Chapter 4 Notes
... The Royal Road stretched 1,677 miles and had stops every 14 miles with food, water, and horses Messengers could travel it in seven days ...
... The Royal Road stretched 1,677 miles and had stops every 14 miles with food, water, and horses Messengers could travel it in seven days ...
Chapter 4 First Age of Empires
... The Royal Road stretched 1,677 miles and had stops every 14 miles with food, water, and horses Messengers could travel it in seven days ...
... The Royal Road stretched 1,677 miles and had stops every 14 miles with food, water, and horses Messengers could travel it in seven days ...
Document
... • The Nile’s flooding coated the land around it with a rich silt that made the soil ideal for farming. • Without the floods, people could never have farmed in Egypt. ...
... • The Nile’s flooding coated the land around it with a rich silt that made the soil ideal for farming. • Without the floods, people could never have farmed in Egypt. ...
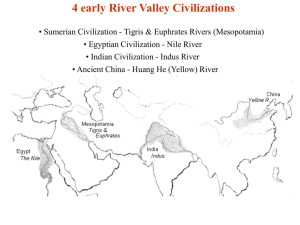
4 early River Valley Civilizations
... and the red crown of Lower Egypt. When Egypt was united, these two crowns were combined into the Double Crown of Upper and Lower Egypt. ...
... and the red crown of Lower Egypt. When Egypt was united, these two crowns were combined into the Double Crown of Upper and Lower Egypt. ...
Farming - Grade4-BCA
... happens almost 1500 km from dry Egypt, yet the Nile floods in Egypt between June and September. The Egyptians called this the inundation. It happened every year almost without fail. If the flooding didn’t happen, Egypt experienced famine (not enough food). If too much water came down the river, Egyp ...
... happens almost 1500 km from dry Egypt, yet the Nile floods in Egypt between June and September. The Egyptians called this the inundation. It happened every year almost without fail. If the flooding didn’t happen, Egypt experienced famine (not enough food). If too much water came down the river, Egyp ...
This is Jeopardy - Town of Mansfield, CT
... • His tomb was the only complete one ever found. • Who is Tutankhamen? Why this was important. Gave information to historians/scientists about Egyptian burial practices ...
... • His tomb was the only complete one ever found. • Who is Tutankhamen? Why this was important. Gave information to historians/scientists about Egyptian burial practices ...
Ancient Egypt Society Map—Semenza Galbo Government and Laws
... his government? (p. 94) Often, he used resources found in the Kingdom. He would have the farmers harvest plants, and give them money for well harvested crops. He would also steal from other parts of Egypt, often Nubia. 2. In Our World, read pages 97-100, and 104-106. Answer the following questions. ...
... his government? (p. 94) Often, he used resources found in the Kingdom. He would have the farmers harvest plants, and give them money for well harvested crops. He would also steal from other parts of Egypt, often Nubia. 2. In Our World, read pages 97-100, and 104-106. Answer the following questions. ...
Name: Period: PHARAOHS
... kingdom in the south. Southern Egypt is on higher land than northern Egypt, so unlike most rivers, the Nile River flows north. Menes (MEN-es) came from a village in Upper Egypt. About 3100BCE, Menes became the first ruler of a united Egypt when he conquered Lower Egypt. Menes wore a double crown of ...
... kingdom in the south. Southern Egypt is on higher land than northern Egypt, so unlike most rivers, the Nile River flows north. Menes (MEN-es) came from a village in Upper Egypt. About 3100BCE, Menes became the first ruler of a united Egypt when he conquered Lower Egypt. Menes wore a double crown of ...
WebQuest
... The ancient Egyptians thought of Egypt as being divided into two types of land, the ______ land and the and the ____land. The _____ ____ was the fertile land on the banks of the Nile. The ancient Egyptians used this land for growing their _____. This was the only land in ancient Egypt that could be ...
... The ancient Egyptians thought of Egypt as being divided into two types of land, the ______ land and the and the ____land. The _____ ____ was the fertile land on the banks of the Nile. The ancient Egyptians used this land for growing their _____. This was the only land in ancient Egypt that could be ...
Ancient Egypt The geography of Egypt played a great role in the
... comfortable lifestyle. Yet every craftsman's lifestyle and social standing depended on the quality of his skills and experience. Thus, some craftsmen had more difficult lives than others. ...
... comfortable lifestyle. Yet every craftsman's lifestyle and social standing depended on the quality of his skills and experience. Thus, some craftsmen had more difficult lives than others. ...
Egypt Notes 2015 - Hewlett
... Scribes: kept records and worked for the rulers, priests, and traders, carved hieroglyphics onto stone walls and monuments and invented simpler script and wrote or painted on papyrus ...
... Scribes: kept records and worked for the rulers, priests, and traders, carved hieroglyphics onto stone walls and monuments and invented simpler script and wrote or painted on papyrus ...
Ancient Egypt Notes Overview Powerpoint - Mrs. Moore
... The Nile begins in the Highlands of Ethiopia with two branches: ...
... The Nile begins in the Highlands of Ethiopia with two branches: ...
Chapter 4, Section 1: Geography and Ancient Egypt
... Mediterranean Sea Nile River Direction of the current Upper Egypt Lower Egypt Western Desert and Eastern Desert (red land) Nile Delta (black land) Nubia Kush Cataracts Sinai Peninsula The Canaan ...
... Mediterranean Sea Nile River Direction of the current Upper Egypt Lower Egypt Western Desert and Eastern Desert (red land) Nile Delta (black land) Nubia Kush Cataracts Sinai Peninsula The Canaan ...
pharaohs
... believed their kings were also gods. Modern people refer to ancient Egyptian rulers as pharaohs, but pharaoh originally referred to the palace where the king lived. Pharaoh was not used as a title for the Egyptian ruler until the later part of ancient Egyptian history, but today we use the term to d ...
... believed their kings were also gods. Modern people refer to ancient Egyptian rulers as pharaohs, but pharaoh originally referred to the palace where the king lived. Pharaoh was not used as a title for the Egyptian ruler until the later part of ancient Egyptian history, but today we use the term to d ...
The Rulers of Egypt - Manasquan Public Schools
... Men were usually appointed as Pharaoh. Women have made their appearance on the throne Hatshepsut is an example of a powerful woman Pharaoh. ...
... Men were usually appointed as Pharaoh. Women have made their appearance on the throne Hatshepsut is an example of a powerful woman Pharaoh. ...
WHPP Unit 1 Section 3 Ancient Egypt
... in the afterlife, the Egyptians perfected the process of mummification. Mummification was expensive, however, and during the Old Kingdom was a luxury of the rich. First the body was washed and the internal organs including the lungs, stomach, liver and intestines were removed. The heart was left in ...
... in the afterlife, the Egyptians perfected the process of mummification. Mummification was expensive, however, and during the Old Kingdom was a luxury of the rich. First the body was washed and the internal organs including the lungs, stomach, liver and intestines were removed. The heart was left in ...
Guided Notes - History with Ms. Osborn
... In Southwest Asia a large crescent shaped band of fertile land forms an oasis in the midst of deserts and mountains between two rivers – the _____________________________________________________________, this land is often referred to as the __________________________________________________________ ...
... In Southwest Asia a large crescent shaped band of fertile land forms an oasis in the midst of deserts and mountains between two rivers – the _____________________________________________________________, this land is often referred to as the __________________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 3
... Black Land and Red Land • Ancient Egyptians called their land Kemet or “the black land” because of the silt. • Unlike Mesopotamians, the Egyptians usually didn’t have to worry about flash floods. • Dry years, wile rare, caused famine. • “Red land” was the vast desert on either side of the river- Sa ...
... Black Land and Red Land • Ancient Egyptians called their land Kemet or “the black land” because of the silt. • Unlike Mesopotamians, the Egyptians usually didn’t have to worry about flash floods. • Dry years, wile rare, caused famine. • “Red land” was the vast desert on either side of the river- Sa ...
Chapter 3
... Black Land and Red Land • Ancient Egyptians called their land Kemet or “the black land” because of the silt. • Unlike Mesopotamians, the Egyptians usually didn’t have to worry about flash floods. • Dry years, wile rare, caused famine. • “Red land” was the vast desert on either side of the river- Sa ...
... Black Land and Red Land • Ancient Egyptians called their land Kemet or “the black land” because of the silt. • Unlike Mesopotamians, the Egyptians usually didn’t have to worry about flash floods. • Dry years, wile rare, caused famine. • “Red land” was the vast desert on either side of the river- Sa ...
Vocabulary, Section 1 Nubia
... • In “Upper Egypt” it had a narrow strip of approximately 6 miles on each side, then desert ...
... • In “Upper Egypt” it had a narrow strip of approximately 6 miles on each side, then desert ...
File
... C. It improved their quality of life by adapting and adopting what they needed D. Competition for resources caused alliances. 21. What does it mean in the selection by, “new technology?” A. The Egyptians had advanced developments such as tools and techniques for their time period. B. Technology, suc ...
... C. It improved their quality of life by adapting and adopting what they needed D. Competition for resources caused alliances. 21. What does it mean in the selection by, “new technology?” A. The Egyptians had advanced developments such as tools and techniques for their time period. B. Technology, suc ...
Chapter 5 Lesson 3 Outline KEY Revised
... 1. The Middle Kingdom lasted from about 2055 B.C. to 1650 B.C. It was a time of power, wealth, and achievement for Egypt. 2. During the Middle Kingdom, Egypt took control of new lands. 3. The pharaoh required tribute, or payments from the conquered peoples. The pharaoh used this wealth to build dams ...
... 1. The Middle Kingdom lasted from about 2055 B.C. to 1650 B.C. It was a time of power, wealth, and achievement for Egypt. 2. During the Middle Kingdom, Egypt took control of new lands. 3. The pharaoh required tribute, or payments from the conquered peoples. The pharaoh used this wealth to build dams ...