, they took a very long time to build and were very expensive structure to create. After a while, Pharaohs began to dig tombs into the Valley of the Kings becau ...
... Read the sentences below. Which word correctly completes the sentence? Pyramids were built as tombs for Pharaohs and their families. However, they took a very long time to build and were very expensive structure to create. After a while, Pharaohs began to dig tombs into the Valley of the Kings becau ...
Geofarming
... • The Nile flows from south to north because of the geography of the land. • Mountains are to the south and low lying plains are in the north. ...
... • The Nile flows from south to north because of the geography of the land. • Mountains are to the south and low lying plains are in the north. ...
egypt practice quiz
... B. The Land of the Black-Haired People, because everyone had black hair C. Kemet, the Black Land, because of the fertile soil D. The Land of the Rising Sun, because they worshiped the sun 3. What is silt? A. Silt is desert sand B. Silt is rich, fertile soil deposited by a river C. Silt is the fabric ...
... B. The Land of the Black-Haired People, because everyone had black hair C. Kemet, the Black Land, because of the fertile soil D. The Land of the Rising Sun, because they worshiped the sun 3. What is silt? A. Silt is desert sand B. Silt is rich, fertile soil deposited by a river C. Silt is the fabric ...